Chapter 34 – Geometric Optics and Optical Instruments
... A glass rod 40 cm long and index 1.50 has one end that is convex of radius 20 cm and the other end has a convex surface of radius 30 cm. An object is placed 100 cm in front of the 20 cm convex surface. Where, what size, and what orientation is the final image? ...
... A glass rod 40 cm long and index 1.50 has one end that is convex of radius 20 cm and the other end has a convex surface of radius 30 cm. An object is placed 100 cm in front of the 20 cm convex surface. Where, what size, and what orientation is the final image? ...
startest
... The careful visual examination of the image of a point source formed by a lens being evaluated is one of the most basic and important tests that can be performed. The interpretation of the image in terms of aberrations is to a large degree a matter of experience, and the visual examination of a poin ...
... The careful visual examination of the image of a point source formed by a lens being evaluated is one of the most basic and important tests that can be performed. The interpretation of the image in terms of aberrations is to a large degree a matter of experience, and the visual examination of a poin ...
A tutorial for designing fundamental imaging systems
... At first, we design optical system ignoring elements surface error. In practice, there are defects or distortion on the surfaces of optical elements, which effect to wavefront error. Wavefront error cause degradation of optical resolution.[1] Wavefront error is important in high-resolution system, b ...
... At first, we design optical system ignoring elements surface error. In practice, there are defects or distortion on the surfaces of optical elements, which effect to wavefront error. Wavefront error cause degradation of optical resolution.[1] Wavefront error is important in high-resolution system, b ...
Focal length
... Principal axis - a radius drawn to the mirror surface from the center of curvature of the mirror - normal to mirror surface Focus - the point where light rays parallel to principal axis converge; the focus is always found on the inner part of the "circle" of which the mirror is a small arc; the focu ...
... Principal axis - a radius drawn to the mirror surface from the center of curvature of the mirror - normal to mirror surface Focus - the point where light rays parallel to principal axis converge; the focus is always found on the inner part of the "circle" of which the mirror is a small arc; the focu ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... incidence for a reflected ray of light. The angles are defined with respect to the direction perpendicular to the reflecting surface called the normal. 2. Concave mirrors focus rays so that they converge at a common focal point in front of the mirror. Convex mirrors produce diverging rays with a foc ...
... incidence for a reflected ray of light. The angles are defined with respect to the direction perpendicular to the reflecting surface called the normal. 2. Concave mirrors focus rays so that they converge at a common focal point in front of the mirror. Convex mirrors produce diverging rays with a foc ...
Beam-Based Diagnostics - Stanford Synchrotron Radiation
... Charged particle storage rings are used for a variety of science and technology applications --- for example as synchrotron radiation light sources for biology, chemistry, and materials science, as colliders for high-energy physics or as damping rings to reduce the beam emittance for linear collider ...
... Charged particle storage rings are used for a variety of science and technology applications --- for example as synchrotron radiation light sources for biology, chemistry, and materials science, as colliders for high-energy physics or as damping rings to reduce the beam emittance for linear collider ...
GGN PUBLIC SCHOOL, LUDHIANA XII PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT
... 8. How the power of convex lens vary when, if the incident red light is replaced by violet light. 9. When light travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium, its speed decreases. Does this increase in speed imply a decrease in the energy carried by the light wave? 10. When does a convex lens behav ...
... 8. How the power of convex lens vary when, if the incident red light is replaced by violet light. 9. When light travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium, its speed decreases. Does this increase in speed imply a decrease in the energy carried by the light wave? 10. When does a convex lens behav ...
microscope instructions ppt
... The oculars can also be focused differently for each eye. Start by selecting the 10X objective and rotating it into place. You always want to start at this low power because is easier to find the specimen and the approximate focus. Place a specimen slide on the stage and focus on it. The left ocular ...
... The oculars can also be focused differently for each eye. Start by selecting the 10X objective and rotating it into place. You always want to start at this low power because is easier to find the specimen and the approximate focus. Place a specimen slide on the stage and focus on it. The left ocular ...
Refraction and Lenses Learning Guide
... 8. When light is passing from a medium with a high index of refraction to one with a lower index of refraction at the critical angle, what is the angle of refraction? 90o 9. If the light is incident at a greater angle what happens? total internal reflection 10. Describe the lenses (number and type) ...
... 8. When light is passing from a medium with a high index of refraction to one with a lower index of refraction at the critical angle, what is the angle of refraction? 90o 9. If the light is incident at a greater angle what happens? total internal reflection 10. Describe the lenses (number and type) ...
Optics in Confocal Microscopy
... focussed spot expands asymmetrically on either side of focus, indicating spherical aberration. ...
... focussed spot expands asymmetrically on either side of focus, indicating spherical aberration. ...
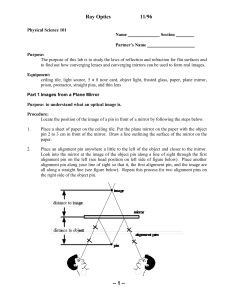
LAB #10 - GEOCITIES.ws
... To relate image and object distances to focal lengths for various lenses. To be able to determine focal length, image size, brightness, and f-numbers for various lenses. To understand the differences between telescopic systems and astronomical telescopes of various types. To construct a simple refra ...
... To relate image and object distances to focal lengths for various lenses. To be able to determine focal length, image size, brightness, and f-numbers for various lenses. To understand the differences between telescopic systems and astronomical telescopes of various types. To construct a simple refra ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.