Articles Oxidation Numbers in the Study of Metabolism
... ions, e.g. NaCl, the concept is easily understood; the oxidation number of each atom is actually equal to the charge on the respective ion. For covalent compounds the charges under consideration are hypothetical or notional. Both electrons of a covalent electron-pair bond between non-identical atoms ...
... ions, e.g. NaCl, the concept is easily understood; the oxidation number of each atom is actually equal to the charge on the respective ion. For covalent compounds the charges under consideration are hypothetical or notional. Both electrons of a covalent electron-pair bond between non-identical atoms ...
Student Solutions Manual Errata
... bonds are the attractions of oppositely charged ions to one another. We can think of the ions (or the spheres in the diagram) as being separate from, but strongly attracted to, one another. Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms are mutually attracted to a pair (or pairs) of electrons. Because the a ...
... bonds are the attractions of oppositely charged ions to one another. We can think of the ions (or the spheres in the diagram) as being separate from, but strongly attracted to, one another. Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms are mutually attracted to a pair (or pairs) of electrons. Because the a ...
Gas-phase study of the reactivity of optical coating desktop-size extreme-ultraviolet laser
... cluster can absorb a photon through low-lying electronic states and relax back to the ground electronic state many times, thus heating the cluster until thermionic emission occurs, and (2) vertical absorption of two or more photons can occur without rapid relaxation between absorption steps for both ...
... cluster can absorb a photon through low-lying electronic states and relax back to the ground electronic state many times, thus heating the cluster until thermionic emission occurs, and (2) vertical absorption of two or more photons can occur without rapid relaxation between absorption steps for both ...
2. The Magic of Chemical Reactions
... chemicalchanges/poperties of substances. In day today life we observe many chemical changes such as conversion of milk into curd, Ripening of fruits, farmentation of idli and dora etc. We observes that these changes are permanent. Similary we observe about conversion of water into ice, sublimation o ...
... chemicalchanges/poperties of substances. In day today life we observe many chemical changes such as conversion of milk into curd, Ripening of fruits, farmentation of idli and dora etc. We observes that these changes are permanent. Similary we observe about conversion of water into ice, sublimation o ...
Kinetic models of metabolism: model construction, model
... are inadequate and instead a kinetic modelling approach is necessary. Given the large number of reactions included in the network, a pipeline has been built to automatically generate kinetic laws from reaction stoichiometries. In this context a precise description of the reactional mechanism is impo ...
... are inadequate and instead a kinetic modelling approach is necessary. Given the large number of reactions included in the network, a pipeline has been built to automatically generate kinetic laws from reaction stoichiometries. In this context a precise description of the reactional mechanism is impo ...
Document
... engineer NMR observables at specific protein sites. For incell NMR applications, the isotope effect is exploited in a selective, filter-like manner. By analyzing isotope-labeled proteins in complex but NMR-inactive mixtures, that is, intracellular environments, in-cell NMR directly assesses the conf ...
... engineer NMR observables at specific protein sites. For incell NMR applications, the isotope effect is exploited in a selective, filter-like manner. By analyzing isotope-labeled proteins in complex but NMR-inactive mixtures, that is, intracellular environments, in-cell NMR directly assesses the conf ...
BIS103-002 (Spring 2008) - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... Erythrocytes are exposed to high levels of oxygen, which generates toxic ‘reactive oxygen species’ (or ROS). NADPH, a major product of the pentose phosphate pathway, is used to fully reduce (or detoxify) those ROS. ...
... Erythrocytes are exposed to high levels of oxygen, which generates toxic ‘reactive oxygen species’ (or ROS). NADPH, a major product of the pentose phosphate pathway, is used to fully reduce (or detoxify) those ROS. ...
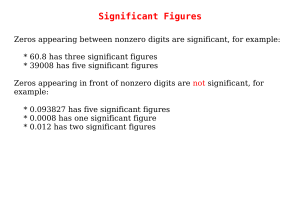
Significant Figures
... – undergo the exact same chemical reactions all isotopes of an element have the same number of protons isotopes of an element have different masses isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons isotopes are identified by their mass numbers – protons + neutrons ...
... – undergo the exact same chemical reactions all isotopes of an element have the same number of protons isotopes of an element have different masses isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons isotopes are identified by their mass numbers – protons + neutrons ...
CHAPTER 12 Study Guide
... • A balanced chemical equation provides the same kind of quantitative information that a recipe does. • Chemists use balanced chemical equations as a basis to calculate how much reactant is needed or product is formed in a reaction. • A balanced chemical equation can be interpreted in terms of diffe ...
... • A balanced chemical equation provides the same kind of quantitative information that a recipe does. • Chemists use balanced chemical equations as a basis to calculate how much reactant is needed or product is formed in a reaction. • A balanced chemical equation can be interpreted in terms of diffe ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... Holoenzyme only has biological activity when cofactor is bound. Cofactor (or coenzyme) = small non-amino acid molecule required for the catalytic activity of an enzyme. Often derived from dietary vitamins and minerals. Cofactor can be an organic molecule, metal ion, or organometallic complex. Cofact ...
... Holoenzyme only has biological activity when cofactor is bound. Cofactor (or coenzyme) = small non-amino acid molecule required for the catalytic activity of an enzyme. Often derived from dietary vitamins and minerals. Cofactor can be an organic molecule, metal ion, or organometallic complex. Cofact ...
The Bio-Organometallic Chemistry of Technetium and Rhenium
... of an atom in a compound is determined by the following rules: a. The oxidation number of an atom in the elemental form is zero b. The oxidation number of an atom in a simple ionic compound is typically equal to the charge on that atom (with the appropriate sign) c. The oxidation number of an atom i ...
... of an atom in a compound is determined by the following rules: a. The oxidation number of an atom in the elemental form is zero b. The oxidation number of an atom in a simple ionic compound is typically equal to the charge on that atom (with the appropriate sign) c. The oxidation number of an atom i ...
The intertwined metabolism of Medicago truncatula and its nitrogen
... The intertwined metabolism of Medicago truncatula and its nitrogen fixing symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti elucidated by genome-scale metabolic models. ...
... The intertwined metabolism of Medicago truncatula and its nitrogen fixing symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti elucidated by genome-scale metabolic models. ...
Coordinated concentration changes of transcript and metabolites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
... However, it is possible that other types of regulation, such as posttranslational protein modifications and feedback inhibition, could be more predominant in the aggregate than transcriptional regulation [11]. Accordingly, a major limitation with these computational techniques is that the extent to ...
... However, it is possible that other types of regulation, such as posttranslational protein modifications and feedback inhibition, could be more predominant in the aggregate than transcriptional regulation [11]. Accordingly, a major limitation with these computational techniques is that the extent to ...
Practice Biochem Test
... e. They are one of several factors that contribute to heart disease. ____ 16. A molecule with the formula C18H54O2 is probably a a. carbohydrate. b. fatty acid. c. protein. d. glycerol e. hydrocarbon. ____ 17. Which of the following statements is false for the class of biological molecules known as ...
... e. They are one of several factors that contribute to heart disease. ____ 16. A molecule with the formula C18H54O2 is probably a a. carbohydrate. b. fatty acid. c. protein. d. glycerol e. hydrocarbon. ____ 17. Which of the following statements is false for the class of biological molecules known as ...
Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... b) C3H8O1: 3*(12.01 g) + 8*(1.01 g) + 1*(16.00 g) = 60.05 grams c) (NH4)2S : 2*(14.01 g) + 8*(1.01 g) + 1*(32.07 g) = 68.17 grams d) Mg(NO3)2: 1*(24.31 g) + 2*(14.01 g) + 6*(16.00 g) = 148.33 grams e) C8H10N4O2: 8*(12.01 g) + 10*(1.01 g) + 4*(14.01 g) + 2*(16.00 g) ...
... b) C3H8O1: 3*(12.01 g) + 8*(1.01 g) + 1*(16.00 g) = 60.05 grams c) (NH4)2S : 2*(14.01 g) + 8*(1.01 g) + 1*(32.07 g) = 68.17 grams d) Mg(NO3)2: 1*(24.31 g) + 2*(14.01 g) + 6*(16.00 g) = 148.33 grams e) C8H10N4O2: 8*(12.01 g) + 10*(1.01 g) + 4*(14.01 g) + 2*(16.00 g) ...
5. Stoichiometry - Sakshi Education
... Weighed amounts of solid and solid KI are dissolved in water separately and their solutions are mixed. The following reaction takes place ...
... Weighed amounts of solid and solid KI are dissolved in water separately and their solutions are mixed. The following reaction takes place ...
1.1 Molar Mass 1.2 Molar Mass 1.3 Conversion
... What mass of CH4 could form when combining these reactants? What mass of the unused reactant is left over? ...
... What mass of CH4 could form when combining these reactants? What mass of the unused reactant is left over? ...
2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
... atoms in the cyclic structure is other than carbon. Heterocyclic componds may be aliphatic or aromatic 15. Isomers: These are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Isomers are further subdivided into: (a) structural isomers, (b) geometrical isomers and (c) stereoisomers(optical i ...
... atoms in the cyclic structure is other than carbon. Heterocyclic componds may be aliphatic or aromatic 15. Isomers: These are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Isomers are further subdivided into: (a) structural isomers, (b) geometrical isomers and (c) stereoisomers(optical i ...
The Mole
... elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles. ...
... elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles. ...
Deuterium fractionation of methylamine through atomic grain
... subjected to various processes on them. Deuterium (D) fractionation of interstellar molecules is an important issue when considering chemical evolution in MCs. Previous studies revealed that atomic grain-surface reactions play a significant role for the D enrichment of interstellar molecules such as ...
... subjected to various processes on them. Deuterium (D) fractionation of interstellar molecules is an important issue when considering chemical evolution in MCs. Previous studies revealed that atomic grain-surface reactions play a significant role for the D enrichment of interstellar molecules such as ...
C:\Documents and Settings\mrh70950\My Documents
... Silicon, which is isoelectronic with carbon, can be found immediately below carbon in the periodic table. Not surprisingly, silicon is very similar to carbon: it is tetravalent, and readily makes tetrahedral analogs of alkanes. Thus, tetramethylsilane, Si(CH3)4 (bp 27EC), like 2,2dimethylpropane C(C ...
... Silicon, which is isoelectronic with carbon, can be found immediately below carbon in the periodic table. Not surprisingly, silicon is very similar to carbon: it is tetravalent, and readily makes tetrahedral analogs of alkanes. Thus, tetramethylsilane, Si(CH3)4 (bp 27EC), like 2,2dimethylpropane C(C ...
+ 2
... Question: Is fermentation a catabolic process or is it an anabolic process? Fermentation may be considered as two metabolic pathways, glycolysis and the extending reactions. It may also be considered as a single metabolic pathway from glucose to the final fermentation products. ...
... Question: Is fermentation a catabolic process or is it an anabolic process? Fermentation may be considered as two metabolic pathways, glycolysis and the extending reactions. It may also be considered as a single metabolic pathway from glucose to the final fermentation products. ...
Chapter 2 The Components of Matter
... Since elements are found in nature as mixtures of isotopes, and each isotope is found in a fixed amount in nature, and rarely are these amounts equal among the given isotopes of an element we must have a way to take this into account when talking about a naturally occurring element; enter Average Ma ...
... Since elements are found in nature as mixtures of isotopes, and each isotope is found in a fixed amount in nature, and rarely are these amounts equal among the given isotopes of an element we must have a way to take this into account when talking about a naturally occurring element; enter Average Ma ...
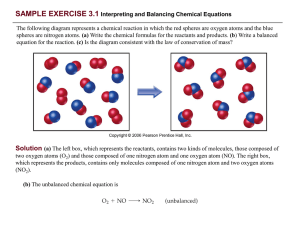
PRACTICE EXERCISE - Needham.K12.ma.us
... (c) The left box (reactants) contains four O2 molecules and eight NO molecules. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO as required by the balanced equation. The right box (products) contains eight NO 2 molecules. The number of NO2 molecules on the right equals the number of NO molecules ...
... (c) The left box (reactants) contains four O2 molecules and eight NO molecules. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO as required by the balanced equation. The right box (products) contains eight NO 2 molecules. The number of NO2 molecules on the right equals the number of NO molecules ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.