PowerPoint (PPT) One: The theories of light in historical perspective
... a spherical shell acts as a concave mirror, and a beam of parallel rays is incident on it,then all rays after being reflected pass through the same point, call it F, or the “focal point”. The distance between F and the mirror surface (usually denoted as f ) is ½ R, where R is the radius of the spher ...
... a spherical shell acts as a concave mirror, and a beam of parallel rays is incident on it,then all rays after being reflected pass through the same point, call it F, or the “focal point”. The distance between F and the mirror surface (usually denoted as f ) is ½ R, where R is the radius of the spher ...
Measuring the Real Point Spread Function of High Numerical
... computers. A bewildering array of techniques is described in Malacara’s classic reference book on the subject (Malacara, 1992). Several of these techniques, in particular the Twyman–Green interferometer and the star test, are applicable to testing of microscope objective lens. Characterizing high nu ...
... computers. A bewildering array of techniques is described in Malacara’s classic reference book on the subject (Malacara, 1992). Several of these techniques, in particular the Twyman–Green interferometer and the star test, are applicable to testing of microscope objective lens. Characterizing high nu ...
Photo Resists 6.6.2 Resist and Steppers
... And somehow you have to control the stage movement; i.e. you must measure where you are with respect to some alignment marks on the chip with the same kind of precision. We need some alignment module in the stepper. Alignment is done optically, too, as an integral (and supremely important) part of s ...
... And somehow you have to control the stage movement; i.e. you must measure where you are with respect to some alignment marks on the chip with the same kind of precision. We need some alignment module in the stepper. Alignment is done optically, too, as an integral (and supremely important) part of s ...
Refraction and Reflection Lab
... c. Another way to do this is to use a curved mirror. Set up the light box with the four slit gate. There are two curved mirrors in the light box kit. A concave mirror can also be used in place of plane mirrors to bring light beams to a common focus. Determine the focal distance (the distance from th ...
... c. Another way to do this is to use a curved mirror. Set up the light box with the four slit gate. There are two curved mirrors in the light box kit. A concave mirror can also be used in place of plane mirrors to bring light beams to a common focus. Determine the focal distance (the distance from th ...
Presentation - University of Arizona
... Each space (object or image) extends from -∞ to +∞ for each optical surface being encountered. Gaussian Imagery is a collinear transformation mapping the object plane to the image plane. And Cardinal points result. Use paraxial analysis for the Gaussian properties of optical system. ...
... Each space (object or image) extends from -∞ to +∞ for each optical surface being encountered. Gaussian Imagery is a collinear transformation mapping the object plane to the image plane. And Cardinal points result. Use paraxial analysis for the Gaussian properties of optical system. ...
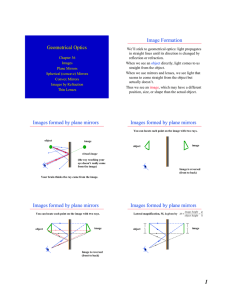
Geometrical Optics Image Formation Images formed by plane
... – We have a physical path length which is just what you measure with your ruler. – Multiply that by the index of refraction and you have the optical path length. ...
... – We have a physical path length which is just what you measure with your ruler. – Multiply that by the index of refraction and you have the optical path length. ...
Telescopes.
... • Large diameter telescopes have small fringes and we can see smaller details. Therefore the larger the telescope, the better its resolving power. ...
... • Large diameter telescopes have small fringes and we can see smaller details. Therefore the larger the telescope, the better its resolving power. ...
Fourier Optics
... of the screen. In this way, the picture is passed unchanged and the lines are eliminated. 4. Image correlation. More complicated filters can be made by photography. One interesting application is the comparison of various objects with a reference one, for example, a set of alphanumeric characters. W ...
... of the screen. In this way, the picture is passed unchanged and the lines are eliminated. 4. Image correlation. More complicated filters can be made by photography. One interesting application is the comparison of various objects with a reference one, for example, a set of alphanumeric characters. W ...
Ultra–large field-of-view two-photon microscopy
... The design of the scan system begins with the selection of the objective. We seek a field-ofview that encompasses 10 mm, a numerical aperture (NA) to achieve 1-µm resolution, and a back aperture that does not exceed 25 mm. The singular choice is a 4-times magnification (f = 45 mm), 0.28 NA air-immer ...
... The design of the scan system begins with the selection of the objective. We seek a field-ofview that encompasses 10 mm, a numerical aperture (NA) to achieve 1-µm resolution, and a back aperture that does not exceed 25 mm. The singular choice is a 4-times magnification (f = 45 mm), 0.28 NA air-immer ...
52.3: An Improved Polarizing Beamsplitter LCOS Projection
... Transmission data was generated for the two systems for both polarizations. Figure 6 depicts the P transmission data. In the case of the MacNeille PBS, the light was incident on the cube face at 0 degrees +11.5 degrees (f/2.5). In the case of the Proflux™ plate PBS, the light was incident on the str ...
... Transmission data was generated for the two systems for both polarizations. Figure 6 depicts the P transmission data. In the case of the MacNeille PBS, the light was incident on the cube face at 0 degrees +11.5 degrees (f/2.5). In the case of the Proflux™ plate PBS, the light was incident on the str ...
Ophthalmic lens
... Bull’s eye effect causes poor cosmetic appearance More conspicuous than other lens. ...
... Bull’s eye effect causes poor cosmetic appearance More conspicuous than other lens. ...
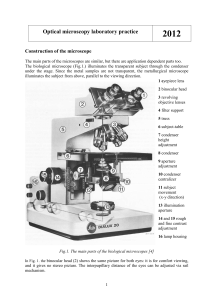
Optical microscopy laboratory practice 2012
... 3. Body: The main structural support of the microscope which connects the lens apparatus to the base. 4. Nose Piece: This connects the objective lens to the microscope body. With a turret, or rotating nose piece as many as five objectives can be attached to create different powers of magnification w ...
... 3. Body: The main structural support of the microscope which connects the lens apparatus to the base. 4. Nose Piece: This connects the objective lens to the microscope body. With a turret, or rotating nose piece as many as five objectives can be attached to create different powers of magnification w ...
Orbital Dynamics of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna
... any higher order diffractions and insure a clean Gaussian beam. The light is then reflected off a mirror (6) and sent through a λ/2 wave plate (7) and onto the SLM (8). The λ/2 wave plate has two purposes. The first purpose is to allow the user to control the orientation of the plane polarized light ...
... any higher order diffractions and insure a clean Gaussian beam. The light is then reflected off a mirror (6) and sent through a λ/2 wave plate (7) and onto the SLM (8). The λ/2 wave plate has two purposes. The first purpose is to allow the user to control the orientation of the plane polarized light ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.