Chem 1A Final Exam – Fall 2005
... What is ionization energy? Describe and explain the general trend in the periodic table for the IE. ...
... What is ionization energy? Describe and explain the general trend in the periodic table for the IE. ...
Final Exam Chemistry B2A Mr. Kimball`s Class 2003
... compared to what one would predict. b) Water has a bond angle of 105øC. c) Water has a relatively high boiling point compared to what one would predict. d) Water has a relatively large heat of vaporization compared to other compounds of similar size and shape. e) Water is soluble in other polar solv ...
... compared to what one would predict. b) Water has a bond angle of 105øC. c) Water has a relatively high boiling point compared to what one would predict. d) Water has a relatively large heat of vaporization compared to other compounds of similar size and shape. e) Water is soluble in other polar solv ...
(1) Dissolves, accompanied by evolution of flammable gas (2
... (b) The difference between the atomic radii of Na and K is relatively large compared to the difference between the atomic radii of Rb and Cs. (c) A sample of solid nickel chloride is attracted into a magnetic field, whereas a sample of solid zinc chloride is not. (d) Phosphorus forms the fluorides P ...
... (b) The difference between the atomic radii of Na and K is relatively large compared to the difference between the atomic radii of Rb and Cs. (c) A sample of solid nickel chloride is attracted into a magnetic field, whereas a sample of solid zinc chloride is not. (d) Phosphorus forms the fluorides P ...
Barnard Castle School Chemistry Department
... To obtain a solvent from a solute in a solution use distillation. To separate miscible liquids (liquids that mix together), use fractional distillation. The liquid with the lowest boiling point will be collected first. To separate immiscible liquids, use a separating funnel. The least dense li ...
... To obtain a solvent from a solute in a solution use distillation. To separate miscible liquids (liquids that mix together), use fractional distillation. The liquid with the lowest boiling point will be collected first. To separate immiscible liquids, use a separating funnel. The least dense li ...
Nanostructures and Computation—S.G. Johnson
... by the photonic crystal [ a waveguide described in Johnson et al., Phys. Rev. B 62:8212 (2000) ], in which case the experimental roughness amplitude cancels and we obtain a universal figure of merit. There are two interesting features of this graph. First, it confirms prediction by our paper last ye ...
... by the photonic crystal [ a waveguide described in Johnson et al., Phys. Rev. B 62:8212 (2000) ], in which case the experimental roughness amplitude cancels and we obtain a universal figure of merit. There are two interesting features of this graph. First, it confirms prediction by our paper last ye ...
Superprism effect based on phase velocities 745
... recent attention.1 – 8 One particular example is the superprism effect.2 This is most commonly understood as an effect due to group-velocity dispersion: a large change in the propagation direction of the refracted ray within the photonic crystal is achieved with respect to a small variation in incid ...
... recent attention.1 – 8 One particular example is the superprism effect.2 This is most commonly understood as an effect due to group-velocity dispersion: a large change in the propagation direction of the refracted ray within the photonic crystal is achieved with respect to a small variation in incid ...
Chapter 4 Minerals
... specific chemical composition and a definite crystalline structure. Inorganic: Are not alive, nor were ever alive during any part of their existence. Solids: Definite shape and definite volume Some minerals are elements like sulfur or copper but most are compounds like quartz. ...
... specific chemical composition and a definite crystalline structure. Inorganic: Are not alive, nor were ever alive during any part of their existence. Solids: Definite shape and definite volume Some minerals are elements like sulfur or copper but most are compounds like quartz. ...
In-Class Exam - Fayetteville State University
... 26. One method for removal of metal ions from a solution is to convert the metal to its elemental form so it can be filtered out as a solid. Which metal can be used to remove aluminum ions from solution? A) cobalt B) copper C) lead D) zinc E) none of these 27. What is the concentration of chloride i ...
... 26. One method for removal of metal ions from a solution is to convert the metal to its elemental form so it can be filtered out as a solid. Which metal can be used to remove aluminum ions from solution? A) cobalt B) copper C) lead D) zinc E) none of these 27. What is the concentration of chloride i ...
RESEARCH/RESEARCHERS
... cently, a number of groups have shown that four-wave-mixing (4WM) in silica optical fibers can generate high-quality quantum-correlated photon pairs with much higher spectral brightness than achievable by PDC, but this approach appears to be limited by spontaneous Raman scattering (SRS) in the amorp ...
... cently, a number of groups have shown that four-wave-mixing (4WM) in silica optical fibers can generate high-quality quantum-correlated photon pairs with much higher spectral brightness than achievable by PDC, but this approach appears to be limited by spontaneous Raman scattering (SRS) in the amorp ...
chapter 4 review: types of chemical reactions and solution
... 1. State whether each of the following is a strong, weak, or nonelectrolyte: (a) HClO4 (d) NH3 (b) C6H12 (e) CaCl2 (c) LiOH (f) HC2H3O2 Determine the molarity of a solution. Calculate the molarity of each ion in a solution. Determine the mass and/or volume of reagents necessary to prepare a solution ...
... 1. State whether each of the following is a strong, weak, or nonelectrolyte: (a) HClO4 (d) NH3 (b) C6H12 (e) CaCl2 (c) LiOH (f) HC2H3O2 Determine the molarity of a solution. Calculate the molarity of each ion in a solution. Determine the mass and/or volume of reagents necessary to prepare a solution ...
Packet 2- Chemistry of Life
... B. Law of mass action says that the ratio of products to reactants in a reaction at equalibrium is always the same. C. Significance? If you remove (or add) product or reactant, you can MOVE the direction that the equation will happen. 2. Acids and bases usually exist in equilibrium. A. (You migh ...
... B. Law of mass action says that the ratio of products to reactants in a reaction at equalibrium is always the same. C. Significance? If you remove (or add) product or reactant, you can MOVE the direction that the equation will happen. 2. Acids and bases usually exist in equilibrium. A. (You migh ...
Review 3
... 10. In a titration, 45.0 mL of KOH is neutralized by 75.0 mL of 0.30M HBr. How much KOH is in 1.0 liter of the KOH solution? ...
... 10. In a titration, 45.0 mL of KOH is neutralized by 75.0 mL of 0.30M HBr. How much KOH is in 1.0 liter of the KOH solution? ...
Amorphous phosphates
... rich in phosphates) but can also represent a pathological situation. Usually, the presence of these crystals is non significant. The distinction between amorphous urates and amorphous phosphates is often made on the urinary pH basis. With a simple examination of the centrifuge pellet, the precipitat ...
... rich in phosphates) but can also represent a pathological situation. Usually, the presence of these crystals is non significant. The distinction between amorphous urates and amorphous phosphates is often made on the urinary pH basis. With a simple examination of the centrifuge pellet, the precipitat ...
Name ……………………………..………...… …….. Index No
... b) 20g of potassium chloride were placed in a glass beaker and 40.0cm3 of water were added. The beaker was heated until all the potassium chloride had dissolved and then allowed to cool. When crystals first appear the temperature was noted. An extra 5.0cm3 of water were added and the experiment was ...
... b) 20g of potassium chloride were placed in a glass beaker and 40.0cm3 of water were added. The beaker was heated until all the potassium chloride had dissolved and then allowed to cool. When crystals first appear the temperature was noted. An extra 5.0cm3 of water were added and the experiment was ...
1. Why aren`t the following substances minerals?
... 10. What is the difference between igneous rock that cools above and below ground? • Igneous rock that cools above ground cools quickly and has small or no crystals. • Igneous rock that cools below ground cools slowly and has large crystals. ...
... 10. What is the difference between igneous rock that cools above and below ground? • Igneous rock that cools above ground cools quickly and has small or no crystals. • Igneous rock that cools below ground cools slowly and has large crystals. ...
AHSGE Review
... involved in chemical reactions. The number of electrons being transferred determines the properties of the substances being combined, as well as that of the resulting substance. The location of the electrons involved in the reaction determines the amount of energy involved in the reaction. ...
... involved in chemical reactions. The number of electrons being transferred determines the properties of the substances being combined, as well as that of the resulting substance. The location of the electrons involved in the reaction determines the amount of energy involved in the reaction. ...
Spring 2014 Chemistry Review
... 98) In the solvation of solids, solubility rates increase with (high / low) temperatures. 99) In the solvation of gases, solubility rates increase with (high / low) temperatures and (high / low) pressure. 100) Agitation of a solution will (increase / decrease) the dissolving rate of a solid; whereas ...
... 98) In the solvation of solids, solubility rates increase with (high / low) temperatures. 99) In the solvation of gases, solubility rates increase with (high / low) temperatures and (high / low) pressure. 100) Agitation of a solution will (increase / decrease) the dissolving rate of a solid; whereas ...
mineralcards17 - PAMS-Doyle
... What are the 4 parts Where do minerals of the definition of a form? mineral? ...
... What are the 4 parts Where do minerals of the definition of a form? mineral? ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review
... 5. What is the effect on the number of dissolved particles on: vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point? Colligative properties 6. Which of the following will have the higher boiling point, .100M NaNO 3 or .100 M MgBr2? 7. Write the dissociation equations for the following compounds in wate ...
... 5. What is the effect on the number of dissolved particles on: vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point? Colligative properties 6. Which of the following will have the higher boiling point, .100M NaNO 3 or .100 M MgBr2? 7. Write the dissociation equations for the following compounds in wate ...
LECTURE_Solutions2013(1)
... • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
... • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
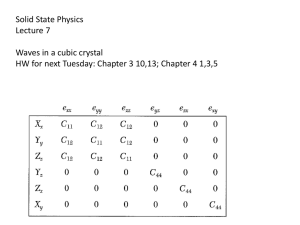
Solid State Physics Lectures 7 Waves in a cubic crystal
... Take a crystal for which C12 ≠ C13, but otherwise has all the same matrix elements as for a cubic crystal. How do you modify the equations for u and v? ...
... Take a crystal for which C12 ≠ C13, but otherwise has all the same matrix elements as for a cubic crystal. How do you modify the equations for u and v? ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.