ESO - ENCIGA
... order to be able to predict its behaviour and understand its history. Science is based on systematic experimentation and on observation of natural phenomena to discover facts about them and to formulate laws and principles based on these facts. The organized knowledge that is derived from scientific ...
... order to be able to predict its behaviour and understand its history. Science is based on systematic experimentation and on observation of natural phenomena to discover facts about them and to formulate laws and principles based on these facts. The organized knowledge that is derived from scientific ...
IGCSE® Chemistry - Hodder Plus Home
... 2 (a) Gas particles from the coffee are moving randomly, from the coffee shop, colliding with other particles in the air until they reach you. They are diffusing. [2] (b) When the temperature rises, the steel tracks will expand. The gaps allow the tracks to expand without buckling the railway line ...
... 2 (a) Gas particles from the coffee are moving randomly, from the coffee shop, colliding with other particles in the air until they reach you. They are diffusing. [2] (b) When the temperature rises, the steel tracks will expand. The gaps allow the tracks to expand without buckling the railway line ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... concise way by chemical equations. ...
... concise way by chemical equations. ...
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Nature has invented several ways to synthesize ATP. One solution is a series of coupled chemical reactions catalyzed by soluble enzymes in the cytoplasm that result in substrate-level phosphorylation. The most prevalent starting substrate for such an energy-yielding pathway is glucose, which is deco ...
... Nature has invented several ways to synthesize ATP. One solution is a series of coupled chemical reactions catalyzed by soluble enzymes in the cytoplasm that result in substrate-level phosphorylation. The most prevalent starting substrate for such an energy-yielding pathway is glucose, which is deco ...
Size-Selective Hydrogenation of Olefins by Dendrimer
... open to the atmosphere at the top. All of the hydrogenation reactions were run at atmospheric pressure and room temperature (25 ( 2 °C). Hydrogenation Reactions. 50 mL of the catalytic solution and a magnetic stir bar were placed in a Schlenk flask. All of the joints of the apparatus were sealed wit ...
... open to the atmosphere at the top. All of the hydrogenation reactions were run at atmospheric pressure and room temperature (25 ( 2 °C). Hydrogenation Reactions. 50 mL of the catalytic solution and a magnetic stir bar were placed in a Schlenk flask. All of the joints of the apparatus were sealed wit ...
Beginning Chemistry
... Chemistry is the study of matter, including its composition, its properties, its structure, the changes which it undergoes, and the laws governing those changes. Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Any material object, no matter how large or small, is composed of matter. In contrast ...
... Chemistry is the study of matter, including its composition, its properties, its structure, the changes which it undergoes, and the laws governing those changes. Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Any material object, no matter how large or small, is composed of matter. In contrast ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... need to be sharply reduced, if not banned. The transportation sector will have to find solutions where gasoline is substituted by other means of vehicle propulsion. This is the challenge for all modern societies, and at the same time it is likely to be the most brilliant opportunity for science in t ...
... need to be sharply reduced, if not banned. The transportation sector will have to find solutions where gasoline is substituted by other means of vehicle propulsion. This is the challenge for all modern societies, and at the same time it is likely to be the most brilliant opportunity for science in t ...
Document
... ligands in trigonal bipyramidal structures. Asymmetric. Lacking all symmetry elements (pointing group C1). All asymmetric molecules are chiral. Asymmetric carbon atom. Traditional term used to describe a carbon with four different ligands attached. Not recommended in modern usage. Atactic. A term de ...
... ligands in trigonal bipyramidal structures. Asymmetric. Lacking all symmetry elements (pointing group C1). All asymmetric molecules are chiral. Asymmetric carbon atom. Traditional term used to describe a carbon with four different ligands attached. Not recommended in modern usage. Atactic. A term de ...
Developement of strategies for the isotopic labeling of methyl
... Nowadays, it is unequivocally recognized that the strategy of specific isotope labeling of methyl groups in a perdeuterated protein has significantly extended the frontier of this technique. Indeed, proteins as large as 1 MDa could be investigated by NMR. Conversely, this strategy presents an import ...
... Nowadays, it is unequivocally recognized that the strategy of specific isotope labeling of methyl groups in a perdeuterated protein has significantly extended the frontier of this technique. Indeed, proteins as large as 1 MDa could be investigated by NMR. Conversely, this strategy presents an import ...
Moles
... For example, if you have 100.0 g of Na and react that with 100.0 g of Chlorine they would not react completely. •Chlorine starts out with a mass of 35.5 and Na has a mass of 23 •As a result, we would have a bunch of Na atoms unused. •In chemistry it is much easier to use a quantity of atoms rather t ...
... For example, if you have 100.0 g of Na and react that with 100.0 g of Chlorine they would not react completely. •Chlorine starts out with a mass of 35.5 and Na has a mass of 23 •As a result, we would have a bunch of Na atoms unused. •In chemistry it is much easier to use a quantity of atoms rather t ...
1002_4th Exam_1010620
... B) The alpha particle is two protons and two neutrons. C) It often leaves the nucleus in an excited state. D) It involves nuclides with atomic number larger than 83 and mass number larger than 200. Answer: A 41) A nuclide has a decay constant of 4.28 × 10-4 /h. If the activity of a sample is 3.14 × ...
... B) The alpha particle is two protons and two neutrons. C) It often leaves the nucleus in an excited state. D) It involves nuclides with atomic number larger than 83 and mass number larger than 200. Answer: A 41) A nuclide has a decay constant of 4.28 × 10-4 /h. If the activity of a sample is 3.14 × ...
Downloaded - Maynooth University ePrints and eTheses Archive
... attack the carbonyl carbon atom, resulting in the bonding of the alcohol to the carbonyl carbon atom. Loss of a proton followed by a rearrangement of the electrons gives the amide carbonyl group back, which is still bonded to the mercury ion, and also cleaves the C–N amide bond to give the ester and ...
... attack the carbonyl carbon atom, resulting in the bonding of the alcohol to the carbonyl carbon atom. Loss of a proton followed by a rearrangement of the electrons gives the amide carbonyl group back, which is still bonded to the mercury ion, and also cleaves the C–N amide bond to give the ester and ...
Chem 2A Final Review
... 35. Potassium nitrate decomposes on heating, producing potassium oxide, gaseous nitrogen and gaseous oxygen. Choose the closest number of grams of KNO3 that must decompose in order to produce 1.35 g of O2 (in the original exam the chemical formula was given…but I want you to write chemical equation ...
... 35. Potassium nitrate decomposes on heating, producing potassium oxide, gaseous nitrogen and gaseous oxygen. Choose the closest number of grams of KNO3 that must decompose in order to produce 1.35 g of O2 (in the original exam the chemical formula was given…but I want you to write chemical equation ...
Preparatory Problems - American Chemical Society
... Boron-nitrogen chemistry has attracted significant attention in part because a B–N unit is isoelectronic with C–C. Furthermore, the radius of carbon and its electronegativity are roughly the average of those properties for B and N. One of the simplest boron-nitrogen compounds is H3N–BH3, the ammonia ...
... Boron-nitrogen chemistry has attracted significant attention in part because a B–N unit is isoelectronic with C–C. Furthermore, the radius of carbon and its electronegativity are roughly the average of those properties for B and N. One of the simplest boron-nitrogen compounds is H3N–BH3, the ammonia ...
A fluorophore ligase for site-specific protein labeling inside living cells
... fluorophore is removed from cells via the action of organic anionic transporters (22). We found that one AM protecting group was not sufficient for membrane permeability; however, coumarin-AM2 entered cells readily (Fig. S4A). We used the “wedge method” (see SI Methods) to measure the intracellular ...
... fluorophore is removed from cells via the action of organic anionic transporters (22). We found that one AM protecting group was not sufficient for membrane permeability; however, coumarin-AM2 entered cells readily (Fig. S4A). We used the “wedge method” (see SI Methods) to measure the intracellular ...
Stoichiometry - VernonScienceLSA
... chemical #1 is involved in a chemical reaction based on the amount of chemical #2 involved. A typical problem might be “How many grams of chemical #1 must be reacted to produce 25.0 g of chemical #2?” or “What volume of chemical #1 at STP will be produced when 15.0 g of chemical #2 is reacted?” In m ...
... chemical #1 is involved in a chemical reaction based on the amount of chemical #2 involved. A typical problem might be “How many grams of chemical #1 must be reacted to produce 25.0 g of chemical #2?” or “What volume of chemical #1 at STP will be produced when 15.0 g of chemical #2 is reacted?” In m ...
Growth of E. coli BL21 in minimal media with different
... Zhong et al. 2005; Gilsdorf et al. 2006; Lee and Keasling 2006). For many methods of protein analysis, large quantities of protein are often required and, therefore, the ability to achieve the maximum protein yield from a specific culture volume is important (Vanatalu et al. 1993; Sosa-Peinado et al ...
... Zhong et al. 2005; Gilsdorf et al. 2006; Lee and Keasling 2006). For many methods of protein analysis, large quantities of protein are often required and, therefore, the ability to achieve the maximum protein yield from a specific culture volume is important (Vanatalu et al. 1993; Sosa-Peinado et al ...
3.2 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... 100% - % mass C - % mass H = % mass O = 53.2% O (c) Assuming having 100 g of CxHyOz, there will be 40.1g C , 6.74g H, and 53.2g O. # mol of C = 40.1g C × [1 mol C / 12.01 g C] = 3.34 mol C In the same way: we get 6.67 mol H and 3.33 mol O. (d) Finding the smallest whole number ratio by dividing by 3 ...
... 100% - % mass C - % mass H = % mass O = 53.2% O (c) Assuming having 100 g of CxHyOz, there will be 40.1g C , 6.74g H, and 53.2g O. # mol of C = 40.1g C × [1 mol C / 12.01 g C] = 3.34 mol C In the same way: we get 6.67 mol H and 3.33 mol O. (d) Finding the smallest whole number ratio by dividing by 3 ...
Chemistry Standards Clarification
... Academy, in collaboration with the Michigan Mathematics and Science Center Network and the Michigan Science Teachers Association, worked in partnership with Michigan Department of Education to develop this companion document. Our goal is for each student to master the science content expectations as ...
... Academy, in collaboration with the Michigan Mathematics and Science Center Network and the Michigan Science Teachers Association, worked in partnership with Michigan Department of Education to develop this companion document. Our goal is for each student to master the science content expectations as ...
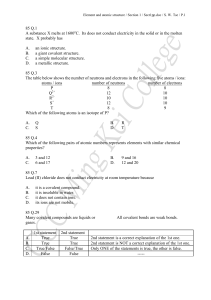
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... X Which of the following statements are correct? (1) There is one electron in the outermost shell of an atom of X. (2) There are five electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of Y. (3) There are eight electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of Z. A. C. ...
... X Which of the following statements are correct? (1) There is one electron in the outermost shell of an atom of X. (2) There are five electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of Y. (3) There are eight electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of Z. A. C. ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... (a) The left box, which represents reactants, contains two kinds of molecules, those composed of two oxygen atoms (O2) and those composed of one nitrogen atom and one oxygen atom (NO). The right box, which represents products, contains only molecules composed of one nitrogen atom and two oxygen atom ...
... (a) The left box, which represents reactants, contains two kinds of molecules, those composed of two oxygen atoms (O2) and those composed of one nitrogen atom and one oxygen atom (NO). The right box, which represents products, contains only molecules composed of one nitrogen atom and two oxygen atom ...
Stoich chem reactions practice Answer Section
... ____ 21. For the reaction 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2, how many grams of sodium hydroxide are produced from 3.0 mol of water? a. 40. g c. 120 g b. 80. g d. 240 g ____ 22. For the reaction 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl, how many grams of chlorine gas are required to react completely with 2.00 mol of sodium? a. 35.5 ...
... ____ 21. For the reaction 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2, how many grams of sodium hydroxide are produced from 3.0 mol of water? a. 40. g c. 120 g b. 80. g d. 240 g ____ 22. For the reaction 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl, how many grams of chlorine gas are required to react completely with 2.00 mol of sodium? a. 35.5 ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Molar Mass • By definition, these are the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol) – The molar mass of an element is the mass number for the element that we find on the periodic table – The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol) Stoichiometry ...
... Molar Mass • By definition, these are the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol) – The molar mass of an element is the mass number for the element that we find on the periodic table – The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol) Stoichiometry ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.