Insertional inactivation studies of the csmA and csmC genes of the
... all transformants tested, the hybridization pattern showed the presence of both the 1.57-kb HindIII fragment wild-type fragment as well as the two smaller HindIII fragments of 0.85-kb and 0.72-kb that arise from the introduced HindIII sites that £ank the 6 cartridge in the insertionally inactivated ...
... all transformants tested, the hybridization pattern showed the presence of both the 1.57-kb HindIII fragment wild-type fragment as well as the two smaller HindIII fragments of 0.85-kb and 0.72-kb that arise from the introduced HindIII sites that £ank the 6 cartridge in the insertionally inactivated ...
Characterizing a Lambda Red Recombinase Induced Presumptive
... from the forward primer used by Jaeger et al. (6), where changes were made at the 34th-36th nucleotide. The forward primer was designed to contain last 33 nucleotides of E.coli C29 lacI DNA binding domain gene, followed by the stop codon “TAA” and 20 nucleotides flanking the kanamycin resistance cas ...
... from the forward primer used by Jaeger et al. (6), where changes were made at the 34th-36th nucleotide. The forward primer was designed to contain last 33 nucleotides of E.coli C29 lacI DNA binding domain gene, followed by the stop codon “TAA” and 20 nucleotides flanking the kanamycin resistance cas ...
SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to
... • Change in an organisms DNA is called a mutation. • Not uncommon • May or may not affect the phenotype of an organism – Physical characteristics ...
... • Change in an organisms DNA is called a mutation. • Not uncommon • May or may not affect the phenotype of an organism – Physical characteristics ...
beautiful bicolours - tuxedo and magpie cats
... least one white spotting gene should not, in theory, produce solid-coloured cats. An alternative hypothesis is that the cats have the dominant white gene (the one related to deafness) and that a second gene is causing this to break down so that spotting appears. It is possible to produce coloured ca ...
... least one white spotting gene should not, in theory, produce solid-coloured cats. An alternative hypothesis is that the cats have the dominant white gene (the one related to deafness) and that a second gene is causing this to break down so that spotting appears. It is possible to produce coloured ca ...
Ch. 14 Mendelian Genetics
... • The traits he studied were, in fact, on nonhomologous chromosomes ...
... • The traits he studied were, in fact, on nonhomologous chromosomes ...
NRT2 - Clark University
... H.velutipes clade has, in fact, been demonstrated (Aanen, 2001). ∆ Problems with these hypotheses include the likelihood of these events being of some debate, and also the lack of additional corroborative molecular evidence such as additional ITS sequences in H. helodes. These are not necessarily fa ...
... H.velutipes clade has, in fact, been demonstrated (Aanen, 2001). ∆ Problems with these hypotheses include the likelihood of these events being of some debate, and also the lack of additional corroborative molecular evidence such as additional ITS sequences in H. helodes. These are not necessarily fa ...
SNP Analysis (GAW15 data)
... shown to confer increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis, with odds ratios ranging between 1.5-2.0 for heterozygotes, and over 3.0 for homozygous carriers of the variant. ...
... shown to confer increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis, with odds ratios ranging between 1.5-2.0 for heterozygotes, and over 3.0 for homozygous carriers of the variant. ...
Gene Section TYR (tyrosinase (oculocutaneous albinism IA)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... complete loss of tyrosinase activity. Complete loss of activity results in the absence of melanin in the skin and eyes and is classified as OCA1A and the presence of only reduced tyrosinase activity is classified as OCA1B. Complete loss of tyrosinase activity results in the total absence of melanin ...
... complete loss of tyrosinase activity. Complete loss of activity results in the absence of melanin in the skin and eyes and is classified as OCA1A and the presence of only reduced tyrosinase activity is classified as OCA1B. Complete loss of tyrosinase activity results in the total absence of melanin ...
Evolutionary significance of stress- induced mutagenesis in
... focus of this paper, as the molecular mechanisms that lead to a preferential generation of adaptive mutations in the target gene are very specific to the system used and it is therefore difficult to assess their evolutionary relevance (Box 2). The second class of experiments, which showed that stres ...
... focus of this paper, as the molecular mechanisms that lead to a preferential generation of adaptive mutations in the target gene are very specific to the system used and it is therefore difficult to assess their evolutionary relevance (Box 2). The second class of experiments, which showed that stres ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... e. only two amino acids have a unique code UGG trp and AUG met f. all proteins must start with met as AUG is the start code; this may be removed later g. there is no amino acid that is coded by UAA, UAG or UGA and so the protein breaks here and these are called STOP codes ...
... e. only two amino acids have a unique code UGG trp and AUG met f. all proteins must start with met as AUG is the start code; this may be removed later g. there is no amino acid that is coded by UAA, UAG or UGA and so the protein breaks here and these are called STOP codes ...
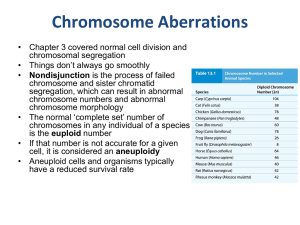
Chromosome Aberrations
... • No, it predicts that organisms will adapt over time to become more effective at reproducing. If becoming less complex accomplishes that task, so be it. 2. “… it would seem logical … that organisms with least number of chromosomes were the first ones to evolve and those with the most chromosomes ar ...
... • No, it predicts that organisms will adapt over time to become more effective at reproducing. If becoming less complex accomplishes that task, so be it. 2. “… it would seem logical … that organisms with least number of chromosomes were the first ones to evolve and those with the most chromosomes ar ...
Role of Genomics in Selection of Beef Cattle for Healthfulness
... Genomic Prediction Involves finding the location and effects of the genes (known as QTL=Quantitative Trait Loci) that cause variation in the trait of interest in a discovery phase ...
... Genomic Prediction Involves finding the location and effects of the genes (known as QTL=Quantitative Trait Loci) that cause variation in the trait of interest in a discovery phase ...
X-linked
... chromosomes often affect sex determination (whether a person has the sexual characteristics of a male or a female), sexual development, and the ability to have children (fertility). The signs and symptoms of these conditions vary widely and range from mild ...
... chromosomes often affect sex determination (whether a person has the sexual characteristics of a male or a female), sexual development, and the ability to have children (fertility). The signs and symptoms of these conditions vary widely and range from mild ...
Marker Development for Rice Blast Resistance Gene Pi66(t) and
... for MAS (Xu, 2003). Compared with conventional breeding methods, MAS provides a simple and efficient way to identify and transfer the target R genes or resistance QTLs to an elite variety (Jia, 2003; Collard and Mackill, 2008). DNA can be prepared from seeds, sheath, root, grain, or leaves, and user ...
... for MAS (Xu, 2003). Compared with conventional breeding methods, MAS provides a simple and efficient way to identify and transfer the target R genes or resistance QTLs to an elite variety (Jia, 2003; Collard and Mackill, 2008). DNA can be prepared from seeds, sheath, root, grain, or leaves, and user ...
Genome-Wide Dissection of Hybrid Sterility in
... groups (Dobzhansky 1935; Mayr 1942), remains one of the most widely used criteria for species definition. Among isolation barriers, postzygotic isolation mechanisms (predominantly hybrid inviability and sterility) have long captured the attention of evolutionists (Dobzhansky 1936). Despite decades o ...
... groups (Dobzhansky 1935; Mayr 1942), remains one of the most widely used criteria for species definition. Among isolation barriers, postzygotic isolation mechanisms (predominantly hybrid inviability and sterility) have long captured the attention of evolutionists (Dobzhansky 1936). Despite decades o ...
biofundamentals - virtual laboratories
... chemistry, they are more than just highly complex chemical and physical systems. Why is that, you might ask? Because each organism is a unique entity, distinguishable from others by the genetic information it carries and, at the molecular and cellular levels, by the various stochastic events that ha ...
... chemistry, they are more than just highly complex chemical and physical systems. Why is that, you might ask? Because each organism is a unique entity, distinguishable from others by the genetic information it carries and, at the molecular and cellular levels, by the various stochastic events that ha ...
Repeated Sequences in CASPASE-5 and FANCD2 but not NF1 Are
... MMR is particularly efficient at reversing unpaired nucleotides that arise during replication of DNA regions comprising extensive mononucleotide or dinucleotide repeats of the type found in microsatellites. If they remain uncorrected, these structural aberrations cause insertion/ deletion mutations, ...
... MMR is particularly efficient at reversing unpaired nucleotides that arise during replication of DNA regions comprising extensive mononucleotide or dinucleotide repeats of the type found in microsatellites. If they remain uncorrected, these structural aberrations cause insertion/ deletion mutations, ...
Improving Virus C type 4 Interferon using Bioinformatics Techniques
... ribosomes bind to the mRNA close to the translation start site. Transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosomes, to enable the ribosomes to put this amino acid on the protein that is being synthesized as an elongating chain of amino acid residues, using the information on the mRNA to "know" ...
... ribosomes bind to the mRNA close to the translation start site. Transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosomes, to enable the ribosomes to put this amino acid on the protein that is being synthesized as an elongating chain of amino acid residues, using the information on the mRNA to "know" ...
Specification of floral organs in Arabidopsis
... of A function in the original ABC model), it also suppresses the expression of the B function genes AP3 and PI (Krogan et al., 2012). AP2 is therefore, in all probability, not involved in promoting petal development (for which B function gene activity is essential) as predicted by the original ABC m ...
... of A function in the original ABC model), it also suppresses the expression of the B function genes AP3 and PI (Krogan et al., 2012). AP2 is therefore, in all probability, not involved in promoting petal development (for which B function gene activity is essential) as predicted by the original ABC m ...
P57: Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
... Tests for BWS Bone X-ray Blood tests for low sugar Ultrasound of the abdomen X-ray of the abdomen MRI of the abdomen Chromosome studies ...
... Tests for BWS Bone X-ray Blood tests for low sugar Ultrasound of the abdomen X-ray of the abdomen MRI of the abdomen Chromosome studies ...
G enetics - Lantern Publishing
... In Chapter 2 the main principles of inheritance were explained. This chapter focuses on the inheritance of autosomal single gene disorders. Over 10,000 human diseases are due to single gene alterations and, although rare, they affect one per cent of the human population. Single gene disorders are al ...
... In Chapter 2 the main principles of inheritance were explained. This chapter focuses on the inheritance of autosomal single gene disorders. Over 10,000 human diseases are due to single gene alterations and, although rare, they affect one per cent of the human population. Single gene disorders are al ...
Lesson Overview - Dr. Thornton`s Courses
... From Molecule to Phenotype How do small changes in DNA molecules affect human traits? Changes in a gene’s DNA sequence can change proteins by altering their amino acid sequences, which may directly affect one’s phenotype. ...
... From Molecule to Phenotype How do small changes in DNA molecules affect human traits? Changes in a gene’s DNA sequence can change proteins by altering their amino acid sequences, which may directly affect one’s phenotype. ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.