ETEE3212 Spring 2006 Test #1
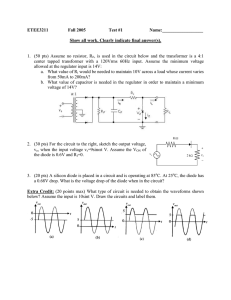
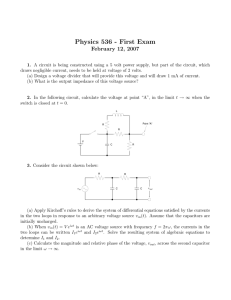
... ideal capacitors and determine: a. RC and CMRR b. Differential mode voltage gain and common mode voltage gain for the total system c. Differential mode input voltage (vdi) for maximum output ...
... ideal capacitors and determine: a. RC and CMRR b. Differential mode voltage gain and common mode voltage gain for the total system c. Differential mode input voltage (vdi) for maximum output ...
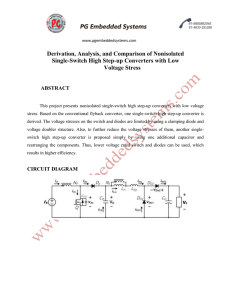
Proposed System
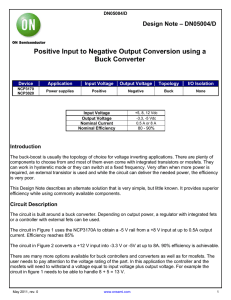
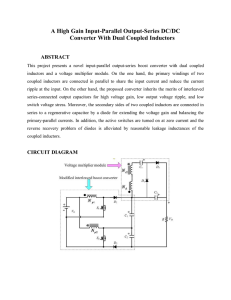
... inductors and a voltage multiplier module. On the one hand, the primary windings of two coupled inductors are connected in parallel to share the input current and reduce the current ripple at the input. On the other hand, the proposed converter inherits the merits of interleaved series-connected out ...
... inductors and a voltage multiplier module. On the one hand, the primary windings of two coupled inductors are connected in parallel to share the input current and reduce the current ripple at the input. On the other hand, the proposed converter inherits the merits of interleaved series-connected out ...
Analog-to-Digital Converter and Multivibrators
... output (usually zero). • It also has an unstable state. Certain input will put the circuit into its unstable state, which lasts for a set length of time before returning to the stable state. – Unstable states are still robust to noise ...
... output (usually zero). • It also has an unstable state. Certain input will put the circuit into its unstable state, which lasts for a set length of time before returning to the stable state. – Unstable states are still robust to noise ...
The Comparator
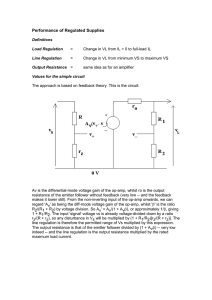
... A voltage divider is a circuit that produces an output voltage (Vout) that is a fraction of its input Vout is the voltage across the R2 Worked out by the resistor ratio ...
... A voltage divider is a circuit that produces an output voltage (Vout) that is a fraction of its input Vout is the voltage across the R2 Worked out by the resistor ratio ...
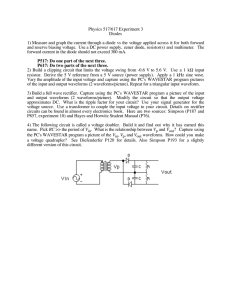
Physics 517/617 Experiment 3 Diodes
... resistor. Derive the 5 V reference from a 5 V source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) Build a full ...
... resistor. Derive the 5 V reference from a 5 V source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) Build a full ...
AC voltage controller
... higher than single-phase circuit. Harmonics in the input current is a little lower thanthe single- phase circuit due to the cancellation of some harmonics among the 3 phases. To improve the input power factor: –Use DC bias or 3k order component bias on each of the 3 output phase voltages ...
... higher than single-phase circuit. Harmonics in the input current is a little lower thanthe single- phase circuit due to the cancellation of some harmonics among the 3 phases. To improve the input power factor: –Use DC bias or 3k order component bias on each of the 3 output phase voltages ...
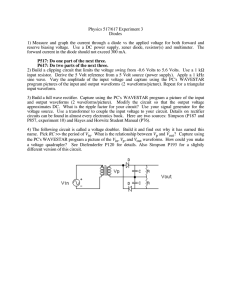
Physics 517/617 Experiment 3 Diodes
... input resistor. Derive the 5 Volt reference from a 5 Volt source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) B ...
... input resistor. Derive the 5 Volt reference from a 5 Volt source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) B ...
May 2004 Boost Converter Drives 1A White LEDs
... up to 4A of load current. Efficiency is as high as 90% and is shown in Figure 2. The switching frequency for this circuit is set at 2MHz by a single external resistor, ROSC. Operating at a frequency this high allows the use of a lower valued and physically smaller inductor. During start-up, the outp ...
... up to 4A of load current. Efficiency is as high as 90% and is shown in Figure 2. The switching frequency for this circuit is set at 2MHz by a single external resistor, ROSC. Operating at a frequency this high allows the use of a lower valued and physically smaller inductor. During start-up, the outp ...
pdf
... gate-source voltage does not turn the transistor off enough to allow proper integration. It is possible that the edgeless H-gate designs solve this problem; SPICE does not have an easy way to account for gate shapes. Lowering the reset drain voltage allowed the simulation of the APS-2 pixel operatin ...
... gate-source voltage does not turn the transistor off enough to allow proper integration. It is possible that the edgeless H-gate designs solve this problem; SPICE does not have an easy way to account for gate shapes. Lowering the reset drain voltage allowed the simulation of the APS-2 pixel operatin ...
EUP2644 TFT LCD DC-DC Converter with Integrated LDO, OP-AMP and GPM Switch
... monitors and notebooks operation from 3V to 5.5V input supply. The device integrates a step-up converter, a high speed VCOM buffer, a 350mA low dropout (LDO) linear regulator, and a Gate Pulse Modulator (GPM). The external compensated step up converter features an internal power MOSFET and high freq ...
... monitors and notebooks operation from 3V to 5.5V input supply. The device integrates a step-up converter, a high speed VCOM buffer, a 350mA low dropout (LDO) linear regulator, and a Gate Pulse Modulator (GPM). The external compensated step up converter features an internal power MOSFET and high freq ...
feedback current amplifier
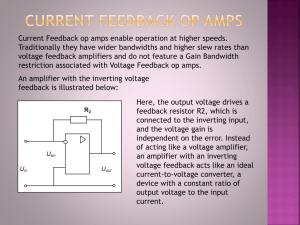
... Current Feedback op amps enable operation at higher speeds. Traditionally they have wider bandwidths and higher slew rates than voltage feedback amplifiers and do not feature a Gain Bandwidth restriction associated with Voltage Feedback op amps. An amplifier with the inverting voltage feedback is il ...
... Current Feedback op amps enable operation at higher speeds. Traditionally they have wider bandwidths and higher slew rates than voltage feedback amplifiers and do not feature a Gain Bandwidth restriction associated with Voltage Feedback op amps. An amplifier with the inverting voltage feedback is il ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.