Heterogeneous Catalysis and Solid Catalysts
... The main aim of environmental catalysis is environmental protection. Examples are the reduction of NOx in stack gases with NH3 on V2O5 – TiO2 catalysts and the removal of NOx, CO, and hydrocarbons from automobile exhaust gases by using the so-called three-way catalyst consisting of Rh – Pt – CeO2 – ...
... The main aim of environmental catalysis is environmental protection. Examples are the reduction of NOx in stack gases with NH3 on V2O5 – TiO2 catalysts and the removal of NOx, CO, and hydrocarbons from automobile exhaust gases by using the so-called three-way catalyst consisting of Rh – Pt – CeO2 – ...
Enhancement of anaerobic digestion of actual industrial
... Results showed that the rate order statistically increased with increasing initial COD content, demonstrating that conventional kinetic modeling is inadequate for these WW of complex composition. COD degradation models revealed the Monod model gave the best overall fit to experimental data throughou ...
... Results showed that the rate order statistically increased with increasing initial COD content, demonstrating that conventional kinetic modeling is inadequate for these WW of complex composition. COD degradation models revealed the Monod model gave the best overall fit to experimental data throughou ...
Carbon dioxide capture and utilization in petrochemical industry
... Resulting in system corrosion ...
... Resulting in system corrosion ...
Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis with Transition
... photoredox reductive dehalogenation of activated alkyl halides mediated by the same catalyst.13 The combined efforts of these three research groups have helped to initiate a renewed interest in this field, prompting a diversity of studies into the utility of photoredox catalysis as a conceptually nove ...
... photoredox reductive dehalogenation of activated alkyl halides mediated by the same catalyst.13 The combined efforts of these three research groups have helped to initiate a renewed interest in this field, prompting a diversity of studies into the utility of photoredox catalysis as a conceptually nove ...
21 More About Amines • Heterocyclic Compounds
... not as good a leaving group as Cl-, Br -, or I -. As a result, a partial negative charge builds up on the carbon from which the proton is being removed. This gives the transition state a carbanion-like structure rather than an alkene-like structure. By removing a proton from the b -carbon bonded to ...
... not as good a leaving group as Cl-, Br -, or I -. As a result, a partial negative charge builds up on the carbon from which the proton is being removed. This gives the transition state a carbanion-like structure rather than an alkene-like structure. By removing a proton from the b -carbon bonded to ...
PART 6-ICHO-26-30
... The overall catalytic reaction is simple, whereas the reaction mechanism in the homogeneous phase is very complicated with a large number of reaction steps, and the course is difficult to control owing to a distinct chain character. With platinum as catalyst the significant reaction steps are: (i) A ...
... The overall catalytic reaction is simple, whereas the reaction mechanism in the homogeneous phase is very complicated with a large number of reaction steps, and the course is difficult to control owing to a distinct chain character. With platinum as catalyst the significant reaction steps are: (i) A ...
Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... Relating Avogadro's number to molar mass: calculation of the mass of Avogadro's number of sodium atoms Converting moles to atoms. Converting atoms to moles. Converting moles of a substance to mass in grams. Converting kilograms to moles. Converting grams to number of atoms. Calculating formula weigh ...
... Relating Avogadro's number to molar mass: calculation of the mass of Avogadro's number of sodium atoms Converting moles to atoms. Converting atoms to moles. Converting moles of a substance to mass in grams. Converting kilograms to moles. Converting grams to number of atoms. Calculating formula weigh ...
DOE Chemistry 1
... for use by DOE category A reactors. The subject areas, subject matter content, and level of detail of the Reactor Operator Fundamentals Manuals were determined from several sources. DOE Category A reactor training managers determined which materials should be included, and served as a primary refere ...
... for use by DOE category A reactors. The subject areas, subject matter content, and level of detail of the Reactor Operator Fundamentals Manuals were determined from several sources. DOE Category A reactor training managers determined which materials should be included, and served as a primary refere ...
Grossmont College Chemistry 120 Laboratory Manual 6th Edition
... directly in your final report as you obtain it. (Data entered on scraps of paper will be confiscated.) Where calculations of data are involved, show an orderly calculation for the first set of data, but do not clutter the calculation section with arithmetic details. Likewise, think through and answe ...
... directly in your final report as you obtain it. (Data entered on scraps of paper will be confiscated.) Where calculations of data are involved, show an orderly calculation for the first set of data, but do not clutter the calculation section with arithmetic details. Likewise, think through and answe ...
Document
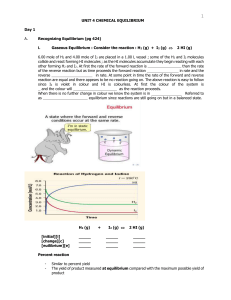
... reaction is started with [H2 ]0 = 0.76 M, [N2]0 = 0.60 M and [NH3]0= 0.48 M. Which of the following is correct as the reaction comes to equilibrium? A) The concentration of N2will increase B) The concentration of H2will decrease C) The concentration of NH3will decrease D) The concentration of both N ...
... reaction is started with [H2 ]0 = 0.76 M, [N2]0 = 0.60 M and [NH3]0= 0.48 M. Which of the following is correct as the reaction comes to equilibrium? A) The concentration of N2will increase B) The concentration of H2will decrease C) The concentration of NH3will decrease D) The concentration of both N ...
Changing Matter
... This occurs because of side reactions and the fact that many reactions are reversible. ...
... This occurs because of side reactions and the fact that many reactions are reversible. ...
Unit 4 - Chemical Equilibrium
... _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. This means the products can react together and turn back into the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ reactants. In other words, the reaction can go _ _ _ _ ways. When a reversible reaction is set up in a _ _ _ _ _ _ container, the forward reaction happens much faster than the reverse reaction at f ...
... _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. This means the products can react together and turn back into the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ reactants. In other words, the reaction can go _ _ _ _ ways. When a reversible reaction is set up in a _ _ _ _ _ _ container, the forward reaction happens much faster than the reverse reaction at f ...
Chemical thermodynamics - Mahesh Tutorials Science
... A 5-litre cylinder contained 10 moles of oxygen gas at 27oC. Due to sudden leakage through the hole, all the gas escaped into the atmosphere and the cylinder got empty. If the atmospheric pressure is 1.0 atmosphere, calculate the work done by the gas. (1 L atm = 101.3 J) ...
... A 5-litre cylinder contained 10 moles of oxygen gas at 27oC. Due to sudden leakage through the hole, all the gas escaped into the atmosphere and the cylinder got empty. If the atmospheric pressure is 1.0 atmosphere, calculate the work done by the gas. (1 L atm = 101.3 J) ...
Document
... More Making Pizzas, Continued • The tomato sauce limits the amount of pizzas we can make. In chemical reactions we call this the limiting reactant. also known as the limiting reagent ...
... More Making Pizzas, Continued • The tomato sauce limits the amount of pizzas we can make. In chemical reactions we call this the limiting reactant. also known as the limiting reagent ...
CHM 4XX. Organometallic Chemistry (0.5
... and bonding of organometallic compounds, their reactions and reaction mechanisms, spectroscopy, and their use in industrial processes and organic synthesis. Pre- or corequisite: CHM 331 or permission of instructor. Course Rationale Organometallic chemistry lies at the interface of organic chemistry ...
... and bonding of organometallic compounds, their reactions and reaction mechanisms, spectroscopy, and their use in industrial processes and organic synthesis. Pre- or corequisite: CHM 331 or permission of instructor. Course Rationale Organometallic chemistry lies at the interface of organic chemistry ...
PDF - Chemistry - University of Canterbury
... – nanoparticles – that they behave in ways that mediaeval Alchemists would have wondered at. Chemists understand the workings of the cells in our bodies at the molecular level, they work with doctors to understand the basis of diseases, and they design and synthesize new drug molecules to treat them ...
... – nanoparticles – that they behave in ways that mediaeval Alchemists would have wondered at. Chemists understand the workings of the cells in our bodies at the molecular level, they work with doctors to understand the basis of diseases, and they design and synthesize new drug molecules to treat them ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... pizzas, we burn a pizza, drop one on the floor, or other uncontrollable events happen so that we only make two pizzas. The actual amount of product made in a chemical reaction is called the actual yield. We can determine the efficiency of making pizzas by calculating the percentage of the maximum nu ...
... pizzas, we burn a pizza, drop one on the floor, or other uncontrollable events happen so that we only make two pizzas. The actual amount of product made in a chemical reaction is called the actual yield. We can determine the efficiency of making pizzas by calculating the percentage of the maximum nu ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... More Making Pizzas, Continued • The tomato sauce limits the amount of pizzas we can make. In chemical reactions we call this the limiting reactant. also known as the limiting reagent ...
... More Making Pizzas, Continued • The tomato sauce limits the amount of pizzas we can make. In chemical reactions we call this the limiting reactant. also known as the limiting reagent ...