Mineralogy and crystal structures of barium silicate minerals from
... Glasser & Glasser (1968) solved the crystal structure of walstromite and refined it to an R index of 16% using photographic methods. In this study it was refined in space group P1 to an R index of 3.8%. The refined cell parameters are a 6.733(1), b 9.608(2), c 6.685(1) Å, α 69.64(3), β 102.29(3), γ ...
... Glasser & Glasser (1968) solved the crystal structure of walstromite and refined it to an R index of 16% using photographic methods. In this study it was refined in space group P1 to an R index of 3.8%. The refined cell parameters are a 6.733(1), b 9.608(2), c 6.685(1) Å, α 69.64(3), β 102.29(3), γ ...
Are You suprised ?
... A) Adding Cl2 will increase heat. B) The equilibrium will move to the left when we remove Cl2. C) Increasing the pressure has no effect on this system. D) Adding catalyst will cool the system. ...
... A) Adding Cl2 will increase heat. B) The equilibrium will move to the left when we remove Cl2. C) Increasing the pressure has no effect on this system. D) Adding catalyst will cool the system. ...
9/21 properties of matter ppt
... heated, the liquid with the lowest boiling point is distilled first. This liquid turns into a vapor (gas) and flows out the distillation flask. As it enters the condensing tube, it is cooled and condenses back into a liquid. It is then collected in a graduated cylinder. When the liquid is almost com ...
... heated, the liquid with the lowest boiling point is distilled first. This liquid turns into a vapor (gas) and flows out the distillation flask. As it enters the condensing tube, it is cooled and condenses back into a liquid. It is then collected in a graduated cylinder. When the liquid is almost com ...
File
... • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
... • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
1 - Study Hungary
... 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 19 electrons 19 protons, 20 neutrons, 18 electrons 39 protons, 19 neutrons, 38 electrons 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 20 electrons 40 protons, 20 neutrons, 19 electrons ...
... 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 19 electrons 19 protons, 20 neutrons, 18 electrons 39 protons, 19 neutrons, 38 electrons 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 20 electrons 40 protons, 20 neutrons, 19 electrons ...
November 29, 2011 - Perry Local Schools
... Rocks: Rocks are composed of minerals-- most have many (two or more), some have one. Rocks such as granite, basalt and sandstone contain a variety of minerals. Rocks are classified according to their origin (how they were formed). A. Igneous B. Sedimentary C. Metamorphic Igneous: Cooling and solidif ...
... Rocks: Rocks are composed of minerals-- most have many (two or more), some have one. Rocks such as granite, basalt and sandstone contain a variety of minerals. Rocks are classified according to their origin (how they were formed). A. Igneous B. Sedimentary C. Metamorphic Igneous: Cooling and solidif ...
JUPARANA BORDEAUX
... the earth crust, residual melts circulated in the occurring cooling clefts. These melts were liquid and mobile due to high content of dissolved water vapour and other components. This is the reason, why very large crystal grains could form during cooling. Some pegmatite deposits have not gained impo ...
... the earth crust, residual melts circulated in the occurring cooling clefts. These melts were liquid and mobile due to high content of dissolved water vapour and other components. This is the reason, why very large crystal grains could form during cooling. Some pegmatite deposits have not gained impo ...
Final Preparation
... 75. Some molecules and ions are transported across a membrane via _____ which requires energy. A. osmosis B. diffusion C. facilitate diffusion D. active transport 76. In a lipid bilayer: A) the hydrophilic heads of the molecules point towards each other B) all the molecules are triglycerides C) the ...
... 75. Some molecules and ions are transported across a membrane via _____ which requires energy. A. osmosis B. diffusion C. facilitate diffusion D. active transport 76. In a lipid bilayer: A) the hydrophilic heads of the molecules point towards each other B) all the molecules are triglycerides C) the ...
Crucibles for Single Crystal Growing
... for growing single crystals from oxide melts. The crucible shape is generally cylindrical. The melting temperature, the atmosphere and the constituents of the melt determine the choice of material. For this reason iridium crucibles are used at temperatures up to approx. 2300° C for growing crystals ...
... for growing single crystals from oxide melts. The crucible shape is generally cylindrical. The melting temperature, the atmosphere and the constituents of the melt determine the choice of material. For this reason iridium crucibles are used at temperatures up to approx. 2300° C for growing crystals ...
Physical and Chemical Properties
... States of Matter • There are different “states” of matter. No, not like Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico. States of matter are also known as phases (a physical state of matter). Elements and compounds can move from one phase to another phase when special physical forces are present. • Solid • Liquid • G ...
... States of Matter • There are different “states” of matter. No, not like Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico. States of matter are also known as phases (a physical state of matter). Elements and compounds can move from one phase to another phase when special physical forces are present. • Solid • Liquid • G ...
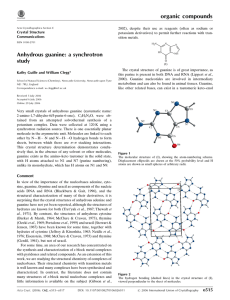
Anhydrous guanine: a synchrotron study
... Very small crystals of anhydrous guanine (systematic name: 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one), C5H5N5O, were obtained from an attempted solvothermal synthesis of a potassium complex. Data were collected at 120 K using a synchrotron radiation source. There is one essentially planar molecule in the a ...
... Very small crystals of anhydrous guanine (systematic name: 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one), C5H5N5O, were obtained from an attempted solvothermal synthesis of a potassium complex. Data were collected at 120 K using a synchrotron radiation source. There is one essentially planar molecule in the a ...
Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination
... reached slowly so that only a few nucleation sites are created which, with time, will grow larger. Thousands of solution conditions may be tried before finding one that succeeds in crystallizing the molecules, and ultimate success is never guaranteed. ...
... reached slowly so that only a few nucleation sites are created which, with time, will grow larger. Thousands of solution conditions may be tried before finding one that succeeds in crystallizing the molecules, and ultimate success is never guaranteed. ...
Slide () - Journal of Heat Transfer
... Diagrams in (a) of the ratios λmax/λbulk (black circles), ⟨l⟩max/⟨l⟩bulk (black upward triangles) and ⟨Cv⟩/⟨Cv⟩bulk (black downward triangles) versus temperature T for the atomic-scale 3D phononic crystals with the largest nanoparticle size (M=3). Data of the same group are interpolated by a black d ...
... Diagrams in (a) of the ratios λmax/λbulk (black circles), ⟨l⟩max/⟨l⟩bulk (black upward triangles) and ⟨Cv⟩/⟨Cv⟩bulk (black downward triangles) versus temperature T for the atomic-scale 3D phononic crystals with the largest nanoparticle size (M=3). Data of the same group are interpolated by a black d ...
notes-Minerals
... Solids with a specific composition mean that they are solids, not liquids or gases. It also means that they are made up of specific elements or compounds. Quartz is made up of silicon and oxygen. Other minerals may also be made up of silicon and oxygen, but quartz has a specific arrangement and prop ...
... Solids with a specific composition mean that they are solids, not liquids or gases. It also means that they are made up of specific elements or compounds. Quartz is made up of silicon and oxygen. Other minerals may also be made up of silicon and oxygen, but quartz has a specific arrangement and prop ...
The lustre of pearls
... My first thoughts were that maybe the layers are too friend that the value of pearls is appraised by thick or maybe of non-uniform thickness in ordinary evaluating the following factors: Size; shape; nacre. I wasted a lot of time trying to calculate the recolour and lustre (a term used for the quali ...
... My first thoughts were that maybe the layers are too friend that the value of pearls is appraised by thick or maybe of non-uniform thickness in ordinary evaluating the following factors: Size; shape; nacre. I wasted a lot of time trying to calculate the recolour and lustre (a term used for the quali ...
Test3_sp2012with answers
... A) is endothermic B) is exothermic C) could be either exo or endothermic D) is equal to the sum of the first two reactions. _B__12. The temperature of a liquid is decreased. What happens to the vapor pressure of the liquid as a result? A) it increases B) it decreases C) it is not changed D) it incre ...
... A) is endothermic B) is exothermic C) could be either exo or endothermic D) is equal to the sum of the first two reactions. _B__12. The temperature of a liquid is decreased. What happens to the vapor pressure of the liquid as a result? A) it increases B) it decreases C) it is not changed D) it incre ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... 1. The oxidation number of an element in its natural form is 0. Examples: the oxidation number is zero for each element in H2, O2, Cl2, P4, Na, etc. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion. Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidation #’s: Na = +1 and N = -3. In ...
... 1. The oxidation number of an element in its natural form is 0. Examples: the oxidation number is zero for each element in H2, O2, Cl2, P4, Na, etc. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion. Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidation #’s: Na = +1 and N = -3. In ...
Chapter 13 Rocks and Minerals
... Mineral Formation Minerals form in many different ways. - melted rock inside the earth (magma). - melted rock that reaches the earths surface (lava). -evaporation of water leaving minerals behind. (ocean water, salt in cup after ocean water evaporates) - precipitation of minerals suspended in water ...
... Mineral Formation Minerals form in many different ways. - melted rock inside the earth (magma). - melted rock that reaches the earths surface (lava). -evaporation of water leaving minerals behind. (ocean water, salt in cup after ocean water evaporates) - precipitation of minerals suspended in water ...
Rocks - Curriculum Club
... Evaporation is a technique used to separate liquid from solid parts of a mixture. ...
... Evaporation is a technique used to separate liquid from solid parts of a mixture. ...
File
... (b) (i) a solution made from a non-volatile solute has a higher boiling point than the pure solvent because the solution has a lower vapor pressure than the water (Raoult’s Law) . the temperature of the solution has be higher to produce enough vapor pressure to equal the atmospheric pressure (i.e., ...
... (b) (i) a solution made from a non-volatile solute has a higher boiling point than the pure solvent because the solution has a lower vapor pressure than the water (Raoult’s Law) . the temperature of the solution has be higher to produce enough vapor pressure to equal the atmospheric pressure (i.e., ...
Lecture 2 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Solubility Equilibria • When we put an ionic compound in a solvent, even if it is considered to be insoluble, some small number of ions dissolve into the bulk phase • For an ionic solid of formula AB, this can be expressed as the equilibrium reaction: AB (s) A+ (aq) + B- (aq) ...
... Solubility Equilibria • When we put an ionic compound in a solvent, even if it is considered to be insoluble, some small number of ions dissolve into the bulk phase • For an ionic solid of formula AB, this can be expressed as the equilibrium reaction: AB (s) A+ (aq) + B- (aq) ...
Fe3O(OOCC(CH3)3)6(C5H5N)3
... energy was calibrated by measuring the K absorption edge of an Fe foil. A double-crystal Si(111) fixed-exit monochromator was used for monochromatization. To maximize the energy resolution, the focusing mirror was not inserted into the optical path. Repeated measurements of the Fe edge, using an iro ...
... energy was calibrated by measuring the K absorption edge of an Fe foil. A double-crystal Si(111) fixed-exit monochromator was used for monochromatization. To maximize the energy resolution, the focusing mirror was not inserted into the optical path. Repeated measurements of the Fe edge, using an iro ...
chapter 4 review: types of chemical reactions and
... 1. State whether each of the following is a strong, weak, or nonelectrolyte: (a) HClO4 (d) NH3 (b) C6H12 (e) CaCl2 (c) LiOH (f) HC2H3O2 Determine the molarity of a solution. Calculate the molarity of each ion in a solution. Determine the mass and/or volume of reagents necessary to prepare a solution ...
... 1. State whether each of the following is a strong, weak, or nonelectrolyte: (a) HClO4 (d) NH3 (b) C6H12 (e) CaCl2 (c) LiOH (f) HC2H3O2 Determine the molarity of a solution. Calculate the molarity of each ion in a solution. Determine the mass and/or volume of reagents necessary to prepare a solution ...
Minerals
... -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings ...
... -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.