The Truth About Base Curves - ABO-NCLE
... charts. Standardized base curve charts are designed on a monocular principle. In anisometropic patients however, this is not practical since both eyes are used in unison. A large difference between each base curve may induce aniseikonia. Aniseikonia occurs when the ocular image of an object as seen ...
... charts. Standardized base curve charts are designed on a monocular principle. In anisometropic patients however, this is not practical since both eyes are used in unison. A large difference between each base curve may induce aniseikonia. Aniseikonia occurs when the ocular image of an object as seen ...
12. confocal microscopy.
... Most commonly, confocal microscopy is used with fluorescence, which provides significantly higher contrast. Theoretically, the contrast in a fluorescence image is infinite, i.e. untagged structures (background) give zero signal. However, practical issues related to dark signals in the detector, limi ...
... Most commonly, confocal microscopy is used with fluorescence, which provides significantly higher contrast. Theoretically, the contrast in a fluorescence image is infinite, i.e. untagged structures (background) give zero signal. However, practical issues related to dark signals in the detector, limi ...
Sign convention
... 1. A ray through the center of the lens is undeviated 2. An incident ray parallel to the optic axis appears to emerge from the front focal point 3. An incident ray directed towards the back focal point emerges parallel to the optic axis. and occasionally useful 4. Two rays that are parallel in front ...
... 1. A ray through the center of the lens is undeviated 2. An incident ray parallel to the optic axis appears to emerge from the front focal point 3. An incident ray directed towards the back focal point emerges parallel to the optic axis. and occasionally useful 4. Two rays that are parallel in front ...
PHYS 202 Notes, Week 10
... first case is called myopia, or nearsightedness, because it causes images of far-away objects to appear out of focus. The second is called hyperopia, or farsightedness, because it causes close-up images to be out of focus. Drawings of these are shown in Figure 3. Each of these vision problems can be ...
... first case is called myopia, or nearsightedness, because it causes images of far-away objects to appear out of focus. The second is called hyperopia, or farsightedness, because it causes close-up images to be out of focus. Drawings of these are shown in Figure 3. Each of these vision problems can be ...
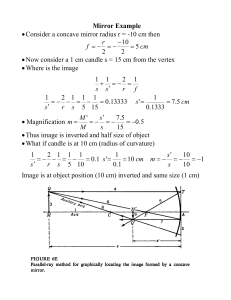
Mirror Example • Consider a concave mirror radius r =
... This correctly shows both position and magnification of object This really shows how the light rays are travelling Eg Ray through the focal point F (ray 6) becomes parallel (ray 7) Intersects ray 5 again at image Q’ Can use graphics to solve exactly But often sketch this to see if optic ...
... This correctly shows both position and magnification of object This really shows how the light rays are travelling Eg Ray through the focal point F (ray 6) becomes parallel (ray 7) Intersects ray 5 again at image Q’ Can use graphics to solve exactly But often sketch this to see if optic ...
04_HMDs
... Focal Length - The distance from the surface of a lens (or mirror) at which rays of light converge. Diopter - The power of a lens is measured in diopters, where the number of diopters is equal to 1/(focal length of the lens measured in meters). Larry F. Hodges ...
... Focal Length - The distance from the surface of a lens (or mirror) at which rays of light converge. Diopter - The power of a lens is measured in diopters, where the number of diopters is equal to 1/(focal length of the lens measured in meters). Larry F. Hodges ...
Lens 101 review
... These elements are able to focus different wave lengths of one light ray in one point (see picture below). These elements are quite expensive and usually not used for cheaper lenses. The problem is however that the quality of these special elements varies heavily so the effect is often downgraded to ...
... These elements are able to focus different wave lengths of one light ray in one point (see picture below). These elements are quite expensive and usually not used for cheaper lenses. The problem is however that the quality of these special elements varies heavily so the effect is often downgraded to ...
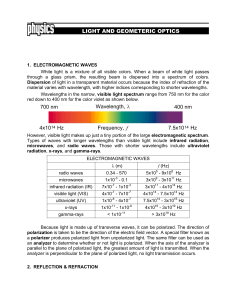
700 nm 400 nm Wavelength, λ Frequency, f 4x1014 Hz
... When looking at a plane mirror, the image appears to be located behind the mirror. Because light rays do not actually pass through this image, it is known as a virtual image. In the case of a plane mirror, the image distance si from the mirror is the same as the object distance so from the mirror. T ...
... When looking at a plane mirror, the image appears to be located behind the mirror. Because light rays do not actually pass through this image, it is known as a virtual image. In the case of a plane mirror, the image distance si from the mirror is the same as the object distance so from the mirror. T ...
as a PDF - Department of Engineering Science
... speed at which this can be done by using piezoelectric elements [2,3] however this speed is still limited by the fact that the imaging lenses and/or the specimen are relatively heavy. Apart from the speed limitations, these methods can also suffer from other disadvantages, which make imaging of deli ...
... speed at which this can be done by using piezoelectric elements [2,3] however this speed is still limited by the fact that the imaging lenses and/or the specimen are relatively heavy. Apart from the speed limitations, these methods can also suffer from other disadvantages, which make imaging of deli ...
Basic Optics - Lynn`s Lecture Help
... When light is not focused on the retina, an ametropia is present... for example, a myopic eye focuses light in front of the retina... ...
... When light is not focused on the retina, an ametropia is present... for example, a myopic eye focuses light in front of the retina... ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.