Hematology Case Histories
... It increases the amount of RBCs in the blood. 10. What is a normal value for arterial oxygen saturation? ...
... It increases the amount of RBCs in the blood. 10. What is a normal value for arterial oxygen saturation? ...
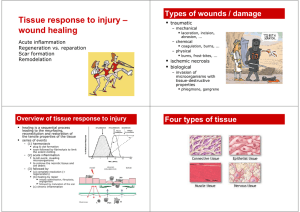
Tissue response to injury wound healing
... activated protein C is an enzyme that destroys certain clotting factors and inhibits coagulation ...
... activated protein C is an enzyme that destroys certain clotting factors and inhibits coagulation ...
Hypertension Objective Treatment Based on Measurement by
... At last follow-up (median 5.3 years), 1759 TC compared with 1759 UC patients used more antihypertensive drugs (1.82 vs. 1.74 defined daily doses, p=0.045), had more home BP reduction (21.3/13.1 mm Hg vs. 22.7/13.9 mm Hg, p=0.018/0.020), but less frequently achieved the lower home BP targets (37.4% v ...
... At last follow-up (median 5.3 years), 1759 TC compared with 1759 UC patients used more antihypertensive drugs (1.82 vs. 1.74 defined daily doses, p=0.045), had more home BP reduction (21.3/13.1 mm Hg vs. 22.7/13.9 mm Hg, p=0.018/0.020), but less frequently achieved the lower home BP targets (37.4% v ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 02. Define the term: universal donor. 03. What is occult blood? 04. Distinguish type 1 from type 2 Diabetes mellitus. 05. What is meant by storage lesion. 06. Distinguish leucopenia from polycythemia. 07. Write the procedure for the detection of bile salts in urine sample. 08. Give the names of any ...
... 02. Define the term: universal donor. 03. What is occult blood? 04. Distinguish type 1 from type 2 Diabetes mellitus. 05. What is meant by storage lesion. 06. Distinguish leucopenia from polycythemia. 07. Write the procedure for the detection of bile salts in urine sample. 08. Give the names of any ...
Blood Component Preparation: From Benchtop to Bedside Brochure
... Blood Bag Systems and Automated Separators Production of BC-Derived Platelet Concentrates BC-Reduced Red Cell Concentrates and Plasma Overnight Hold of Whole Blood Further Automation of Centrifugation and Separation ...
... Blood Bag Systems and Automated Separators Production of BC-Derived Platelet Concentrates BC-Reduced Red Cell Concentrates and Plasma Overnight Hold of Whole Blood Further Automation of Centrifugation and Separation ...
What you should know about platelet donation
... Platelets are much smaller than red and white cells and are actually fragments of cells made in the bone marrow. There are about 250 million per millilitre of blood and their main function is to help clot the blood and seal wounds. If a blood vessel is damaged, platelets clump together to help “plug ...
... Platelets are much smaller than red and white cells and are actually fragments of cells made in the bone marrow. There are about 250 million per millilitre of blood and their main function is to help clot the blood and seal wounds. If a blood vessel is damaged, platelets clump together to help “plug ...
HW 1
... Living with sickle cell “I have an illness called sickle cell. This means that my red blood cells are a different shape to everyone else's. Mine are sickle shaped (a sickle is a curved tool), normal blood cells are round. The shape of my cells makes it difficult for the blood to go around my body. T ...
... Living with sickle cell “I have an illness called sickle cell. This means that my red blood cells are a different shape to everyone else's. Mine are sickle shaped (a sickle is a curved tool), normal blood cells are round. The shape of my cells makes it difficult for the blood to go around my body. T ...
Carter BloodCare
... Your blood is typed: 0, A, B, or AB, as well as Rh factor (either positive or negative.) Your blood is also tested for infectious diseases such as syphilis, hepatitis Band C, HIV and West Nile virus. ...
... Your blood is typed: 0, A, B, or AB, as well as Rh factor (either positive or negative.) Your blood is also tested for infectious diseases such as syphilis, hepatitis Band C, HIV and West Nile virus. ...
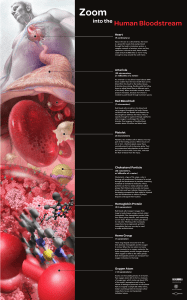
Zoom into the Human Bloodstream Annotated
... times smaller than the heart itself) that carries blood from the heart to the body’s tissues. Arterioles have strong, flexible walls that allow them to adjust blood flow to different parts of the body. When arterioles constrict, blood pressure increases, because more force is needed to push blood th ...
... times smaller than the heart itself) that carries blood from the heart to the body’s tissues. Arterioles have strong, flexible walls that allow them to adjust blood flow to different parts of the body. When arterioles constrict, blood pressure increases, because more force is needed to push blood th ...
laboratory services
... Whole blood consists of a biological fluid, the plasma, which contains all blood cells. These cells or "blood elements" are the red blood cells, the white blood cells and the platelets. Whole blood is not a stable product: it spontaneously coagulates within a few minutes outside of the blood vessels ...
... Whole blood consists of a biological fluid, the plasma, which contains all blood cells. These cells or "blood elements" are the red blood cells, the white blood cells and the platelets. Whole blood is not a stable product: it spontaneously coagulates within a few minutes outside of the blood vessels ...
Bartonella quintana
... Intraerythrocytic bacteremia subsides due to strong IgG antibody response (in animal models) ...
... Intraerythrocytic bacteremia subsides due to strong IgG antibody response (in animal models) ...
Hemic/Lymphatic System
... Your blood circulates through your veins, meanwhile being filtered at certain locations, (lymph nodes) before being passed along through the rest of your body. ...
... Your blood circulates through your veins, meanwhile being filtered at certain locations, (lymph nodes) before being passed along through the rest of your body. ...
Blood Types
... Depending on presence or absence of antigen (Agglutinogen),four different blood groups A--if only agglutinogen A is present B--if only agglutinogen B is present AB--if both agglutinogen A and B are present O--if neither agglutinogen A nor agglutinogen B are present ...
... Depending on presence or absence of antigen (Agglutinogen),four different blood groups A--if only agglutinogen A is present B--if only agglutinogen B is present AB--if both agglutinogen A and B are present O--if neither agglutinogen A nor agglutinogen B are present ...
Blood Types
... Depending on presence or absence of antigen (Agglutinogen),four different blood groups A--if only agglutinogen A is present B--if only agglutinogen B is present AB--if both agglutinogen A and B are present O--if neither agglutinogen A nor agglutinogen B are present ...
... Depending on presence or absence of antigen (Agglutinogen),four different blood groups A--if only agglutinogen A is present B--if only agglutinogen B is present AB--if both agglutinogen A and B are present O--if neither agglutinogen A nor agglutinogen B are present ...
Will I need a platelet transfusion?
... rashes, shivering or an increase in body temperature. This is usually mild and easily treated with paracetamol or by slowing down the transfusion. A very small number of people who receive platelets regularly, might fail to show a rise in platelet count despite transfusion. This condition is known a ...
... rashes, shivering or an increase in body temperature. This is usually mild and easily treated with paracetamol or by slowing down the transfusion. A very small number of people who receive platelets regularly, might fail to show a rise in platelet count despite transfusion. This condition is known a ...
Factor XIII: sticking it to platelets
... blood smears. Analysis showed that these platelets lacked a class of granules that are now known as a-granules. GPS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder associated with macrothrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, myelofibrosis, increased serum B12, and mildto-moderate bleeding tendencies.3 Although fatal ...
... blood smears. Analysis showed that these platelets lacked a class of granules that are now known as a-granules. GPS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder associated with macrothrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, myelofibrosis, increased serum B12, and mildto-moderate bleeding tendencies.3 Although fatal ...
Dr. Tessa King, a veterinarian at Pilchuck Veterinary Hospital
... For example, neutrophils are the most common elevated white blood cells because they are one of the first responders to any type of inflammation, including infection. Eosinophils, another type of white blood cells, are typically elevated with parasitic or allergic diseases. Platelets are very import ...
... For example, neutrophils are the most common elevated white blood cells because they are one of the first responders to any type of inflammation, including infection. Eosinophils, another type of white blood cells, are typically elevated with parasitic or allergic diseases. Platelets are very import ...
ELECTRONIC DEMONSTRATION OF BLOOD CELL AGGLUTININS
... gross and composed of few but very large clumps. Inasmuch as there were so few agglutinates, the instrument count was low, although the amplitude of each pulse was high; however, when the threshold was increased from 15 to 70 the background values were minimized, thereby accomplishing a spread that ...
... gross and composed of few but very large clumps. Inasmuch as there were so few agglutinates, the instrument count was low, although the amplitude of each pulse was high; however, when the threshold was increased from 15 to 70 the background values were minimized, thereby accomplishing a spread that ...
File - Incarnation Science
... a. carries needed substances to cells b. carries waste products away from cells. c. contains cells that fight disease ...
... a. carries needed substances to cells b. carries waste products away from cells. c. contains cells that fight disease ...
Case report of a patient with multiorgan failure due to
... After immediate resuscitation the patient developed severe SIRS and multiple organ failure with cardiogenic shock due to refractory cardiac arrhythmia Initial ultrasound of heart function showed diffuse hypokinesia and an ejection fraction (EF) of around 45 %, with a heart rate of 36 bpm 24 hours of ...
... After immediate resuscitation the patient developed severe SIRS and multiple organ failure with cardiogenic shock due to refractory cardiac arrhythmia Initial ultrasound of heart function showed diffuse hypokinesia and an ejection fraction (EF) of around 45 %, with a heart rate of 36 bpm 24 hours of ...
Epogen (Epo) (Erythropoietin)
... Epogen (Epo) (Erythropoietin) What is Epogen? Erythropoietin is a hormone that regulates red blood cell production. Epogen is the synthetic form of erythropoietin, and is dispensed as a medication/drug. Although Epo has several uses, it is used in the NICU to treat or prevent anemia (low red blood c ...
... Epogen (Epo) (Erythropoietin) What is Epogen? Erythropoietin is a hormone that regulates red blood cell production. Epogen is the synthetic form of erythropoietin, and is dispensed as a medication/drug. Although Epo has several uses, it is used in the NICU to treat or prevent anemia (low red blood c ...
Detecting Blood Coagulation On-Chip USF Available Technologies
... Some people use a blood thinner for a short time, but many others take it for years to prevent serious health problems—like stroke or a heart attack. The Food and Drug Administration estimates that more than 31 million prescriptions for warfarin were written in recent years. The human body automatic ...
... Some people use a blood thinner for a short time, but many others take it for years to prevent serious health problems—like stroke or a heart attack. The Food and Drug Administration estimates that more than 31 million prescriptions for warfarin were written in recent years. The human body automatic ...
Lymph II: SPLEEN
... - germinal centers (contains plasmablasts and plasma cells derived from B cells) form after antigenic stimulation can push the central artery into an eccentric position PENICILLI: - straight arteriole branches from the central arteries in the white pulp that lead into red pulp MARGINAL ZONE: - lies ...
... - germinal centers (contains plasmablasts and plasma cells derived from B cells) form after antigenic stimulation can push the central artery into an eccentric position PENICILLI: - straight arteriole branches from the central arteries in the white pulp that lead into red pulp MARGINAL ZONE: - lies ...
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (or haemolytic-uraemic syndrome), abbreviated HUS, is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia (anemia caused by destruction of red blood cells), acute kidney failure (uremia), and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia). It predominantly, but not exclusively, affects children. Most cases are preceded by an episode of infectious, sometimes bloody, diarrhea acquired as a foodborne illness or from a contaminated water supply and caused by E. coli O157:H7, although Shigella, Campylobacter and a variety of viruses have also been implicated. It is now the most common cause of acquired acute renal failure in childhood. It is a medical emergency and carries a 5–10% mortality; of the remainder, the majority recover without major consequences but a small proportion develop chronic kidney disease and become reliant on renal replacement therapy.The primary target appears to be the vascular endothelial cell. This may explain the pathogenesis of HUS, in which a characteristic renal lesion is capillary microangiopathy.HUS was first defined as a syndrome in 1955. The more common form of the disease, Shiga-like toxin-producing E. coli HUS (STEC-HUS), is triggered by the infectious agent E. coli O157:H7. Certain Shiga toxin secreting strains of Shigella dysenteriae can also cause HUS. Approximately 5% of cases are classified as pneumococcal HUS, which results from infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae, the agent that causes traditional lobar pneumonia. There is also a rare, chronic, and severe form known as atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), which is caused by genetic defects resulting in chronic, uncontrolled complement activation. Both STEC-HUS and aHUS cause endothelial damage, leukocyte activation, platelet activation, and widespread inflammation and multiple thromboses in the small blood vessels, a condition known as systemic thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), which leads to thrombotic events as well as organ damage/failure and death.