Chapter 4c - Loy Research Group
... Compression and Shear vs. Tensile Tests Stress-strain curves are very dependent on the test method. A modulus determined under compression is generally higher than one derived from a tensile experiment, as shown below for polystyrene. Tensile testing is most sensitive to material flaws and microsco ...
... Compression and Shear vs. Tensile Tests Stress-strain curves are very dependent on the test method. A modulus determined under compression is generally higher than one derived from a tensile experiment, as shown below for polystyrene. Tensile testing is most sensitive to material flaws and microsco ...
CAUSES OF EARTHQUAKES Ch. 3, pp. 75
... Cold rock is brittle (for example, ocean lithosphere and most of continental lithosphere) Hot rock is ductile (for example, the asthenosphere and some parts of continental plates) Both lithosphere and asthenosphere act elastic if stress change is sudden and small (e.g., seismic waves) In ductile ma ...
... Cold rock is brittle (for example, ocean lithosphere and most of continental lithosphere) Hot rock is ductile (for example, the asthenosphere and some parts of continental plates) Both lithosphere and asthenosphere act elastic if stress change is sudden and small (e.g., seismic waves) In ductile ma ...
MATERIALS OF CONSTRUCTION Introduction The engineering
... The factors which form the basis of various systems of classifications of materials in material science and engineering are: (i) the chemical composition of the material, (ii) the mode of the occurrence of the material in the nature, (iii) the refining and the manufacturing process to which the mate ...
... The factors which form the basis of various systems of classifications of materials in material science and engineering are: (i) the chemical composition of the material, (ii) the mode of the occurrence of the material in the nature, (iii) the refining and the manufacturing process to which the mate ...
Strain Rate Dependent Flow Stress Characterization
... A different perspective for explaining this behavior can be taken by analyzing the mechanical response during compression at various specimen sizes at a specific strain rate. At strain rate 0.1 sec-1, it was found that flow stress throughout all measured strain decreases with miniaturization. This o ...
... A different perspective for explaining this behavior can be taken by analyzing the mechanical response during compression at various specimen sizes at a specific strain rate. At strain rate 0.1 sec-1, it was found that flow stress throughout all measured strain decreases with miniaturization. This o ...
Thermally activated processes in materials probed by nanoindentation
... This talk will first focus on experimental issues and challenges, but also solutions during advanced nanoindentation testing to overcome thermal drift influences, as demonstrated for fused silica and ultrafine grained (ufg) Au. Special focus will be on high temperature testing, different testing met ...
... This talk will first focus on experimental issues and challenges, but also solutions during advanced nanoindentation testing to overcome thermal drift influences, as demonstrated for fused silica and ultrafine grained (ufg) Au. Special focus will be on high temperature testing, different testing met ...
CHE 333 Class 19
... In some materials, mainly steels, ductility can decrease very sharply with temperature, so a ductile materials becomes brittle – know as the ductile brittle transition. The standard test is to use an impact tester – a pendulum type hammer and the energy absorbed in failure is measured by how far the ...
... In some materials, mainly steels, ductility can decrease very sharply with temperature, so a ductile materials becomes brittle – know as the ductile brittle transition. The standard test is to use an impact tester – a pendulum type hammer and the energy absorbed in failure is measured by how far the ...
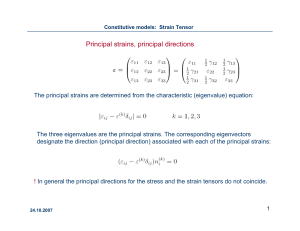
Principal strains, principal directions
... material behavior is time independent (there is only events consequence and no real time length) ; path independence: strains are uniquely determined from the current state of stress and vice versa; any process is reversible: to a closed stress path corresponds a closed strain path; no dependence of ...
... material behavior is time independent (there is only events consequence and no real time length) ; path independence: strains are uniquely determined from the current state of stress and vice versa; any process is reversible: to a closed stress path corresponds a closed strain path; no dependence of ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 20: material science and pressure
... Stress: Tells something about the force causing the deformation Strain: Measure of the degree of deformation For small stress, strain and stress are linearly correlated. Strain = Constant*Stress Constant: elastic modulus The elastic modulus depends on: • Material that is deformed • Type of deformati ...
... Stress: Tells something about the force causing the deformation Strain: Measure of the degree of deformation For small stress, strain and stress are linearly correlated. Strain = Constant*Stress Constant: elastic modulus The elastic modulus depends on: • Material that is deformed • Type of deformati ...
abstract_dingxd_1_new - ic-rmm1
... the elastic regime the distributions of jerk energy are sensitive to temperature and initial configurations. However, in the plastic regime the jerk distributions are rather robust and do not depend much on the details of the configurations, although the geometrical pattern formed after yield is str ...
... the elastic regime the distributions of jerk energy are sensitive to temperature and initial configurations. However, in the plastic regime the jerk distributions are rather robust and do not depend much on the details of the configurations, although the geometrical pattern formed after yield is str ...
chapter 11
... proportional to the volume stress (change in pressure). The corresponding constant ratio of stress to strain is called the bulk modulus, denoted by B. When the pressure on an object changes by a small amount Δp, from p0 to p0 + Δp, and the resulting volume strain is ΔV/V, Hooke’s law takes the form ...
... proportional to the volume stress (change in pressure). The corresponding constant ratio of stress to strain is called the bulk modulus, denoted by B. When the pressure on an object changes by a small amount Δp, from p0 to p0 + Δp, and the resulting volume strain is ΔV/V, Hooke’s law takes the form ...
Laboratory experiments, high angular
... residual stress is likely a function of crystal orientation during deformation. Second, high angular-resolution electron backscatter diffraction (HR-EBSD) allows the residual stresses in deformed single crystals and polycrystals to be mapped with <1 micron spatial resolution. HR-EBSD mapping reveals ...
... residual stress is likely a function of crystal orientation during deformation. Second, high angular-resolution electron backscatter diffraction (HR-EBSD) allows the residual stresses in deformed single crystals and polycrystals to be mapped with <1 micron spatial resolution. HR-EBSD mapping reveals ...
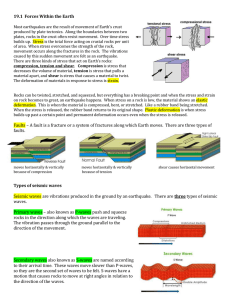
19.1-forces-within-Earth
... 19.1 Forces Within the Earth Most earthquakes are the result of movement of Earth’s crust produced by plate tectonics. Along the boundaries between two plates, rocks in the crust often resist movement. Over time stress builds up. Stress is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area. Wh ...
... 19.1 Forces Within the Earth Most earthquakes are the result of movement of Earth’s crust produced by plate tectonics. Along the boundaries between two plates, rocks in the crust often resist movement. Over time stress builds up. Stress is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area. Wh ...
Faculty Mentor: Dr. Robert Ryan Project Supervisor: Dr. George
... In this research experience, students will fabricate and characterize thin PZT films using spin-coating technique. Piezoelectric materials are of the constituents of multiferroic composite materials. They will then characterize the films to measure electrical properties (synopsis included below) and ...
... In this research experience, students will fabricate and characterize thin PZT films using spin-coating technique. Piezoelectric materials are of the constituents of multiferroic composite materials. They will then characterize the films to measure electrical properties (synopsis included below) and ...
Consider a rod BC of length L and uniform cross-sectional... x which is characteristics of the rod BC.
... The modulus of resilience is equal to the area under the straight-line portion OY of the stressstrain diagram and represents energy per unit volume that the material may absorb without yielding. The capacity of a structure to withstand an impact load without being ; permanently deformed clearly depe ...
... The modulus of resilience is equal to the area under the straight-line portion OY of the stressstrain diagram and represents energy per unit volume that the material may absorb without yielding. The capacity of a structure to withstand an impact load without being ; permanently deformed clearly depe ...
Digital Image Correlation Strain Analysis of Geometric Stress
... In a plate of uniform cross section the stress concentration factor is 1. Stress is evenly displaced across the cross section of the material and yields uniformly when highly stressed. In a non-uniform cross section, e.g. a plate with a circular hole, stress concentration increases by a factor of 2. ...
... In a plate of uniform cross section the stress concentration factor is 1. Stress is evenly displaced across the cross section of the material and yields uniformly when highly stressed. In a non-uniform cross section, e.g. a plate with a circular hole, stress concentration increases by a factor of 2. ...
Polymers composed of a large number of repeating units. Isomers
... Isoelectronic equal numbers of electrons or the same electronic configuration. Copolymer A polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. ...
... Isoelectronic equal numbers of electrons or the same electronic configuration. Copolymer A polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. ...
chapter5
... Example: 30% finite longitudinal strain (|e|= 0.3) is achieved in an experiment that lasts one hour (3600 s). The correspond strain rate is ė = 0.3/3600 = 8.3 x 10–5/s Now let’s see what happens to the strain rate when we change the time interval, but maintain the same amount of finite strain of 30% ...
... Example: 30% finite longitudinal strain (|e|= 0.3) is achieved in an experiment that lasts one hour (3600 s). The correspond strain rate is ė = 0.3/3600 = 8.3 x 10–5/s Now let’s see what happens to the strain rate when we change the time interval, but maintain the same amount of finite strain of 30% ...
1 - The Design Line
... Melting, boiling – what happens to the particles? Pure substances = fixed melting points Mixtures soften over a range of temperatures before melting. ...
... Melting, boiling – what happens to the particles? Pure substances = fixed melting points Mixtures soften over a range of temperatures before melting. ...
3.5 The plastic region of the stress strain curve for a metal is
... b. Allloying : by adding “impurity” atoms we may distort the regular order of the matrix. These local matrix distortions make it harder for defects to move thus increasing “Strengh” I nthe form of yield and tensile strengths. Changing the atomic in attraction through alloying would affect the modulu ...
... b. Allloying : by adding “impurity” atoms we may distort the regular order of the matrix. These local matrix distortions make it harder for defects to move thus increasing “Strengh” I nthe form of yield and tensile strengths. Changing the atomic in attraction through alloying would affect the modulu ...
ch10_shm_16slides
... Resonance is the condition in which a time-dependent force can transmit large amounts of energy to an oscillating object, leading to a large amplitude motion. Resonance occurs when the frequency of the force matches a natural frequency at which the object will oscillate. ...
... Resonance is the condition in which a time-dependent force can transmit large amounts of energy to an oscillating object, leading to a large amplitude motion. Resonance occurs when the frequency of the force matches a natural frequency at which the object will oscillate. ...
Chapter 2: Acoustic Wave Propagation
... • Displacement: movement of a particular point. • Strain: – Displacement variations as a function of position. – Fractional change in length. – Deformation. – Can be extended to volume change. ...
... • Displacement: movement of a particular point. • Strain: – Displacement variations as a function of position. – Fractional change in length. – Deformation. – Can be extended to volume change. ...
Differential seafloor spreading of the North Atlantic and consequent
... of traditional Euler poles, we have used an iterative least-squares method, which minimizes the gaps and overlaps between conjugate anomalies in a plane that is tangent to the Earth’s surface. For this purpose, we have subdivided the northern North Atlantic region into a finite number of oceanic blo ...
... of traditional Euler poles, we have used an iterative least-squares method, which minimizes the gaps and overlaps between conjugate anomalies in a plane that is tangent to the Earth’s surface. For this purpose, we have subdivided the northern North Atlantic region into a finite number of oceanic blo ...
Large-strain time-temperature equivalence in high density
... stable deformation and failure is the progression of damage beyond the incipient condition, which may follow a complicated path under the simultaneous influence of multiple driving forces. It should also be noted that some test conditions will yield only deformation with no damage for a particular m ...
... stable deformation and failure is the progression of damage beyond the incipient condition, which may follow a complicated path under the simultaneous influence of multiple driving forces. It should also be noted that some test conditions will yield only deformation with no damage for a particular m ...
COMPLEX STRESS TUTORIAL 2 STRESS AND STRAIN This
... produces a change in length ∆L. The direct strain produced is ε (epsilon) defined as ε=∆L/L The units of change in length and original length must be the same and the strain has no units. Strains are normally very small so often to indicate a strain of 10-6 we use the name micro strain and write it ...
... produces a change in length ∆L. The direct strain produced is ε (epsilon) defined as ε=∆L/L The units of change in length and original length must be the same and the strain has no units. Strains are normally very small so often to indicate a strain of 10-6 we use the name micro strain and write it ...
PSE4_Lecture_Ch12
... This proportionality holds until the force reaches the proportional limit. Beyond that, the object will still return to its original shape up to the elastic limit. Beyond the elastic limit, the material is permanently deformed, and it breaks at the breaking point. ...
... This proportionality holds until the force reaches the proportional limit. Beyond that, the object will still return to its original shape up to the elastic limit. Beyond the elastic limit, the material is permanently deformed, and it breaks at the breaking point. ...
Deformation (mechanics)
Deformation in continuum mechanics is the transformation of a body from a reference configuration to a current configuration. A configuration is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body.A deformation may be caused by external loads, body forces (such as gravity or electromagnetic forces), or changes in temperature, moisture content, or chemical reactions, etc.Strain is a description of deformation in terms of relative displacement of particles in the body that excludes rigid-body motions. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered.In a continuous body, a deformation field results from a stress field induced by applied forces or is due to changes in the temperature field inside the body. The relation between stresses and induced strains is expressed by constitutive equations, e.g., Hooke's law for linear elastic materials. Deformations which are recovered after the stress field has been removed are called elastic deformations. In this case, the continuum completely recovers its original configuration. On the other hand, irreversible deformations remain even after stresses have been removed. One type of irreversible deformation is plastic deformation, which occurs in material bodies after stresses have attained a certain threshold value known as the elastic limit or yield stress, and are the result of slip, or dislocation mechanisms at the atomic level. Another type of irreversible deformation is viscous deformation, which is the irreversible part of viscoelastic deformation.In the case of elastic deformations, the response function linking strain to the deforming stress is the compliance tensor of the material.