Lens Effectivity (WP)
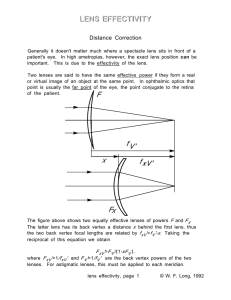
... Distance Correction Generally it doesn't matter much where a spectacle lens sits in front of a patient's eye. In high ametropias, however, the exact lens position can be important. This is due to the effectivity of the lens. Two lenses are said to have the same effective power if they form a real or ...
... Distance Correction Generally it doesn't matter much where a spectacle lens sits in front of a patient's eye. In high ametropias, however, the exact lens position can be important. This is due to the effectivity of the lens. Two lenses are said to have the same effective power if they form a real or ...
PPT
... • Looking at three stars (red, green, blue) through telescope, eye position is important • So is pupil size compared to eye pupil – dark adapted pupil up to 7 mm diameter (2–3 mm in daylight) – sets limit on minimum magnification (if you want to use the full aperture) • 210 mm aperture telescope mus ...
... • Looking at three stars (red, green, blue) through telescope, eye position is important • So is pupil size compared to eye pupil – dark adapted pupil up to 7 mm diameter (2–3 mm in daylight) – sets limit on minimum magnification (if you want to use the full aperture) • 210 mm aperture telescope mus ...
Intraocular Lenses
... e the aperture into circular “zones” (these are the concentric rings in the zone plate pictured above). The edge of each zone is /2 farther away from Po than the edge of the neighboring zone. 2. Notice that the wave that travels along the axis of the aperture experiences constructive interference ...
... e the aperture into circular “zones” (these are the concentric rings in the zone plate pictured above). The edge of each zone is /2 farther away from Po than the edge of the neighboring zone. 2. Notice that the wave that travels along the axis of the aperture experiences constructive interference ...
6,
... sometimes achieved at the price of a limited datahandling capacity. It is also convenient to synthesize desired linear-filtering operations in the frequency domain rather than the space domain. When coherent illumination is used, the desired filtering operation can be synthesized by direct manipulat ...
... sometimes achieved at the price of a limited datahandling capacity. It is also convenient to synthesize desired linear-filtering operations in the frequency domain rather than the space domain. When coherent illumination is used, the desired filtering operation can be synthesized by direct manipulat ...
test - Lyle School of Engineering
... ANALYTICALLY) to determine what the spectral resolution of your optical system. Choose the cheapest lens (lowest performing) that will accomplish your goals. You may elect to “stop down” an aperture on a larger lens of lower quality if you only need the central portion of it. Note if you get stuck o ...
... ANALYTICALLY) to determine what the spectral resolution of your optical system. Choose the cheapest lens (lowest performing) that will accomplish your goals. You may elect to “stop down” an aperture on a larger lens of lower quality if you only need the central portion of it. Note if you get stuck o ...
AQA GCSE Physics P3 Revision Worksheet
... The hydraulic braking system in a car uses the principle of a force multiplier, provided by an incompressible liquid. It uses of different cross-sectional areas on the effort and load sides. This enables a much bigger force applied to the load than the effort force. ...
... The hydraulic braking system in a car uses the principle of a force multiplier, provided by an incompressible liquid. It uses of different cross-sectional areas on the effort and load sides. This enables a much bigger force applied to the load than the effort force. ...
Ray Optics
... another image, the images are said to be just resolved Resolution of a slit: Since λ << a in most situations, sin θ is very small and sin θ ~ θ Therefore, the limiting angle (in rad) of resolution for a slit of width a is ...
... another image, the images are said to be just resolved Resolution of a slit: Since λ << a in most situations, sin θ is very small and sin θ ~ θ Therefore, the limiting angle (in rad) of resolution for a slit of width a is ...
Review - misshoughton.net
... characteristics Using mirror and magnification equations appropriately 4. Refraction of Light Definition, properties, characteristics Index of refraction Dispersion 5. Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection Definition, properties, characteristics Large angles of incidence Cri ...
... characteristics Using mirror and magnification equations appropriately 4. Refraction of Light Definition, properties, characteristics Index of refraction Dispersion 5. Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection Definition, properties, characteristics Large angles of incidence Cri ...
Introduction to Mirrors and Lenses
... three rays described above will appear to come from an enlarged and upright image. Any other ray leaving the tip of the object will appear to come from Three rays are included in the the tip of the image after passing illustration. Following are descriptions through the lens. The three rays used of ...
... three rays described above will appear to come from an enlarged and upright image. Any other ray leaving the tip of the object will appear to come from Three rays are included in the the tip of the image after passing illustration. Following are descriptions through the lens. The three rays used of ...
Thin Lenses
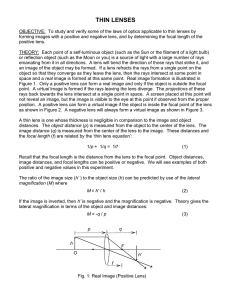
... THEORY: Each point of a self-luminous object (such as the Sun or the filament of a light bulb) or reflection object (such as the Moon or you) is a source of light with a large number of rays emanating from it in all directions. A lens will bend the direction of those rays that strike it, and an imag ...
... THEORY: Each point of a self-luminous object (such as the Sun or the filament of a light bulb) or reflection object (such as the Moon or you) is a source of light with a large number of rays emanating from it in all directions. A lens will bend the direction of those rays that strike it, and an imag ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.