NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS ADVANCED PLACEMENT TEST (SAMPLE)
... Unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on a stack of three polarisers. The transmission axis of the third polariser is always perpendicular to the first polariser, while that of the second polariser is oriented at an angle α with respect to this third polariser (see diagram below). Derive an ...
... Unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on a stack of three polarisers. The transmission axis of the third polariser is always perpendicular to the first polariser, while that of the second polariser is oriented at an angle α with respect to this third polariser (see diagram below). Derive an ...
Microscope
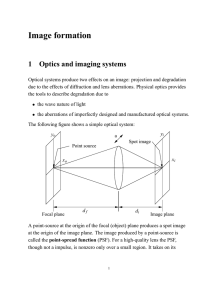
... two points as separate and distinct even when they are so close together that they appear as one to the unaided eye. This distance at which two points appear as one is about 0.1 mm at ten inches for the human eye. This distance is called the resolving power and can be expressed as the relationship o ...
... two points as separate and distinct even when they are so close together that they appear as one to the unaided eye. This distance at which two points appear as one is about 0.1 mm at ten inches for the human eye. This distance is called the resolving power and can be expressed as the relationship o ...
Concave Lenses and Mirrors
... For a mirror, the radius of curvature is related to the focal length of the mirror, f, by the following equation: ...
... For a mirror, the radius of curvature is related to the focal length of the mirror, f, by the following equation: ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... 2. A converging (objective) lens gathers light & forms a smaller real image at the focal point of a 2nd (occular) lens 3. The smaller final image formed by the converging (occular) lens is also located at “infinity” but appears enlarged Angular Magnification: m =- ...
... 2. A converging (objective) lens gathers light & forms a smaller real image at the focal point of a 2nd (occular) lens 3. The smaller final image formed by the converging (occular) lens is also located at “infinity” but appears enlarged Angular Magnification: m =- ...
pupil function - UCT Digital Image Processing
... Note that as the aperture size a increases, the PSF becomes narrower. This allows objects to be imaged with higher resolution, and is (part of) the reason for telescopes having such a large diameter. (They also have a large aperture to capture a larger portion of the incoming light.) Synthetic apert ...
... Note that as the aperture size a increases, the PSF becomes narrower. This allows objects to be imaged with higher resolution, and is (part of) the reason for telescopes having such a large diameter. (They also have a large aperture to capture a larger portion of the incoming light.) Synthetic apert ...
Lab 5. Spherical Mirrors and Lenses
... evaluate the focal lengths of these lenses. They are actually written on the bottom of the lens holders. However, they are written in disguised Japanese. You may need much more efforts to decode them than measure the focal lengths using the optical methods described below. ...
... evaluate the focal lengths of these lenses. They are actually written on the bottom of the lens holders. However, they are written in disguised Japanese. You may need much more efforts to decode them than measure the focal lengths using the optical methods described below. ...
Business Unit Fiber Optics Business Unit Fiber Optics Fiberoptic
... work nicely for this. Placing the fiber output very near the focal point of this lens will result in the 10mm diameter beam with the calculated divergence above. Discussion: The example above is why RoMack uses terms like “Quasi-Collimated” or “Reduced Divergence”. We are trying not to mislead anyon ...
... work nicely for this. Placing the fiber output very near the focal point of this lens will result in the 10mm diameter beam with the calculated divergence above. Discussion: The example above is why RoMack uses terms like “Quasi-Collimated” or “Reduced Divergence”. We are trying not to mislead anyon ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester Lecture 27 – Geometric Optics
... • Can we do better? Can we solve for the paths of the rays exactly? – Sure, no problem! But it is a lot of work. – Computers are good at doing lots of work (without complaining) ...
... • Can we do better? Can we solve for the paths of the rays exactly? – Sure, no problem! But it is a lot of work. – Computers are good at doing lots of work (without complaining) ...
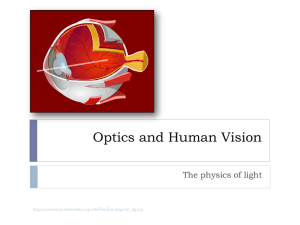
CHAPTER 6 Human Eye Notes FIB
... • Optical fibres: ____________ glass fibres that can transmit light from one place to another. o Total internal reflection – light entering one end of the fibre is reflected from side to side until it emerges from the other end. o Uses: used in ____________ to transmit images of the inside so ...
... • Optical fibres: ____________ glass fibres that can transmit light from one place to another. o Total internal reflection – light entering one end of the fibre is reflected from side to side until it emerges from the other end. o Uses: used in ____________ to transmit images of the inside so ...
Exercise 13 Geometrical and Technical Optics WS 2013/2014
... In this case the aberrations for 40 mm beam diameter are (again first surface at z=-6 mm and second surface at z=0 mm): =587.6 nm: z_Focus: 92.981 mm, spot radius: 0.161 mm, P/V wave aberrations: 20.57 =486.1 nm: z_Focus: 91.955 mm, spot radius: 0.162 mm, P/V wave aberrations: 25.18 =656.3 nm ...
... In this case the aberrations for 40 mm beam diameter are (again first surface at z=-6 mm and second surface at z=0 mm): =587.6 nm: z_Focus: 92.981 mm, spot radius: 0.161 mm, P/V wave aberrations: 20.57 =486.1 nm: z_Focus: 91.955 mm, spot radius: 0.162 mm, P/V wave aberrations: 25.18 =656.3 nm ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.