Chapter 15: Fundamentals of Metal Forming
... dependent variables, and the various means of linking the two. ...
... dependent variables, and the various means of linking the two. ...
Force Tension Compression Shear and Torsion
... How do tension, compression, shear, and torsion differ? D. Torsion is a rotating force. E. All of these stresses, tension, compression, shear, and torsion are very common in building structures. – Each one of these stresses must be fully understood before a structure can be designed and constructed ...
... How do tension, compression, shear, and torsion differ? D. Torsion is a rotating force. E. All of these stresses, tension, compression, shear, and torsion are very common in building structures. – Each one of these stresses must be fully understood before a structure can be designed and constructed ...
Motion in Two and Three Dimensions: Vectors
... • We’ll work usually in two dimensions—the three dimensional description is very similar. • Suppose we move a ball from point A to point B on a tabletop. This displacement can be fully described by giving a distance and a direction. • Both can be represented by an arrow, the length some agreed scale ...
... • We’ll work usually in two dimensions—the three dimensional description is very similar. • Suppose we move a ball from point A to point B on a tabletop. This displacement can be fully described by giving a distance and a direction. • Both can be represented by an arrow, the length some agreed scale ...
Glossary
... Glass transition temperature (Tg): The temperature at which, upon cooling, a noncrystalline ceramic or polymer transforms from a supercooled liquid to a rigid glass. Grain growth: An increase in the average size of the grain in polycrystalline metal, usually as a result of heating at elevated temper ...
... Glass transition temperature (Tg): The temperature at which, upon cooling, a noncrystalline ceramic or polymer transforms from a supercooled liquid to a rigid glass. Grain growth: An increase in the average size of the grain in polycrystalline metal, usually as a result of heating at elevated temper ...
Chapter 1 - Dr. ZM Nizam
... • Measure of deformation representing the displacement between particles in the body relative to a reference length. • Ratio of change in length due to deformation to the original length. ...
... • Measure of deformation representing the displacement between particles in the body relative to a reference length. • Ratio of change in length due to deformation to the original length. ...
9. Short overview of rheology very short for 2 credit course
... Stress is applied to sample instantaneously, t1, and ...
... Stress is applied to sample instantaneously, t1, and ...
capacitive transducer
... polymer films can also be used as piezoelectric materials. For piezoelectric effect, the crystal should have natural asymmetrical charge distribution. Because of this asymmetric charge distribution, the lattice deformation takes place. The lattice deformation is nothing but relative displacement of ...
... polymer films can also be used as piezoelectric materials. For piezoelectric effect, the crystal should have natural asymmetrical charge distribution. Because of this asymmetric charge distribution, the lattice deformation takes place. The lattice deformation is nothing but relative displacement of ...
(You may use Matlab or any other computer code, but the procedure
... (You may use Matlab or any other computer code, but the procedure must be given in detail in the report) Question: Consider the simplest problem of a 1D bar of uniform cross-section, as shown in Figure 1. The bar is of length l 1 and section area A 1 . It is subjected to a uniform body force b ...
... (You may use Matlab or any other computer code, but the procedure must be given in detail in the report) Question: Consider the simplest problem of a 1D bar of uniform cross-section, as shown in Figure 1. The bar is of length l 1 and section area A 1 . It is subjected to a uniform body force b ...
Laminate Materials Stress and Failure Calculations Using Sage
... derived, assembled, and inverted. The thermal and moisture expansion coefficients for each ply are then calculated and combined with the transformed reduced stiffness matrices to determine the thermal and moisture resultants. At this point, the program has all the information it needs to derive the ...
... derived, assembled, and inverted. The thermal and moisture expansion coefficients for each ply are then calculated and combined with the transformed reduced stiffness matrices to determine the thermal and moisture resultants. At this point, the program has all the information it needs to derive the ...
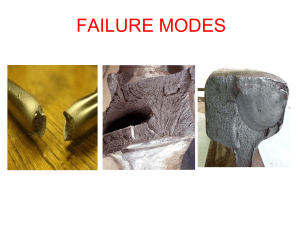
Failure Modes
... elastically & regains the original position after removal of load. • Point ‘B’ denotes the elastic limit • As the load is increased beyond point B, there comes a point at which there is a sudden extension & continued extension with a lower load ...
... elastically & regains the original position after removal of load. • Point ‘B’ denotes the elastic limit • As the load is increased beyond point B, there comes a point at which there is a sudden extension & continued extension with a lower load ...
RHEOLOGY
... Rheology is the study of flow of matter- in this case, rocks. Our aim is to describe the general behaviour of rheology by introducing strain rate and what the creep curve is. From this we introduce equations that represent the behaviour of different materials that we can calculate the motion and def ...
... Rheology is the study of flow of matter- in this case, rocks. Our aim is to describe the general behaviour of rheology by introducing strain rate and what the creep curve is. From this we introduce equations that represent the behaviour of different materials that we can calculate the motion and def ...
Catastrophic vs Gradual Collapse of Thin-Walled
... difference between these two sets of samples is the cylinder wall thickness, as they were prepared by the same electroless plating process for different time durations, resulting in identical internal microstructure. We find that the collapse strength of thick samples is in good agreement with finite el ...
... difference between these two sets of samples is the cylinder wall thickness, as they were prepared by the same electroless plating process for different time durations, resulting in identical internal microstructure. We find that the collapse strength of thick samples is in good agreement with finite el ...
Fluids - Northern Illinois University
... body is described at each point in space. • Difficult for a fluid with many particles. ...
... body is described at each point in space. • Difficult for a fluid with many particles. ...
10 - PSU MNE
... measure of the ductility of the material (i.e. how much can the material deform before failing). As deformation proceeds, the neck becomes progressively thinner until the material fractures. The strain at which this occurs is the fracture strain, f, and represents another measure of material ductil ...
... measure of the ductility of the material (i.e. how much can the material deform before failing). As deformation proceeds, the neck becomes progressively thinner until the material fractures. The strain at which this occurs is the fracture strain, f, and represents another measure of material ductil ...
Chapter 10 – Simple Harmonic Motion and Elasticity
... Stress is directly proportional to strain. SI Unit of Stress: newton per square meter = pascal (Pa) SI Unit of Strain: Strain is a unit less quantity. In reality objects obey Hooke’s law up to a certain limit. When stress remains proportional to strain the law is obeyed but as soon as the material b ...
... Stress is directly proportional to strain. SI Unit of Stress: newton per square meter = pascal (Pa) SI Unit of Strain: Strain is a unit less quantity. In reality objects obey Hooke’s law up to a certain limit. When stress remains proportional to strain the law is obeyed but as soon as the material b ...
Force Measurement
... Strain Gauge or LVDT could be employed to measure displacement related to Force applied. In case of LVDT compression of the ring , the relationship between displacement and Load P and is given by: ...
... Strain Gauge or LVDT could be employed to measure displacement related to Force applied. In case of LVDT compression of the ring , the relationship between displacement and Load P and is given by: ...
Stress, Strain, Virtual Power and Conservation Principles
... surface of a body is transmitted through its interior but notions of atomic bonding need not be invoked. The e ect of applied external loads is examined in terms of the force acting on a selected area inside the material. The resulting displacements of points in the body are used to describe deforma ...
... surface of a body is transmitted through its interior but notions of atomic bonding need not be invoked. The e ect of applied external loads is examined in terms of the force acting on a selected area inside the material. The resulting displacements of points in the body are used to describe deforma ...
History and Current Status of the Plastics Industry
... Relationships between external loads applied to an elastic body Intensity of the internal forces within the body Statics: all bodies are rigid. Strength of materials: all bodies are deformable ...
... Relationships between external loads applied to an elastic body Intensity of the internal forces within the body Statics: all bodies are rigid. Strength of materials: all bodies are deformable ...
PHYS430_22
... • Stage II: Initially few dislocations exist in other slip systems, but they start to lead to cross-slips and locks, impeding dislocation ...
... • Stage II: Initially few dislocations exist in other slip systems, but they start to lead to cross-slips and locks, impeding dislocation ...
Cellular materials made of stacked tubes : influence of the
... In order to discuss the influence of the manufacturing process of tube stackings on the mechanical properties of their constitutive material an Inconel 600® here, it has been proposed to perform uniaxial tensile tests at various strain rates on tubular specimens for the three different material conf ...
... In order to discuss the influence of the manufacturing process of tube stackings on the mechanical properties of their constitutive material an Inconel 600® here, it has been proposed to perform uniaxial tensile tests at various strain rates on tubular specimens for the three different material conf ...
MSE 170A Midterm 07
... b. Describe briefly mechanisms related to vacancy and interstitial diffusion and give two reasons why interstitial diffusion is more rapidly than vacancy diffusion. ...
... b. Describe briefly mechanisms related to vacancy and interstitial diffusion and give two reasons why interstitial diffusion is more rapidly than vacancy diffusion. ...
3.6 Yield Phenomena 3.6.1 Introduction
... Serrated stress/strain curves are similar to those observed in twinned specimens, but their origin is different, as mentioned. In Fig. 3.18, a set of curves is shown along with the effect of temperature on their appearance. Such behavior, although observed initially in ’ Fe, is exhibited by several ...
... Serrated stress/strain curves are similar to those observed in twinned specimens, but their origin is different, as mentioned. In Fig. 3.18, a set of curves is shown along with the effect of temperature on their appearance. Such behavior, although observed initially in ’ Fe, is exhibited by several ...
Deformation (mechanics)
Deformation in continuum mechanics is the transformation of a body from a reference configuration to a current configuration. A configuration is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body.A deformation may be caused by external loads, body forces (such as gravity or electromagnetic forces), or changes in temperature, moisture content, or chemical reactions, etc.Strain is a description of deformation in terms of relative displacement of particles in the body that excludes rigid-body motions. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered.In a continuous body, a deformation field results from a stress field induced by applied forces or is due to changes in the temperature field inside the body. The relation between stresses and induced strains is expressed by constitutive equations, e.g., Hooke's law for linear elastic materials. Deformations which are recovered after the stress field has been removed are called elastic deformations. In this case, the continuum completely recovers its original configuration. On the other hand, irreversible deformations remain even after stresses have been removed. One type of irreversible deformation is plastic deformation, which occurs in material bodies after stresses have attained a certain threshold value known as the elastic limit or yield stress, and are the result of slip, or dislocation mechanisms at the atomic level. Another type of irreversible deformation is viscous deformation, which is the irreversible part of viscoelastic deformation.In the case of elastic deformations, the response function linking strain to the deforming stress is the compliance tensor of the material.