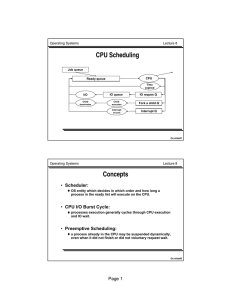
Ready queue is partitioned into separate queues
... Clustered systems: A uses multiple CPUs to complete a task. It is different from parallel system in that clustered system consists of two or more individual systems tied together and share storage and are closely linked via LAN networking. ...
... Clustered systems: A uses multiple CPUs to complete a task. It is different from parallel system in that clustered system consists of two or more individual systems tied together and share storage and are closely linked via LAN networking. ...
02_OperatingSystemOverview
... • Resident Monitor is software always in memory • Monitor reads in job and ...
... • Resident Monitor is software always in memory • Monitor reads in job and ...
col
... affect your class attendance? A) The clickers do not affect my class attendance. B) I attend this class slightly more often because of the clickers. C) If there were no clickers, I would be here way less often. D) My clicker is answering this question, because my friend is holding my clicker. I a ...
... affect your class attendance? A) The clickers do not affect my class attendance. B) I attend this class slightly more often because of the clickers. C) If there were no clickers, I would be here way less often. D) My clicker is answering this question, because my friend is holding my clicker. I a ...
Ceng 334 - Operating Systems
... per second that the process has had during the past few seconds • Nice is a value between –20 to 20 (default 0). Nice system call can be used to set this value 0-20 • Base is a system parameter in UNIX source code • The scheduler forces CPU bound (on positive queues) get any service that is left ove ...
... per second that the process has had during the past few seconds • Nice is a value between –20 to 20 (default 0). Nice system call can be used to set this value 0-20 • Base is a system parameter in UNIX source code • The scheduler forces CPU bound (on positive queues) get any service that is left ove ...
Solaris Symmetric Multiprocessing
... Windows 2000 Symmetric Multiprocessing Windows 2000 is a symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) operating system. There is no master processor. Windows 2000 incorporates several features that are crucial to its success as a multiprocessor operating system: •The ability to run operating system code on any ...
... Windows 2000 Symmetric Multiprocessing Windows 2000 is a symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) operating system. There is no master processor. Windows 2000 incorporates several features that are crucial to its success as a multiprocessor operating system: •The ability to run operating system code on any ...
- Mitra.ac.in
... • The linux virtual memory system is responsible for maintaining the address space visible to each process. • It creates pages of virtual memory on demand and manages the loading of ...
... • The linux virtual memory system is responsible for maintaining the address space visible to each process. • It creates pages of virtual memory on demand and manages the loading of ...
Operating Systems
... Operating systems are those programs that interface the machine with the applications programs. The main function of these systems is to dynamically allocate the shared system resources to the executing programs. As such, research in this area is clearly concerned with the management and scheduling ...
... Operating systems are those programs that interface the machine with the applications programs. The main function of these systems is to dynamically allocate the shared system resources to the executing programs. As such, research in this area is clearly concerned with the management and scheduling ...
Page 1 • Scheduler: • CPU I/O Burst Cycle: • Preemptive Scheduling:
... OS entity which decides in which order and how long a process in the ready list will execute on the CPU. ...
... OS entity which decides in which order and how long a process in the ready list will execute on the CPU. ...
Operating Systems - Computer Science
... Operating systems are those programs that interface the machine with the applications programs. The main function of these systems is to dynamically allocate the shared system resources to the executing programs. As such, research in this area is clearly concerned with the management and scheduling ...
... Operating systems are those programs that interface the machine with the applications programs. The main function of these systems is to dynamically allocate the shared system resources to the executing programs. As such, research in this area is clearly concerned with the management and scheduling ...
Unit OS2: Operating Systems Principles
... running in the context of the Windows Subsystem process to a set of callable services running in kernel mode. The primary reason for this shift was to improve overall system performance. Having a separate server process that contains the Windows graphics subsystem required multiple thread and proces ...
... running in the context of the Windows Subsystem process to a set of callable services running in kernel mode. The primary reason for this shift was to improve overall system performance. Having a separate server process that contains the Windows graphics subsystem required multiple thread and proces ...
Lecture slides
... • Identifier: A unique integer associated with a process • State : A currently executing process is in running state • Priority : Priority level relative to other processes • Program counter : Address of the next instruction of the program to be executed. • Memory pointers: pointers to the program c ...
... • Identifier: A unique integer associated with a process • State : A currently executing process is in running state • Priority : Priority level relative to other processes • Program counter : Address of the next instruction of the program to be executed. • Memory pointers: pointers to the program c ...
Unix and shell programming
... root is the user name or account that by default has access to all commands and files on a Linux or other Unix-like operating system. The root directory, which is the top level directory on a system That is, it is the directory in which all other directories, including their subdirectories and f ...
... root is the user name or account that by default has access to all commands and files on a Linux or other Unix-like operating system. The root directory, which is the top level directory on a system That is, it is the directory in which all other directories, including their subdirectories and f ...
Slide 2: Operating System Overview
... Operating systems are those programs that interface the machine with the applications programs. The main function of these systems is to dynamically allocate the shared system resources to the executing programs. As such, research in this area is clearly concerned with the management and scheduling ...
... Operating systems are those programs that interface the machine with the applications programs. The main function of these systems is to dynamically allocate the shared system resources to the executing programs. As such, research in this area is clearly concerned with the management and scheduling ...
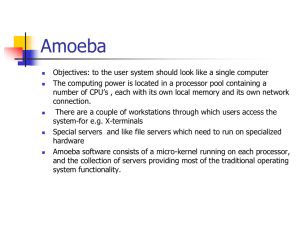
Chorusamoeba
... Function: provide mapping from ASCII names to capabilities. Operation are provided to create and delete directories . The directories are not immutable and therefore new entries can be added to directory. Each file entry in the director has three protection domain User presents a directory server wi ...
... Function: provide mapping from ASCII names to capabilities. Operation are provided to create and delete directories . The directories are not immutable and therefore new entries can be added to directory. Each file entry in the director has three protection domain User presents a directory server wi ...
Answers to Even-numbered Exercises
... 4. What is the Free Software Foundation/GNU? What is Linux? Which parts of the Linux operating system did each provide? Who else has helped build and refine this operating system? The Free Software Foundation (www.fsf.org) is the principal organizational sponsor of the GNU Project. GNU developed man ...
... 4. What is the Free Software Foundation/GNU? What is Linux? Which parts of the Linux operating system did each provide? Who else has helped build and refine this operating system? The Free Software Foundation (www.fsf.org) is the principal organizational sponsor of the GNU Project. GNU developed man ...
03-os-design
... Microkernel. The kernel is very small and only implements some fundamental things like processes and scheduling. The operating system then consists of several subsystems along with the kernel. I ...
... Microkernel. The kernel is very small and only implements some fundamental things like processes and scheduling. The operating system then consists of several subsystems along with the kernel. I ...
Operating System Structures
... – Easier to port to a new architecture – More robust (less code works in kernel mode) – More secure • Exampled: Tru64 UNIX, MacOS X, QNX, also somewhat Windows NT ...
... – Easier to port to a new architecture – More robust (less code works in kernel mode) – More secure • Exampled: Tru64 UNIX, MacOS X, QNX, also somewhat Windows NT ...
Mohammad Husain
... The permissions defined by ACLs are a superset of the permissions specified by the file permission bits. The permissions defined for the file owner correspond to the permissions of the ACL_USER_OBJ entry. The permissions defined for the file group correspond to the permissions of the ACL_GROUP_OBJ e ...
... The permissions defined by ACLs are a superset of the permissions specified by the file permission bits. The permissions defined for the file owner correspond to the permissions of the ACL_USER_OBJ entry. The permissions defined for the file group correspond to the permissions of the ACL_GROUP_OBJ e ...
Operating System - GCG-42
... MS-DOS is an acronym for MicroSoft Disk Operating System It is a CUI based operating system. It provides user with a command prompt (generally called as C:\) where various command could be typed. When one operates in the DOS environment, one interacts with the command interpreter, which inte ...
... MS-DOS is an acronym for MicroSoft Disk Operating System It is a CUI based operating system. It provides user with a command prompt (generally called as C:\) where various command could be typed. When one operates in the DOS environment, one interacts with the command interpreter, which inte ...
Introduction to UNIX/Linux - gozips.uakron.edu
... Multiuser, multitasking operating systems with built-in ...
... Multiuser, multitasking operating systems with built-in ...
Introduction
... – A process can cause other processes to be created – Unix for example implements processes as a hierarchy • Process 0 is the O/S memory manager (swapper) • Process 1 is the process that creates all others • All processes are descendants of process 1 ...
... – A process can cause other processes to be created – Unix for example implements processes as a hierarchy • Process 0 is the O/S memory manager (swapper) • Process 1 is the process that creates all others • All processes are descendants of process 1 ...
Lecture 5
... Platform-independence is not practical. • In a system without an OS, such as a microcontroller used with a small embedded system, we either use Assembly or very low level C code. I/O often involves addressing specific bits in memory that are mapped to particular input or output devices. ...
... Platform-independence is not practical. • In a system without an OS, such as a microcontroller used with a small embedded system, we either use Assembly or very low level C code. I/O often involves addressing specific bits in memory that are mapped to particular input or output devices. ...
Operating System Overview
... • Modular structure for flexibility • Executes on a variety of hardware ...
... • Modular structure for flexibility • Executes on a variety of hardware ...
Operating System Architecture and Distributed Systems
... while coexisting with a non-real-time application such as web browsing. That is kernel would provide only the most basic mechanisms upon which the general resource management tasks at a node are carried out. Server modules would be dynamically loaded as required, to implement the required RM policie ...
... while coexisting with a non-real-time application such as web browsing. That is kernel would provide only the most basic mechanisms upon which the general resource management tasks at a node are carried out. Server modules would be dynamically loaded as required, to implement the required RM policie ...
Introduction
... System calls to create and terminate processes System calls to allocate/deallocate memory System calls for communication - signals ...
... System calls to create and terminate processes System calls to allocate/deallocate memory System calls for communication - signals ...