powerpoint
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
Genetics - Mr. Coleman's Biology
... Multiple alleles – more than two alleles for a gene are found within a population. Polygenic traits – many genes contribute to a phenotype. ...
... Multiple alleles – more than two alleles for a gene are found within a population. Polygenic traits – many genes contribute to a phenotype. ...
File
... Multiple alleles – more than two alleles for a gene are found within a population. Polygenic traits – many genes contribute to a phenotype. ...
... Multiple alleles – more than two alleles for a gene are found within a population. Polygenic traits – many genes contribute to a phenotype. ...
Genetic Engineering
... organism to another therefore, useful genes can be taken from a donor organism and given to a host organism where the gene will continue to produce its product. a gene carried the genetic code for the production of an enzyme (an enzyme is a protein) for example, the human gene for insulin can be ext ...
... organism to another therefore, useful genes can be taken from a donor organism and given to a host organism where the gene will continue to produce its product. a gene carried the genetic code for the production of an enzyme (an enzyme is a protein) for example, the human gene for insulin can be ext ...
MUTATIONS
... DNA just happen. Our DNA can change without warning, which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
... DNA just happen. Our DNA can change without warning, which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
word doc - CSUN.edu
... The other 22 pairs (44 chromosomes) are called autosomes. All egg cells carry a single X chromosome (23X). However, half of all the sperm carry an X chromosome (23X) and half carry a Y… ½ girls and ½ boys. ...
... The other 22 pairs (44 chromosomes) are called autosomes. All egg cells carry a single X chromosome (23X). However, half of all the sperm carry an X chromosome (23X) and half carry a Y… ½ girls and ½ boys. ...
here - St Vincent College
... One human genetic disorder causes damage to nerve cells in the brain.This disorder is caused by a small change in the DNA of the HEXA gene. People with this disorder make a changed HEXA enzyme that does not work. Explain how a change in the DNA of the HEXA gene can result in the production of a chan ...
... One human genetic disorder causes damage to nerve cells in the brain.This disorder is caused by a small change in the DNA of the HEXA gene. People with this disorder make a changed HEXA enzyme that does not work. Explain how a change in the DNA of the HEXA gene can result in the production of a chan ...
APGenomes and Evolution 15 16
... • Movement of transposable elements – Occasionally generates new sequence combinations that are beneficial to the organism ...
... • Movement of transposable elements – Occasionally generates new sequence combinations that are beneficial to the organism ...
AP Bio
... • The only possible gametes are AB and ab… • BUT, wierdly, when scored… a few offspring did illustrate the unexpected: A_bb and aaB_ ...
... • The only possible gametes are AB and ab… • BUT, wierdly, when scored… a few offspring did illustrate the unexpected: A_bb and aaB_ ...
Term: SPRING 2000 - Washington University in St. Louis
... of the genome, including the identification and analysis of gene structure. In addition, genomic sequence information can be used to explore phylogenetic relationships between organisms. The focus of the tutorial is to train lower division undergraduates to discover (annotation) and understand gene ...
... of the genome, including the identification and analysis of gene structure. In addition, genomic sequence information can be used to explore phylogenetic relationships between organisms. The focus of the tutorial is to train lower division undergraduates to discover (annotation) and understand gene ...
Topics in Ecology and Evolution: Molecular Evolution
... Rooting trees. Molecular clocks. Are vultures storks? Are whales pigs? and Were Tasmanian wolves opossums? The Tree of Life. Lab: your choice of a gene family to reconstruct phylogeny. 4. Evolution of Genetic code and codon usage. Lab: is the genetic code one in a million? 5. Chromosomal evolution. ...
... Rooting trees. Molecular clocks. Are vultures storks? Are whales pigs? and Were Tasmanian wolves opossums? The Tree of Life. Lab: your choice of a gene family to reconstruct phylogeny. 4. Evolution of Genetic code and codon usage. Lab: is the genetic code one in a million? 5. Chromosomal evolution. ...
File
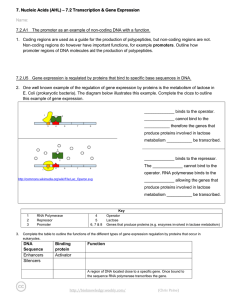
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
7th Grade Science-Chapter 11 Test Study Guide: Human Genetics
... Inbreeding- breeding technique that involves crossing two individuals that have similar desirable characteristics. This process produces organisms that are genetically very similar. This type of breeding leads to a greater chance for genetic disorders. Hybridization-breeding technique where breeders ...
... Inbreeding- breeding technique that involves crossing two individuals that have similar desirable characteristics. This process produces organisms that are genetically very similar. This type of breeding leads to a greater chance for genetic disorders. Hybridization-breeding technique where breeders ...
Gene Regulation and Mutation Notes and Questions
... the protein. Mutated proteins often do not work. Remember the shape is very important to its function (or ability to do its “job) • A mutation can affect a single nucleotide or a large segment of DNA. ...
... the protein. Mutated proteins often do not work. Remember the shape is very important to its function (or ability to do its “job) • A mutation can affect a single nucleotide or a large segment of DNA. ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
pgat biotechnology-2016
... Involves transesterification reaction Involves the nucleopholic attack of an OH group on the sugar phosphate backbone All of the above ...
... Involves transesterification reaction Involves the nucleopholic attack of an OH group on the sugar phosphate backbone All of the above ...
The Human Genome
... wing coloration is affected by temp. • Japanese goby fish can change its sex back and forth in response to changes in its social environment. ...
... wing coloration is affected by temp. • Japanese goby fish can change its sex back and forth in response to changes in its social environment. ...
differential gene expression
... upstream (thousands of nucleotides away) called a enhancers. – DNA enhancers can work by a protein (activator) attaching to the enhancer. – The DNA then loops the DNA back on itself to attach to the promoter region. ...
... upstream (thousands of nucleotides away) called a enhancers. – DNA enhancers can work by a protein (activator) attaching to the enhancer. – The DNA then loops the DNA back on itself to attach to the promoter region. ...
Unit 4 Genetics
... Remember that the phenotype of an organism is determined by its genotype Also, that environmental effects on gene expression are not inherited, genes are ...
... Remember that the phenotype of an organism is determined by its genotype Also, that environmental effects on gene expression are not inherited, genes are ...
Supplementary Table 1
... When one allele masks the effect of another, that allele is called dominant and the other recessive. When an intermediate phenotype occurs and no allele dominates, incomplete dominance results. ...
... When one allele masks the effect of another, that allele is called dominant and the other recessive. When an intermediate phenotype occurs and no allele dominates, incomplete dominance results. ...
- English Longitudinal Study of Ageing
... each gene, no two persons (apart from identical twins) have exactly the same combination of genes, although we all have the same number. ...
... each gene, no two persons (apart from identical twins) have exactly the same combination of genes, although we all have the same number. ...
Hypothesis: Variations in the rate of DNA replication determine the
... hence, if two identical copies of a gene compete for a limited number of RNA polymerases, one copy is expressed and the other silent. Related ideas about the primordial role of the cell cycle in generating not just diversity but coherent diversity have also been developed [6, 4]. ...
... hence, if two identical copies of a gene compete for a limited number of RNA polymerases, one copy is expressed and the other silent. Related ideas about the primordial role of the cell cycle in generating not just diversity but coherent diversity have also been developed [6, 4]. ...
What is Genetic Engineering?
... DNA is cut in the desired place using restriction enzymes. Each different type of restriction enzyme "seeks out" and cuts DNA at a spot marked by a different sequence of base pairs. One restriction enzyme may cut the DNA at every "AATC", for example, while another cuts all "ATG" sequences. The DNA i ...
... DNA is cut in the desired place using restriction enzymes. Each different type of restriction enzyme "seeks out" and cuts DNA at a spot marked by a different sequence of base pairs. One restriction enzyme may cut the DNA at every "AATC", for example, while another cuts all "ATG" sequences. The DNA i ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.