Human Growth and Development Genetics
... To feel loved, have a sense of belonging Self-esteem, approval Desire to live up to one’s potential ...
... To feel loved, have a sense of belonging Self-esteem, approval Desire to live up to one’s potential ...
Title
... c. Remain the same Why is the genetic code degenerate? a. Because the DNA is not precisely copied into RNA. b. Because more than one codon in a mRNA can code for a single amino acid. c. Because more than one amino acid can be specified by the same sequence in the mRNA. d. Because the genetic code wa ...
... c. Remain the same Why is the genetic code degenerate? a. Because the DNA is not precisely copied into RNA. b. Because more than one codon in a mRNA can code for a single amino acid. c. Because more than one amino acid can be specified by the same sequence in the mRNA. d. Because the genetic code wa ...
Mutations & Genetic Engineering
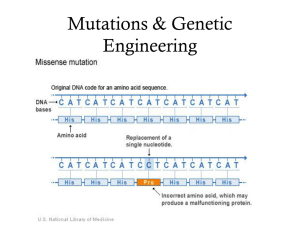
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense • Sickle cell anemia ...
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense • Sickle cell anemia ...
Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss
... Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss how it explains the control of messenger RNA production and the regulation of protein synthesis in bacterial cells. STANDARDS: BACKGROUND: ...
... Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss how it explains the control of messenger RNA production and the regulation of protein synthesis in bacterial cells. STANDARDS: BACKGROUND: ...
Biotechnology Notes
... • Scientist change an organism’s DNA to give it new traits. • Possible because all organisms have the same Genetic Code ...
... • Scientist change an organism’s DNA to give it new traits. • Possible because all organisms have the same Genetic Code ...
Chapter 17 - Denton ISD
... sections called _______, and leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called ___________________. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in evolution. ...
... sections called _______, and leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called ___________________. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in evolution. ...
Bio102: Introduction to Cell Biology and Genetics
... All individuals of a species have the same genes may have different alleles or forms of this gene leads to a different protein (differences may be big or may be subtle) each individual has two alleles of each genes (diploid) that may be same or different allele combination (genotype) determines the ...
... All individuals of a species have the same genes may have different alleles or forms of this gene leads to a different protein (differences may be big or may be subtle) each individual has two alleles of each genes (diploid) that may be same or different allele combination (genotype) determines the ...
[Type the document title] Microbial Genetics Molecular biology is the
... • 1) transcription – DNA transcribed to produce RNA • 2) translation – RNA then translated to produce proteins • Protein Synthesis DNA--------- mRNA---------- Protein Transcription Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Genetics ...
... • 1) transcription – DNA transcribed to produce RNA • 2) translation – RNA then translated to produce proteins • Protein Synthesis DNA--------- mRNA---------- Protein Transcription Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Genetics ...
Practice Multiple Choice- Set 1 - mvhs
... c) The amount of energy indicates what is passed out as feces d) It indicates the diversity of an environment f) Animals can only be at the top level ...
... c) The amount of energy indicates what is passed out as feces d) It indicates the diversity of an environment f) Animals can only be at the top level ...
You are what you eat? Plant nutrient status and the
... Molecules: Transcription and Translation ...
... Molecules: Transcription and Translation ...
Chapter 4: Modern Genetics
... "good" genes for other attributes. Genetically impoverished individuals. ...
... "good" genes for other attributes. Genetically impoverished individuals. ...
Document
... a frame shift mutation C. Transposable elements: DNA segments move spontaneously on chromosome which may inactivate the gene where it inserted itself ...
... a frame shift mutation C. Transposable elements: DNA segments move spontaneously on chromosome which may inactivate the gene where it inserted itself ...
Gregor Mendel - father of Genetics and 18th century Austrian monk
... Reading Strand - Only one side of the ladder is read, the reading strand. Complimentary strand - Opposite strand of reading strand. A copy incase reading is damaged. DNA is read like a book. The words are codons. Codons are 3 nitrogen bases long. Ex: ATT or GTC Each codon codes for an amino acid. T ...
... Reading Strand - Only one side of the ladder is read, the reading strand. Complimentary strand - Opposite strand of reading strand. A copy incase reading is damaged. DNA is read like a book. The words are codons. Codons are 3 nitrogen bases long. Ex: ATT or GTC Each codon codes for an amino acid. T ...
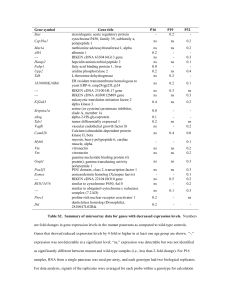
Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
Study Guide 3 Bio 4 C
... Ch 21 Differential Gene Expression Genomics, bioinformatics, proteomics, homeobox, Hox genes, apoptosis You may have multiple choice, true/false, matching, definitions, short answer, essays and fill-in-the-blanks, and "yes" spelling counts!!!! Sample Essays 1. It is very likely you will have genetic ...
... Ch 21 Differential Gene Expression Genomics, bioinformatics, proteomics, homeobox, Hox genes, apoptosis You may have multiple choice, true/false, matching, definitions, short answer, essays and fill-in-the-blanks, and "yes" spelling counts!!!! Sample Essays 1. It is very likely you will have genetic ...
Presentation
... All sexually reproducing organisms naturally exhibit genetic variety among the individuals in the population as a result of mutations and the genetic recombination resulting from meiosis and fertilization. These genetic differences are important for the survival of the species because natural select ...
... All sexually reproducing organisms naturally exhibit genetic variety among the individuals in the population as a result of mutations and the genetic recombination resulting from meiosis and fertilization. These genetic differences are important for the survival of the species because natural select ...
Recombinant DNA
... Cut DNA into pieces Insert DNA into vectors that can replicate in bacteria Transform (introduce) DNA into host cell Plate cells and select those with vectors Each colony has one chunk of DNA The whole set is a library of human DNA ...
... Cut DNA into pieces Insert DNA into vectors that can replicate in bacteria Transform (introduce) DNA into host cell Plate cells and select those with vectors Each colony has one chunk of DNA The whole set is a library of human DNA ...
Supercourse - Scientific Basis for Genetics Part II
... – Recognizes the mRNA code (tri-nucleotide) and brings with it (or transfers) the appropriate amino acid to the protein – Link between mRNA and protein – Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs and tRNAs ...
... – Recognizes the mRNA code (tri-nucleotide) and brings with it (or transfers) the appropriate amino acid to the protein – Link between mRNA and protein – Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs and tRNAs ...
GOALS OF THE HUMAN GENOME PROJECT
... – Recognizes the mRNA code (tri-nucleotide) and brings with it (or transfers) the appropriate amino acid to the protein – Link between mRNA and protein – Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs and tRNAs ...
... – Recognizes the mRNA code (tri-nucleotide) and brings with it (or transfers) the appropriate amino acid to the protein – Link between mRNA and protein – Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs and tRNAs ...
Classical Genetics
... 8. Gene mutations change the arrangement of genetic code in the DNA. So these are called Frame shift mutations. Mis-sense mutation changes the amino acid sequence in the protein. Non sense mutations results in termination codons. Silent mutations do not alter the amino acid sequence in the protein. ...
... 8. Gene mutations change the arrangement of genetic code in the DNA. So these are called Frame shift mutations. Mis-sense mutation changes the amino acid sequence in the protein. Non sense mutations results in termination codons. Silent mutations do not alter the amino acid sequence in the protein. ...
What is some basic information about DNA?
... 4 nucleotides make Up DNA: Nucleotides can be thought of as building blocks. These building blocks can be arranged in sequences. The human genome contains about 3 billion of these building blocks. Some sequences of the building blocks encode genes. Some sequences are related to the regulation of gen ...
... 4 nucleotides make Up DNA: Nucleotides can be thought of as building blocks. These building blocks can be arranged in sequences. The human genome contains about 3 billion of these building blocks. Some sequences of the building blocks encode genes. Some sequences are related to the regulation of gen ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... After the mRNA is transcribed in eukaryotic cells, it must be processed before entering the cytoplasm. Introns are removed and the exons are joined to form a mature mRNA molecule consisting of continuous exons. Translation Translation is the second process by which gene expression leads to protein s ...
... After the mRNA is transcribed in eukaryotic cells, it must be processed before entering the cytoplasm. Introns are removed and the exons are joined to form a mature mRNA molecule consisting of continuous exons. Translation Translation is the second process by which gene expression leads to protein s ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.






![[Type the document title] Microbial Genetics Molecular biology is the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010247892_1-83bf00ba7ef17902054c2b83fe295408-300x300.png)