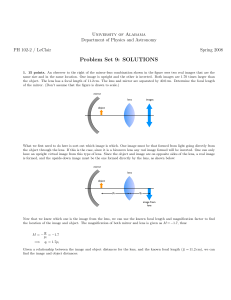
The Fresnel Biprism
... fringes, whereas when the biprism is further away, there are a larger number of fringes with smaller spaces in between them. This can be explained due to the fact that when the biprism is further away, the light that enters the biprism does so at a more acute angle than when the biprism is closer. ...
... fringes, whereas when the biprism is further away, there are a larger number of fringes with smaller spaces in between them. This can be explained due to the fact that when the biprism is further away, the light that enters the biprism does so at a more acute angle than when the biprism is closer. ...
Document
... Some stage micrometers are finely divided only at one end. One of the larger divisions is positioned at one edge of the field of view, so that the fine part of the scale overlaps the opposite side. The field diameter ca then be determined to the maximum available precision ...
... Some stage micrometers are finely divided only at one end. One of the larger divisions is positioned at one edge of the field of view, so that the fine part of the scale overlaps the opposite side. The field diameter ca then be determined to the maximum available precision ...
Report Liquid Lens
... leave plenty to be desired. Part of the problem is their CMOS imaging chips, which typically have a censor array of only about 300 kilo pixels-a quarter or less of the number in a low-end digital camera. But the major problem is their tiny, fixed focus lenses. These fixed focus lenses are very small ...
... leave plenty to be desired. Part of the problem is their CMOS imaging chips, which typically have a censor array of only about 300 kilo pixels-a quarter or less of the number in a low-end digital camera. But the major problem is their tiny, fixed focus lenses. These fixed focus lenses are very small ...
Many other important inventions involve the use of
... is the product of the powers of the ocular (eyepiece), usually about 10×, and the objective lens being used. ...
... is the product of the powers of the ocular (eyepiece), usually about 10×, and the objective lens being used. ...
File
... 16. Brewster’s law : μ = tan ip Where μ is refractive index of material ip is polarizing angle At polarising angle reflected ray and refracted ray are perpendicular to each other. 17. Malus law : It states that if polarized light is passed through an analyser , the intensity of light transmitted is ...
... 16. Brewster’s law : μ = tan ip Where μ is refractive index of material ip is polarizing angle At polarising angle reflected ray and refracted ray are perpendicular to each other. 17. Malus law : It states that if polarized light is passed through an analyser , the intensity of light transmitted is ...
The Visual System Ophthalmic Lenses Basic Optical Formulas
... ...as the crystalline lens ages, it loses its flexibility- and its ability to adjust focus... this condition is called presbyopia and typically becomes noticeable around age 40 ...
... ...as the crystalline lens ages, it loses its flexibility- and its ability to adjust focus... this condition is called presbyopia and typically becomes noticeable around age 40 ...
Optics Observations
... Short wavelength linespread functions are much broader than middle wavelength ...
... Short wavelength linespread functions are much broader than middle wavelength ...
6288-18 talk - LOFT, Large Optics Fabrication and Testing group
... • For system with object or image at infinity, effect of element motion is tilt in the light. ...
... • For system with object or image at infinity, effect of element motion is tilt in the light. ...
Optics Lesson 6
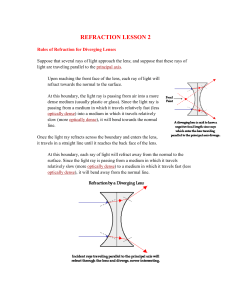
... Because of the different shape of the concave lens, these incident rays are not converged to a point upon refraction through the lens. Rather, these incident rays diverge upon refracting through the lens. What does this mean? A concave lens can never produce a real image. Concave lenses produce ima ...
... Because of the different shape of the concave lens, these incident rays are not converged to a point upon refraction through the lens. Rather, these incident rays diverge upon refracting through the lens. What does this mean? A concave lens can never produce a real image. Concave lenses produce ima ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... spot, i.e. the original beam contains only low spatial frequencies. On the other hand, if we pass this beam through a grating or specimen which introduces many variations on the laser profile, then in the focal plane of the lens we will have several spots indicating that additional spatial frequency ...
... spot, i.e. the original beam contains only low spatial frequencies. On the other hand, if we pass this beam through a grating or specimen which introduces many variations on the laser profile, then in the focal plane of the lens we will have several spots indicating that additional spatial frequency ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.