Human Genetics WF, ML , SFdf
... A Punnett spuare is a chart that shows the traits of the parents of an organism, wether they be dominant of recessive, and give the probability of that organisms gene code for that factor. It will show if it will be dominat, recessive, if it has a hidden recessive, mixed hybrid or all of the above ...
... A Punnett spuare is a chart that shows the traits of the parents of an organism, wether they be dominant of recessive, and give the probability of that organisms gene code for that factor. It will show if it will be dominat, recessive, if it has a hidden recessive, mixed hybrid or all of the above ...
1. Instructions for how an organism develops are found
... 1. Instructions for how an organism develops are found in the nucleus of its cells. 2. Genes are instructions for how a cell makes proteins. 3. Genes are sections of very long DNA molecules that make up chromosomes in the nuclei of cells. 4. Sex cells have only a copy of one chromosome from each pai ...
... 1. Instructions for how an organism develops are found in the nucleus of its cells. 2. Genes are instructions for how a cell makes proteins. 3. Genes are sections of very long DNA molecules that make up chromosomes in the nuclei of cells. 4. Sex cells have only a copy of one chromosome from each pai ...
“FA” Gene Mutations in Familial Breast Cancer The cancer
... FANCD1/BRCA2, may be mutated in 10-20% of cases in which there is a strong family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer. These genes were originally identified as the most common genetic causes of the hereditary breast/ovarian cancer syndrome. In that disorder, only one of the two copies of the ge ...
... FANCD1/BRCA2, may be mutated in 10-20% of cases in which there is a strong family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer. These genes were originally identified as the most common genetic causes of the hereditary breast/ovarian cancer syndrome. In that disorder, only one of the two copies of the ge ...
lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
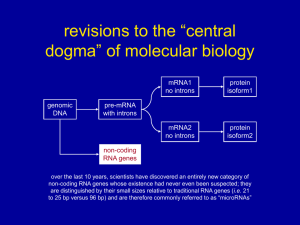
... revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology ...
... revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology ...
Mutation and DNA
... • Differences between closely related organisms show closely matched DNA sequences that diverged at some past time and that was adaptive for a given environment ...
... • Differences between closely related organisms show closely matched DNA sequences that diverged at some past time and that was adaptive for a given environment ...
Heredity and Behavior
... Each parents 23 chromosomes can be scrambled in over 3 million different ways, yielding over 8 million configurations Homozygous condition –two genes in a specific pair are the same Heterozygous condition – two genes in a specific pair are different ...
... Each parents 23 chromosomes can be scrambled in over 3 million different ways, yielding over 8 million configurations Homozygous condition –two genes in a specific pair are the same Heterozygous condition – two genes in a specific pair are different ...
genetics heredity test ANSWERS
... Unit of heredity that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and codes for the inherited trait ...
... Unit of heredity that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and codes for the inherited trait ...
E:Med - uni-freiburg.de
... *To obtain pairs of TF and target regions that influence epigenetic status *Why the miss-regulation?: Miss-regulation TF complex Mutations Needed: *DNA met. & gene expression & SNPs *Experimental validation ...
... *To obtain pairs of TF and target regions that influence epigenetic status *Why the miss-regulation?: Miss-regulation TF complex Mutations Needed: *DNA met. & gene expression & SNPs *Experimental validation ...
12.4 Notes - Trimble County Schools
... • Recessive – traits that only appear when paired with another allele that is recessive (type O) • Genotype – a pair of allele genes • Phenotype – the outward appearance of an individual ...
... • Recessive – traits that only appear when paired with another allele that is recessive (type O) • Genotype – a pair of allele genes • Phenotype – the outward appearance of an individual ...
12.5 Notes - Trimble County Schools
... • Recessive – traits that only appear when paired with another allele that is recessive (type O) • Genotype – a pair of allele genes • Phenotype – the outward appearance of an individual ...
... • Recessive – traits that only appear when paired with another allele that is recessive (type O) • Genotype – a pair of allele genes • Phenotype – the outward appearance of an individual ...
Structure and History of DNA 1-8
... “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material”. • Besides copying, DNA must do ...
... “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material”. • Besides copying, DNA must do ...
EXAM B
... 8. A mutation that involves a single nucleotide is called a(an) A.chromosomal mutation. B.inversion. C.point mutation. D.translocation. ...
... 8. A mutation that involves a single nucleotide is called a(an) A.chromosomal mutation. B.inversion. C.point mutation. D.translocation. ...
Lecture Guide_Regulation of Gene Expression(Ch 7.5-7.6)
... Regulation of Gene Expression (Chapter 7) Reading Guide 1. Why is it important for bacterial cells to be able to regulate gene expression? Provide an example. ...
... Regulation of Gene Expression (Chapter 7) Reading Guide 1. Why is it important for bacterial cells to be able to regulate gene expression? Provide an example. ...
Misconceptions relating to DNA and RNA
... Genes are traits A gene and the expression of the gene as a characteristic or trait are the same thing There are some types of organisms that do not have DNA Only animals have DNA, plants and mushrooms do not have DNA Each DNA molecule is made of more than one chromosome The different cell types fou ...
... Genes are traits A gene and the expression of the gene as a characteristic or trait are the same thing There are some types of organisms that do not have DNA Only animals have DNA, plants and mushrooms do not have DNA Each DNA molecule is made of more than one chromosome The different cell types fou ...
Genetics Webquest Name: What is DNA? http://learn.genetics.utah
... 20) When a sperm and egg join, they create a single cell called a _________. 21) Each child inherits a _________ set of chromosomes. What is a Trait? 22) Give an example of a physical trait: _______________ 23) A dog fetching a bone is an example of what kind of trait. 24) Scientists describe the se ...
... 20) When a sperm and egg join, they create a single cell called a _________. 21) Each child inherits a _________ set of chromosomes. What is a Trait? 22) Give an example of a physical trait: _______________ 23) A dog fetching a bone is an example of what kind of trait. 24) Scientists describe the se ...
A substance formed by the chemical joining of two or more elements
... Variation in human skin color is an example of what? ...
... Variation in human skin color is an example of what? ...
Genetic Engineering of Late Blight Resistance in Potato
... Sanwen Huang, Dongyu Qu, Jianfei Xu, Zhiqi Jia, Cuihua Xin, Ying Li, Zhonghua Zhang ...
... Sanwen Huang, Dongyu Qu, Jianfei Xu, Zhiqi Jia, Cuihua Xin, Ying Li, Zhonghua Zhang ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... Each chromosome consists of a single very long DNA molecule, and each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of the DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes expressed by the cell may be ...
... Each chromosome consists of a single very long DNA molecule, and each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of the DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes expressed by the cell may be ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Transcribed regions present in the mature mRNA would arise from a(n) ________, while transcribed regions NOT present in the mature mRNA would arise from a(n) ________. ...
... Transcribed regions present in the mature mRNA would arise from a(n) ________, while transcribed regions NOT present in the mature mRNA would arise from a(n) ________. ...
Chapter 6, Section 3: Advances in Genetics
... cows so that the cows produce the protein responsible for blood clotting in their milk. The protein is then extracted and used to treat hemophiliacs. Genes have also been inserted into plant DNA which enables plants to survive in cold temperatures or in poor soil. Some genetically engineered plant ...
... cows so that the cows produce the protein responsible for blood clotting in their milk. The protein is then extracted and used to treat hemophiliacs. Genes have also been inserted into plant DNA which enables plants to survive in cold temperatures or in poor soil. Some genetically engineered plant ...
Biology Study Guide CH 12 Part I DNA-RNA
... 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eukaryotic cell? 11. RNA contains the sugar _________. 12. List 3 differences between RNA & DNA. 13. How many types of RNA are there? 14. _______________ molecules are p ...
... 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eukaryotic cell? 11. RNA contains the sugar _________. 12. List 3 differences between RNA & DNA. 13. How many types of RNA are there? 14. _______________ molecules are p ...
14-1 Human Heredity
... 9. What does “polygenic” mean? ________________________________________________ 10. What environmental factor has improved the height of Americans? __________________________ 11. Our complete set of genetic information is called The _________________ ___________________ 12. Compared to peas and frui ...
... 9. What does “polygenic” mean? ________________________________________________ 10. What environmental factor has improved the height of Americans? __________________________ 11. Our complete set of genetic information is called The _________________ ___________________ 12. Compared to peas and frui ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.