Fraunhofer diffraction from gratings In this exercise we use a two
... While Bragg’s law is given by the expression 2d sin n , we get for a two-dimensional grating that d sin 1 sin 2 n . Here , 1 are 2 are the Bragg angle, the angle of incidence and the angle of exit, is the wavelength, d the distance between the lines in the grating (periodicity ...
... While Bragg’s law is given by the expression 2d sin n , we get for a two-dimensional grating that d sin 1 sin 2 n . Here , 1 are 2 are the Bragg angle, the angle of incidence and the angle of exit, is the wavelength, d the distance between the lines in the grating (periodicity ...
Lecture 31 - Purdue Physics
... determines how much light will reach the image plane. • Pupils are typically circular: the area varies as the square of the diameter, 9. • The image area varies as the square of the lateral dimension, : ~ • Light intensity at the image plane varies as 9/ • (9/ ) is called the relative aperture ...
... determines how much light will reach the image plane. • Pupils are typically circular: the area varies as the square of the diameter, 9. • The image area varies as the square of the lateral dimension, : ~ • Light intensity at the image plane varies as 9/ • (9/ ) is called the relative aperture ...
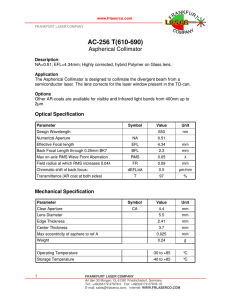
Paraxial Formulas - CVI Laser Optics
... or virtual image is 0.5 mm high and upright. A simple graphical method can also be used to determine paraxial image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the o ...
... or virtual image is 0.5 mm high and upright. A simple graphical method can also be used to determine paraxial image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the o ...
CP Physics - Ms. Lisa Cole-
... 2. The area of the eye on which light is focused is called the ____________________ 3. As a ray of light passes from air into the lens, the speed of light ____________. 4. A diverging lens ____________________________ 5. A magnifying glass is usually a ____________________________. 6. If a person’s ...
... 2. The area of the eye on which light is focused is called the ____________________ 3. As a ray of light passes from air into the lens, the speed of light ____________. 4. A diverging lens ____________________________ 5. A magnifying glass is usually a ____________________________. 6. If a person’s ...
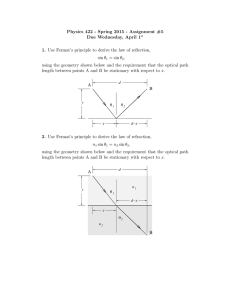
Physics 422 - Spring 2015 - Assignment #5
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
Section 1 Supplement
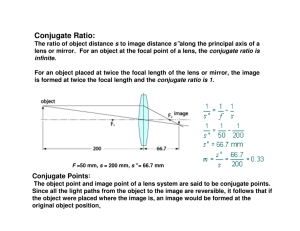
... An object is anything that is being viewed, e.g., when one looks at a tree through a lens, with a mirror or any other optical device the tree is referred to an optical object. Object Distance, s, is the distance from an object to an optical element. An image is the likeness of an object produced at ...
... An object is anything that is being viewed, e.g., when one looks at a tree through a lens, with a mirror or any other optical device the tree is referred to an optical object. Object Distance, s, is the distance from an object to an optical element. An image is the likeness of an object produced at ...
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments
... •Shutter speed refers to the speed of the shutter opening and closing. •F-stop controls the amount of light coming into the light-tight box, by controlling the size of the opening •F-stop=f/D ...
... •Shutter speed refers to the speed of the shutter opening and closing. •F-stop controls the amount of light coming into the light-tight box, by controlling the size of the opening •F-stop=f/D ...
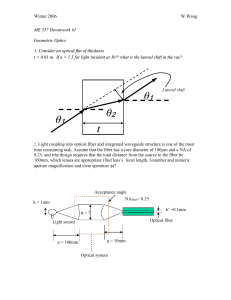
ME 557 Howmwork #1
... Light coupling into optical fiber and integrated waveguide structure is one of the most time consuming task. Assume that the fiber has a core diameter of 100m and a NA of 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find ...
... Light coupling into optical fiber and integrated waveguide structure is one of the most time consuming task. Assume that the fiber has a core diameter of 100m and a NA of 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find ...
OPTICAL BENCH SET using METER STICK
... Set up the optical bench with a light source, object marker, a lens of 15 cm focal length, and screen as shown in photo. Place the object maker on the meter stick using the required distance. Place the light source at the end of the bench, the object marker about 10 cm from the light source, and the ...
... Set up the optical bench with a light source, object marker, a lens of 15 cm focal length, and screen as shown in photo. Place the object maker on the meter stick using the required distance. Place the light source at the end of the bench, the object marker about 10 cm from the light source, and the ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.











![Scalar Diffraction Theory and Basic Fourier Optics [Hecht 10.2.410.2.6, 10.2.8, 11.211.3 or Fowles Ch. 5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008906603_1-55857b6efe7c28604e1ff5a68faa71b2-300x300.png)