Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Wade Fisher
... One mole of an ideal gas initially at 00C undergoes an expansion at constant pressure of one atmosphere to four times its original volume. a) What is the new temperature? b) What is the work done on the gas? a) PV/T=constant so if V x4 then T x4 273K*4=1092 K b) W=-PV use PV=nRT before expansion: P ...
... One mole of an ideal gas initially at 00C undergoes an expansion at constant pressure of one atmosphere to four times its original volume. a) What is the new temperature? b) What is the work done on the gas? a) PV/T=constant so if V x4 then T x4 273K*4=1092 K b) W=-PV use PV=nRT before expansion: P ...
Ahmed Fazary_Click Chemistry
... Click chemistry is a concept introduced by K. Barry Sharpless in 2001 and describes chemistry tailored to generate substances quickly and reliably by joining small units together as nature does. In biochemistry, proteins are made from repeating amino acid units and sugars are made from repeating mon ...
... Click chemistry is a concept introduced by K. Barry Sharpless in 2001 and describes chemistry tailored to generate substances quickly and reliably by joining small units together as nature does. In biochemistry, proteins are made from repeating amino acid units and sugars are made from repeating mon ...
Chemistry - Swami Ramanand Teerth Marathwada University
... processes in isolated systems. Entropy change in Physical transformations: (i) Fusion of a solid. (ii) Vaporization of a liquid. (iii) Transition from one crystalline form to another. Entropy changes for an ideal gas as a function of V and T and as a function of P and T. Entropy changes of an ideal ...
... processes in isolated systems. Entropy change in Physical transformations: (i) Fusion of a solid. (ii) Vaporization of a liquid. (iii) Transition from one crystalline form to another. Entropy changes for an ideal gas as a function of V and T and as a function of P and T. Entropy changes of an ideal ...
crs_tb_ch06 - ChemConnections
... 2) the work done in pushing back the atmosphere. 3) the difference in the H—O bond energy in H2O(l) compared to H2O(g). 4) the value of H itself. 5) none of these Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... 2) the work done in pushing back the atmosphere. 3) the difference in the H—O bond energy in H2O(l) compared to H2O(g). 4) the value of H itself. 5) none of these Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
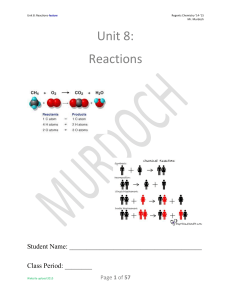
Unit 8: Reactions
... Objective: The amount of matter in reactants equals that in products! The mass on the reactants (left) side of the arrow and the mass on the products (right) side of the arrow MUST equal each other as the Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass may not be created or destroyed in any chemical re ...
... Objective: The amount of matter in reactants equals that in products! The mass on the reactants (left) side of the arrow and the mass on the products (right) side of the arrow MUST equal each other as the Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass may not be created or destroyed in any chemical re ...
1. Bromine exists naturally as a mixture of bromine
... Iron is biologically important in the transport of oxygen by red blood cells from the lungs to the various organs of the body. In the blood of an adult human, there are approximately 2.60 1013 red blood cells with a total of 2.90 g of iron. On the average, how many iron atoms are present in each r ...
... Iron is biologically important in the transport of oxygen by red blood cells from the lungs to the various organs of the body. In the blood of an adult human, there are approximately 2.60 1013 red blood cells with a total of 2.90 g of iron. On the average, how many iron atoms are present in each r ...
1) A clear glass bottle contains white sand, some nails, salt water
... layer of gasoline on top. How many phases are present in this system (excluding the bottle and lid)? Four phases are mentioned: (1) white sand, (2) nails, (3) salt water with some dye dissolved in it and (4) the layer of gasoline. A 5th phase (the air) could be included since it would be above the g ...
... layer of gasoline on top. How many phases are present in this system (excluding the bottle and lid)? Four phases are mentioned: (1) white sand, (2) nails, (3) salt water with some dye dissolved in it and (4) the layer of gasoline. A 5th phase (the air) could be included since it would be above the g ...
James Moir as Inorganic Chemist
... equal and equally distributed as in carbon, but, in addition, conferred an electropositive property on the whole system. In this case the tetrahedral valencies could be satisfied by H or alkyl groups and the combination NR4 or z4xR4 could act as a whole and could simulate an alkali metal. Regarding ...
... equal and equally distributed as in carbon, but, in addition, conferred an electropositive property on the whole system. In this case the tetrahedral valencies could be satisfied by H or alkyl groups and the combination NR4 or z4xR4 could act as a whole and could simulate an alkali metal. Regarding ...
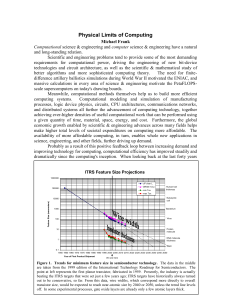
Physical Limits of Computing
... But, as a result of preparing or interacting with a system, we may come to know (or learn) something more about its actual state, besides just that it is one of the N states that were originally considered "possible." ...
... But, as a result of preparing or interacting with a system, we may come to know (or learn) something more about its actual state, besides just that it is one of the N states that were originally considered "possible." ...
Document
... between the system and surroundings Heat exchange occurs when system and surroundings have a difference in temperature Temperature is the measure of the amount of thermal energy within a sample of matter Heat flows from matter with high temperature to matter with low temperature until both objects r ...
... between the system and surroundings Heat exchange occurs when system and surroundings have a difference in temperature Temperature is the measure of the amount of thermal energy within a sample of matter Heat flows from matter with high temperature to matter with low temperature until both objects r ...
Tro Chemistry a Molecular Approach, 3E
... 17.3 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The first candidate in our search for a chemical potential might be enthalpy, which we defined in Chapter 6. Perhaps, just as a mechanical system proceeds in the direction of lowest potential energy, so a chemical system might proceed in the directio ...
... 17.3 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The first candidate in our search for a chemical potential might be enthalpy, which we defined in Chapter 6. Perhaps, just as a mechanical system proceeds in the direction of lowest potential energy, so a chemical system might proceed in the directio ...
CH 151 Companion
... 1. Appropriate attire: Appropriate protective clothing must be worn at all times while in the laboratory. It is a good idea not to wear your best clothing to lab since many chemicals can stain, bleach or generate holes in your clothing. a. Safety goggles approved by the chemistry department must be ...
... 1. Appropriate attire: Appropriate protective clothing must be worn at all times while in the laboratory. It is a good idea not to wear your best clothing to lab since many chemicals can stain, bleach or generate holes in your clothing. a. Safety goggles approved by the chemistry department must be ...
Document
... The point here is that the energy transferred to a system can go entirely into the system’s Emech (the system), into Eth, or some combination of the two. The energy isn’t lost, but where it ends up depends on the circumstances. Here is the problem with conservation of energy from a Phys 4A perspecti ...
... The point here is that the energy transferred to a system can go entirely into the system’s Emech (the system), into Eth, or some combination of the two. The energy isn’t lost, but where it ends up depends on the circumstances. Here is the problem with conservation of energy from a Phys 4A perspecti ...
Chemistry (SPA)
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
Rethinking Quant The Importance of Analytical Thinking
... To determine whether there is a relationship between two variables you must ensure that all other variables remain fixed. A calorimeter will absorb some of the heat released during the reaction. You will need to establish if the amount of heat absorbed by your calorimeter is significant and, if so, ...
... To determine whether there is a relationship between two variables you must ensure that all other variables remain fixed. A calorimeter will absorb some of the heat released during the reaction. You will need to establish if the amount of heat absorbed by your calorimeter is significant and, if so, ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.