Mendelian Genetics Chapter 12 Reading Mendellian Genetics
... sativum, shown in Figure 1. Farmers had done similar experiments before, but Mendel was the first person to develop rules that accurately predict the patterns of heredity in pea plants. V Modern genetics is based on Mendel’s explanations for the patterns of heredity in garden pea plants. As a young ...
... sativum, shown in Figure 1. Farmers had done similar experiments before, but Mendel was the first person to develop rules that accurately predict the patterns of heredity in pea plants. V Modern genetics is based on Mendel’s explanations for the patterns of heredity in garden pea plants. As a young ...
Gene Section DNMT1 (DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 1)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Homologs of DNMT1 have been found in nearly all eukaryotes whose DNA bears 5-methylcytosine, but not in those that lack it. Although DNMT2 contains the full set of conserved motifs of the catalytic domain, it lacks the N-terminal domain charac-teristic of eukaryotic DNMTs. The methyltrans-ferase act ...
... Homologs of DNMT1 have been found in nearly all eukaryotes whose DNA bears 5-methylcytosine, but not in those that lack it. Although DNMT2 contains the full set of conserved motifs of the catalytic domain, it lacks the N-terminal domain charac-teristic of eukaryotic DNMTs. The methyltrans-ferase act ...
Life 9e - Garvness
... 16. Which of the following statements about Mendelian genetics is false? a. Alternative forms of genes are called alleles. b. A locus is a gene’s location on its chromosome. c. Only two alleles can exist for a given gene. d. A genotype is a description of the alleles that represent an individual’s g ...
... 16. Which of the following statements about Mendelian genetics is false? a. Alternative forms of genes are called alleles. b. A locus is a gene’s location on its chromosome. c. Only two alleles can exist for a given gene. d. A genotype is a description of the alleles that represent an individual’s g ...
Ribosomal Protein RPL27a Promotes Female
... RNA (rRNA) and approximately 47 ribosomal proteins, whereas the 40S subunit includes an 18S rRNA and approximately 33 ribosomal proteins. In plants and animals, reduced ribosomal protein function results in specific developmental phenotypes (Byrne, 2009; Warner and McIntosh, 2009; McCann and Baserga, ...
... RNA (rRNA) and approximately 47 ribosomal proteins, whereas the 40S subunit includes an 18S rRNA and approximately 33 ribosomal proteins. In plants and animals, reduced ribosomal protein function results in specific developmental phenotypes (Byrne, 2009; Warner and McIntosh, 2009; McCann and Baserga, ...
Genetics: Mendel and Beyond
... The Law of Dominance: in a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation. The Law of Segregation: each characteristic is controlled by two factors, which separate and go to different gametes when an organism reproduces. ...
... The Law of Dominance: in a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation. The Law of Segregation: each characteristic is controlled by two factors, which separate and go to different gametes when an organism reproduces. ...
Pea Taste Slides - Evo-Ed
... • Gregor Mendel identified heritable units as the mechanism for traits passing from parents to offspring in pea plants. • These heritable units, called alleles, are versions of specific genes that code for proteins – in this case the SBE1 protein (enzyme). ...
... • Gregor Mendel identified heritable units as the mechanism for traits passing from parents to offspring in pea plants. • These heritable units, called alleles, are versions of specific genes that code for proteins – in this case the SBE1 protein (enzyme). ...
SNP - Asia University, Taiwan
... The Nature of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Classification of SNP’s • Most common = changing from one base to another • This could either be transversions or transitions • Could also be insertions and deletions, also termed “indels” • Some geneticists see two-nucleotide changes and small insertio ...
... The Nature of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Classification of SNP’s • Most common = changing from one base to another • This could either be transversions or transitions • Could also be insertions and deletions, also termed “indels” • Some geneticists see two-nucleotide changes and small insertio ...
Identification and mapping of RAPD and RFLP markers linked to a
... placed outside the greenhouse and flowered a second time in July (under natural conditions of light and temperature). During this second flowering period, one observation per plant was made to detect the presence of pollen. For each cross, differences in the segregation of sexual phenotypes between ...
... placed outside the greenhouse and flowered a second time in July (under natural conditions of light and temperature). During this second flowering period, one observation per plant was made to detect the presence of pollen. For each cross, differences in the segregation of sexual phenotypes between ...
Characteristics of the gene encoding pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase (P5CS) in Glycine max
... gene loci of P5CS were discovered in the nuclear genome of tomatoes: a locus encodes for enzymes P5CS and a locus is a polycistronic mRNA encoding for the enzymes γ-glutamyl kinase (γ-GK) and glucose-5-semialdehyde (GSA) dehydrogenase in two separate forms of peptide (Garcia-Rios et al., 1997) [8]. ...
... gene loci of P5CS were discovered in the nuclear genome of tomatoes: a locus encodes for enzymes P5CS and a locus is a polycistronic mRNA encoding for the enzymes γ-glutamyl kinase (γ-GK) and glucose-5-semialdehyde (GSA) dehydrogenase in two separate forms of peptide (Garcia-Rios et al., 1997) [8]. ...
Activation of the JNK pathway during dorsal closure in Drosophila
... rescues embryos mutant for the weaker slpr3P5 allele such that they develop to adulthood. Mutant male flies emerge but are weakly viable and show no gross morphological defects. Taken together, these data support a role for slpr in JNK signal transduction, upstream of bsk. Cloning reveals that slpr ...
... rescues embryos mutant for the weaker slpr3P5 allele such that they develop to adulthood. Mutant male flies emerge but are weakly viable and show no gross morphological defects. Taken together, these data support a role for slpr in JNK signal transduction, upstream of bsk. Cloning reveals that slpr ...
Role for CCG-trinucleotide repeats in the pathogenesis of chronic
... logarithmically with age in adults.1 Sporadic CLL may have a hereditary component because several studies report an elevated risk for hematologic malignancy2,3 and other cancers in first-degree relatives. Familial clustering of CLL does occur; when it does, it is multigenerational and displays verti ...
... logarithmically with age in adults.1 Sporadic CLL may have a hereditary component because several studies report an elevated risk for hematologic malignancy2,3 and other cancers in first-degree relatives. Familial clustering of CLL does occur; when it does, it is multigenerational and displays verti ...
Drug-specific Sites of Topoisomerase II DNA
... age stimulation were lower than those of VM-26 (Fig. 1B). The present findings strongly indicate that the in vivo VM-26 site is also the target for VM-26 stimulation in vitro. Therefore, although satellite ...
... age stimulation were lower than those of VM-26 (Fig. 1B). The present findings strongly indicate that the in vivo VM-26 site is also the target for VM-26 stimulation in vitro. Therefore, although satellite ...
pdf
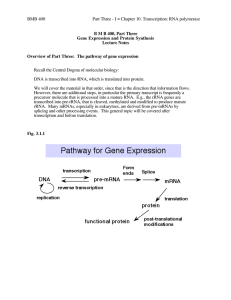
... Recall the Central Dogma of molecular biology: DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into protein. We will cover the material in that order, since that is the direction that information flows. However, there are additional steps, in particular the primary transcript is frequently a precur ...
... Recall the Central Dogma of molecular biology: DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into protein. We will cover the material in that order, since that is the direction that information flows. However, there are additional steps, in particular the primary transcript is frequently a precur ...
Chpt10_TxnRNAPol.doc
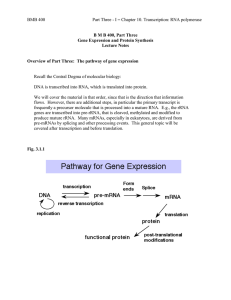
... Recall the Central Dogma of molecular biology: DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into protein. We will cover the material in that order, since that is the direction that information flows. However, there are additional steps, in particular the primary transcript is frequently a precur ...
... Recall the Central Dogma of molecular biology: DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into protein. We will cover the material in that order, since that is the direction that information flows. However, there are additional steps, in particular the primary transcript is frequently a precur ...
A Human Centromere Protein, CENP-B, Has a DNA Binding Domain
... Steuer et al., 1990). Several monoclonal antibodies that recognize the centromeric region of human chromosomes have been isolated using scaffold proteins as antigens (Cooke et al., 1987; Compton et al., 1991); one of the antigens, a 250300-kD protein, was found to be localized to centromere only at ...
... Steuer et al., 1990). Several monoclonal antibodies that recognize the centromeric region of human chromosomes have been isolated using scaffold proteins as antigens (Cooke et al., 1987; Compton et al., 1991); one of the antigens, a 250300-kD protein, was found to be localized to centromere only at ...
peas? - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... • Gregor Mendel identified heritable units as the mechanism for traits passing from parents to offspring in pea plants. • These heritable units, called alleles, are versions of specific genes that code for proteins – in this case the SBE1 protein (enzyme). ...
... • Gregor Mendel identified heritable units as the mechanism for traits passing from parents to offspring in pea plants. • These heritable units, called alleles, are versions of specific genes that code for proteins – in this case the SBE1 protein (enzyme). ...
Campbell`s Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al
... 5) Which of the following statements regarding cross-breeding and hybridization is false? A) The offspring of two different varieties are called hybrids. B) The parental plants of a cross are the P generation. C) The hybrid offspring of a cross are the P1 generation. D) The hybrid offspring of an F ...
... 5) Which of the following statements regarding cross-breeding and hybridization is false? A) The offspring of two different varieties are called hybrids. B) The parental plants of a cross are the P generation. C) The hybrid offspring of a cross are the P1 generation. D) The hybrid offspring of an F ...
The Old World monkey DAZ (Deleted in
... nucleotides. The Y-chromosomal cynDAZ cDNA The cynDAZ cDNA sequence (Fig. 1) is a composite of the partial cDNA of the remaining fifth clone and a 5′-RACE product using adult monkey testis mRNA as a template. The 5′-RACE products overlapped the cDNA insert by 50 nucleotides and extended 471 nucleoti ...
... nucleotides. The Y-chromosomal cynDAZ cDNA The cynDAZ cDNA sequence (Fig. 1) is a composite of the partial cDNA of the remaining fifth clone and a 5′-RACE product using adult monkey testis mRNA as a template. The 5′-RACE products overlapped the cDNA insert by 50 nucleotides and extended 471 nucleoti ...
Chromosomal rearrangements and protein globularity changes in
... PPE53 and PPE24) were found in at least four of the strains. The variants in eight of these genes led to amino acid changes but only two altered genes have known functions: PE_PGRS19, a putative outer membrane protein (Song et al., 2008) and embR which is involved in transcription, the biosynthesis ...
... PPE53 and PPE24) were found in at least four of the strains. The variants in eight of these genes led to amino acid changes but only two altered genes have known functions: PE_PGRS19, a putative outer membrane protein (Song et al., 2008) and embR which is involved in transcription, the biosynthesis ...
Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in fish
... bacteria within the host is generally lower than their optimum growth temperature, this being the opposite of what happens in mammal-pathogenic bacteria. RNA thermometers modulate translation efficiency of a particular mRNA in relation to temperature (Eriksson et al., 2002; Johansson and Cossart, 2003 ...
... bacteria within the host is generally lower than their optimum growth temperature, this being the opposite of what happens in mammal-pathogenic bacteria. RNA thermometers modulate translation efficiency of a particular mRNA in relation to temperature (Eriksson et al., 2002; Johansson and Cossart, 2003 ...
PhenoLink - a web-tool for linking phenotype Lactobacillus plantarum strains
... Background: Linking phenotypes to high-throughput molecular biology information generated by ~omics technologies allows revealing cellular mechanisms underlying an organism’s phenotype. ~Omics datasets are often very large and noisy with many features (e.g., genes, metabolite abundances). Thus, asso ...
... Background: Linking phenotypes to high-throughput molecular biology information generated by ~omics technologies allows revealing cellular mechanisms underlying an organism’s phenotype. ~Omics datasets are often very large and noisy with many features (e.g., genes, metabolite abundances). Thus, asso ...
Cancer Prone Disease Section Fanconi anaemia Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... terminal pancytopenia, and from ANLL as well. ...
... terminal pancytopenia, and from ANLL as well. ...
Alnylam Licenses Intellectual Property from Cold Spring Harbor
... has built in the fundamental patents, technology, and know-how that underlie the discovery, development and commercialization of RNAi therapeutics Under the terms of the agreement, Alnylam receives a non-exclusive license from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory to therapeutic uses of patent applications ...
... has built in the fundamental patents, technology, and know-how that underlie the discovery, development and commercialization of RNAi therapeutics Under the terms of the agreement, Alnylam receives a non-exclusive license from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory to therapeutic uses of patent applications ...
Drosophila Genetics Simulation
... Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Scientists substitute simple organisms for humans when studying inherited diseases and disorders. About 60% of the genes that are known to cause human disease have a recognizable match in the genetic code of the common fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ...
... Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Scientists substitute simple organisms for humans when studying inherited diseases and disorders. About 60% of the genes that are known to cause human disease have a recognizable match in the genetic code of the common fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.