* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lymph II: SPLEEN
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
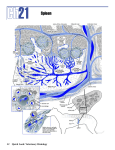
Lymph II: SPLEEN FUNCTIONS: - Filters blood: it removes old and damaged red blood cells and platelets - Iron Retrieval and Heme metabolism - Reserve for red blood cells; it is engorged with blood - Immune response against blood-borne antigens - Fetal hematopoiesis. The spleen is supplied by a single splenic artery and drained by a single splenic vein; all vessels enter the hilum Splenic artery Splenic Vein Trabecular arteries Trabecular veins Central arteries (PALS) Pulp Veins Penicilli (arterioles) Ellipsoids Sinusoids CAPSULE: - histology: - dense, fibrous, irregularly-arranged connective tissue - reticular fibers (Foot’s silver and azo-carmine stain them black) - trabeculae: extensions from the capsule into the parenchyma - capsule and trabeculae also contain smooth muscle - contraction of the spleen pumps stored blood into the circulation. WHITE PULP: (analogous to cortex; note: stains basophilically on H&E & red on silver stain) - functions: - immune function: site of B cell – T cell interaction and antibody production - here, reticular connective tissue is filled with lymphocytes (B and T cells) - the Central Artery is surrounded by the Periarteriolar Lymphatic Sheath (PALS) of T cells - appears basophilic because of the dense heterochromatic nuclei of the lymphocytes - germinal centers (contains plasmablasts and plasma cells derived from B cells) form after antigenic stimulation can push the central artery into an eccentric position PENICILLI: - straight arteriole branches from the central arteries in the white pulp that lead into red pulp MARGINAL ZONE: - lies between White pulp and Red pulp - site where the white pulp capillaries drain - immunologic activity: lymphatic tissue is exposed to blood-borne antigens - there are NO sinusoids here RED PULP: (analogous to medulla) - consists of most of the area inside the capsule - appears red, in fresh states & histologically - macrophages examine and filter blood - blood leaves the circulation through the ellipsoids (sheathed capillaries: wrapped by macrophages) - blood is then filtered through the fenestrated SINUSOIDS - (gaps between the endothelial cells…will see dotted line in the basal lamina) - blood encounters macrophages in the sinusoids so that old/compromised blood cells are phagocytosed CORDS OF BILLROTH: (parenchyma) - reticular tissue bordering splenic sinusoids in the red pulp - contains macrophages, lymphocytes, blood cells