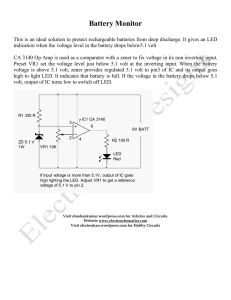
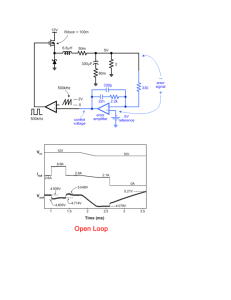
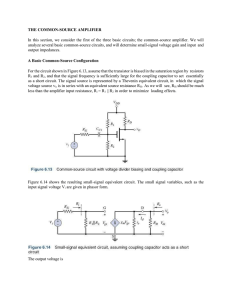
ECE 3041 - ECE Users Pages
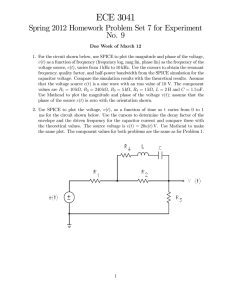
... voltage source, (), varies from 1 kHz to 10 kHz. Use the cursors to obtain the resonant frequency, quality factor, and half-power bandwidth from the SPICE simulation for the capacitor voltage. Compare the simulation results with the theoretical results. Assume that the voltage source () is a sin ...
... voltage source, (), varies from 1 kHz to 10 kHz. Use the cursors to obtain the resonant frequency, quality factor, and half-power bandwidth from the SPICE simulation for the capacitor voltage. Compare the simulation results with the theoretical results. Assume that the voltage source () is a sin ...
DI 507B - Dionics-USA
... The DIONICS DI-507B and DI-512B series circuits are designed for interfacing between MOS or TTL circuitry and gas discharge display panels. Each section of these devices is made up of a switched constant current level shifter-capable of high voltage operation and a PNP-NPN driver transistor pair. Th ...
... The DIONICS DI-507B and DI-512B series circuits are designed for interfacing between MOS or TTL circuitry and gas discharge display panels. Each section of these devices is made up of a switched constant current level shifter-capable of high voltage operation and a PNP-NPN driver transistor pair. Th ...
Measuring Input Offset Voltage
... Input Offset Voltage = (Vref to Vout) / ((R7/R8) + 1) = (Vref to Vout) / 101 Alternatively, with this circuit configuration, the Input Offset Voltage can be measured between the input terminals of the op amp. R9 & R10 eliminate any offset at the output due to Input Bias Currents therefore any offset ...
... Input Offset Voltage = (Vref to Vout) / ((R7/R8) + 1) = (Vref to Vout) / 101 Alternatively, with this circuit configuration, the Input Offset Voltage can be measured between the input terminals of the op amp. R9 & R10 eliminate any offset at the output due to Input Bias Currents therefore any offset ...
SINGLE-PHASE AC/AC CONVERTER BASED ON QUASI
... Is in continuous current mode (CCM) is more sinusoidal than that in DCM. For advantages of CCM operation, the simulation results of proposed qZSAC are compared to those of conventional SZAC with the same condition. The waveform of in we can observe that the proposed qZSAC inherits all the advantages ...
... Is in continuous current mode (CCM) is more sinusoidal than that in DCM. For advantages of CCM operation, the simulation results of proposed qZSAC are compared to those of conventional SZAC with the same condition. The waveform of in we can observe that the proposed qZSAC inherits all the advantages ...
Analog-Digital Conversion
... • Manufacture may be simplified if there are fewer different resistor values to purchase, stock, and sort prior to assembly. • By constructing a different kind of resistor network on the input of our summing circuit, we can achieve the same kind of binary weighting with only two kinds of resistor va ...
... • Manufacture may be simplified if there are fewer different resistor values to purchase, stock, and sort prior to assembly. • By constructing a different kind of resistor network on the input of our summing circuit, we can achieve the same kind of binary weighting with only two kinds of resistor va ...
SIMULATION OF BUCK-BOOST converter
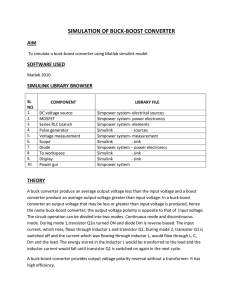
... converter is shown in figure. From t=0 to t=DT,the converter is in ON state, so the switch S is closed. ...
... converter is shown in figure. From t=0 to t=DT,the converter is in ON state, so the switch S is closed. ...
ETEE3212 Spring 2007 Test
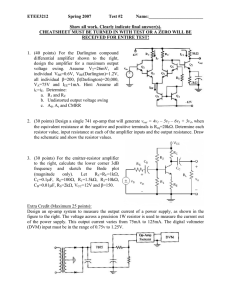
... CHEATSHEET MUST BE TURNED IN WITH TEST OR A ZERO WILL BE RECEIVED FOR ENTIRE TEST! ...
... CHEATSHEET MUST BE TURNED IN WITH TEST OR A ZERO WILL BE RECEIVED FOR ENTIRE TEST! ...
HX11RB External Voltage Reference
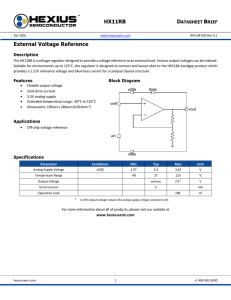
... The HX11RB is a voltage regulator designed to provide a voltage reference to an external load. Various output voltages can be realized. Suitable for environments up to 125°C, the regulator is designed to connect and layout abut to the HX11BA bandgap product which provides a 1.21V reference voltage ...
... The HX11RB is a voltage regulator designed to provide a voltage reference to an external load. Various output voltages can be realized. Suitable for environments up to 125°C, the regulator is designed to connect and layout abut to the HX11BA bandgap product which provides a 1.21V reference voltage ...
THREE-PHASE AC RMS VOLTAGE TRANSDUCER 3VTR- OSI
... ACCURACY ......................................±0.25% F.S. @60Hz (Includes effects of linearity and setpoint from 10-100% of range. ±0.5% F.S. typical over frequency range.) Output Ripple ...................................................... <1.0% F.S. ...
... ACCURACY ......................................±0.25% F.S. @60Hz (Includes effects of linearity and setpoint from 10-100% of range. ±0.5% F.S. typical over frequency range.) Output Ripple ...................................................... <1.0% F.S. ...
Electronics Analog-to
... o Full scale measurement range = -10 to +10 volts o ADC resolution is 14 bits: 214 = 16384 quantization levels o ADC voltage resolution is: (10-(-10))/16384 = 20/16384 = 0.00122 volts = 1.22 mV ...
... o Full scale measurement range = -10 to +10 volts o ADC resolution is 14 bits: 214 = 16384 quantization levels o ADC voltage resolution is: (10-(-10))/16384 = 20/16384 = 0.00122 volts = 1.22 mV ...
Use the proportionality property of linear circuits to find the voltage Vx
... Usually, the input is known, but the output is unknown. So suppose that we know the output -- 1V -- but not the input, which we’ll call xu. We’d say that the output is k*input So the proportionality constant is 1/(xu). Find k by analysis of that circuit. We can then use k to find the output when giv ...
... Usually, the input is known, but the output is unknown. So suppose that we know the output -- 1V -- but not the input, which we’ll call xu. We’d say that the output is k*input So the proportionality constant is 1/(xu). Find k by analysis of that circuit. We can then use k to find the output when giv ...
Three Phase Semi Converter
... semiconverter for different firing angles At any instant thyristor connected to most positive line terminal and diode connected to most negative line terminal conducts.For 0≤α≤π/3 each diode and thyristor conducts for 2π/3 radians.Thefree wheeling diode does not conduct for α<π/2.The free wheeling d ...
... semiconverter for different firing angles At any instant thyristor connected to most positive line terminal and diode connected to most negative line terminal conducts.For 0≤α≤π/3 each diode and thyristor conducts for 2π/3 radians.Thefree wheeling diode does not conduct for α<π/2.The free wheeling d ...
Design Note - Texas Instruments
... The Single Ended Primary Inductance Converter (SEPIC) can convert an input voltage to an output voltage that is higher, lower or equal to the input. Conversion is performed without the use of expensive transformers, making this a good choice for low cost, non-isolated applications. The UC2577 provid ...
... The Single Ended Primary Inductance Converter (SEPIC) can convert an input voltage to an output voltage that is higher, lower or equal to the input. Conversion is performed without the use of expensive transformers, making this a good choice for low cost, non-isolated applications. The UC2577 provid ...
INVERTERS - SolarEdge
... UL1741, UL1699B, UL1998, CSA 22.2 IEEE1547 FCC part15 class B 3/4” minimum / 12-6 AWG 3/4” minimum / 12-6 AWG 2 pairs 3 pairs (with fuses on plus & minus)(4) 21 x 12.5 x 10.5 / 540 x 315 x 260 30.5 x 12.5 x 10.5 / 775 x 315 x 260 ...
... UL1741, UL1699B, UL1998, CSA 22.2 IEEE1547 FCC part15 class B 3/4” minimum / 12-6 AWG 3/4” minimum / 12-6 AWG 2 pairs 3 pairs (with fuses on plus & minus)(4) 21 x 12.5 x 10.5 / 540 x 315 x 260 30.5 x 12.5 x 10.5 / 775 x 315 x 260 ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.