Chapter 6 Section 3
... itself and many other elements Carbon can form single, double or triple bonds—pg. 157 Carbon can form straight chains, branched chains or rings ...
... itself and many other elements Carbon can form single, double or triple bonds—pg. 157 Carbon can form straight chains, branched chains or rings ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... 1. Gamma rays () are high-energy electromagnetic waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state 2. Gamma rays are produced when nuclear particles undergo transitions in energy levels ...
... 1. Gamma rays () are high-energy electromagnetic waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state 2. Gamma rays are produced when nuclear particles undergo transitions in energy levels ...
Building an Atom
... Building an Atom For this extra credit project you must build a 3D model of the atom Sulfur- 33. You can use whatever type of supplies you can think of, as long as it looks semi-professional. (Sloppy or incorrect models will receive little to no credit, don’t waste your time). Your model of the atom ...
... Building an Atom For this extra credit project you must build a 3D model of the atom Sulfur- 33. You can use whatever type of supplies you can think of, as long as it looks semi-professional. (Sloppy or incorrect models will receive little to no credit, don’t waste your time). Your model of the atom ...
Review Packet
... The energy of the level ___________________ as the distance from the nucleus increases, and electrons fill the energy levels from the inside out, or from ____________ to _____________ energy. Atoms can be found in the ground state or the excited state. A _______________ state atom will fill the firs ...
... The energy of the level ___________________ as the distance from the nucleus increases, and electrons fill the energy levels from the inside out, or from ____________ to _____________ energy. Atoms can be found in the ground state or the excited state. A _______________ state atom will fill the firs ...
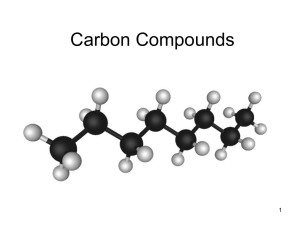
Carbon Compounds
... covalent bonds with many elements including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen. ...
... covalent bonds with many elements including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen. ...
unit plan template
... PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity, mass, volume, and reactivity). PS-2.2 Illustrate the fact that the atoms of elements exist ...
... PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity, mass, volume, and reactivity). PS-2.2 Illustrate the fact that the atoms of elements exist ...
Atoms and Moles
... • All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms that cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed.* • Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. * • Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. • Atoms ...
... • All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms that cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed.* • Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. * • Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. • Atoms ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 1 Outline – 2012-2013
... Chm 1.1.4 Explain the process of radioactive decay using nuclear equations an half life Topics Covered in this Unit ...
... Chm 1.1.4 Explain the process of radioactive decay using nuclear equations an half life Topics Covered in this Unit ...
GCSE Radiation - Bishopston Comprehensive School Moodle
... Each time a Uranium atom splits up it spits out 2 or 3 neutrons, one of which hits another uranium nucleus, causing it to split. This keeps the chain reaction going. ...
... Each time a Uranium atom splits up it spits out 2 or 3 neutrons, one of which hits another uranium nucleus, causing it to split. This keeps the chain reaction going. ...
Chapter 3 Lecture
... cohesion- attractive force between two particles that are the same adhesion- attractive force between two unlike substances capillarity- upward movement of water molecules through narrow tubes ...
... cohesion- attractive force between two particles that are the same adhesion- attractive force between two unlike substances capillarity- upward movement of water molecules through narrow tubes ...
Exemplar exam question – Chapter 2
... The first answer is probably worthy of only 1 mark as it does not make clear that isotopes are different atoms of the same element. The second answer would probably score 0. Although the idea of the same element and different number of neutrons is mentioned, the student has not mentioned different a ...
... The first answer is probably worthy of only 1 mark as it does not make clear that isotopes are different atoms of the same element. The second answer would probably score 0. Although the idea of the same element and different number of neutrons is mentioned, the student has not mentioned different a ...
chapter 2 - Lisle CUSD 202
... Synthesis and Decomposition Reactions Patterns of Chemical Reactions Exchange reaction (AB + CAC + B) Involves both synthesis and decomposition reactions Switch is made between molecule parts and different molecules are ...
... Synthesis and Decomposition Reactions Patterns of Chemical Reactions Exchange reaction (AB + CAC + B) Involves both synthesis and decomposition reactions Switch is made between molecule parts and different molecules are ...
ATOMS: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF MATTER
... packed bundle of matter with a positive electric charge and bundle was called the nucleus. Composition of atomic nuclei: 1) made up of 2 kinds of particles: ____________________________ and ________________________________ 2) protons and electrons must be ___________________________________ 3) the _ ...
... packed bundle of matter with a positive electric charge and bundle was called the nucleus. Composition of atomic nuclei: 1) made up of 2 kinds of particles: ____________________________ and ________________________________ 2) protons and electrons must be ___________________________________ 3) the _ ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... Elements consist of tiny particles called atoms, which are the smallest part of an element that displays the properties of that element. Atoms are made up of positively charged protons, uncharged neutrons, and negatively charged electrons. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons. Thi ...
... Elements consist of tiny particles called atoms, which are the smallest part of an element that displays the properties of that element. Atoms are made up of positively charged protons, uncharged neutrons, and negatively charged electrons. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons. Thi ...
Chemical Changes in Matter Worksheet
... 1. Two atoms of solid lithium react with two molecules of liquid water to produce two units of aqueous lithium hydroxide and one molecule of hydrogen gas. ...
... 1. Two atoms of solid lithium react with two molecules of liquid water to produce two units of aqueous lithium hydroxide and one molecule of hydrogen gas. ...
the Atom
... sizes or materials, but they're all just little solid balls. And when they form molecules or solids, they fit together just like a stack of marbles would ...
... sizes or materials, but they're all just little solid balls. And when they form molecules or solids, they fit together just like a stack of marbles would ...
Atomic mass - cloudfront.net
... The meaning of the terms "atom" and "element" can be confusing because they are often used as if they are the same thing. They are related to one another but they are not the same. An atom is the smallest particle or "building block" of a substance. An element is a substance made up of all the same ...
... The meaning of the terms "atom" and "element" can be confusing because they are often used as if they are the same thing. They are related to one another but they are not the same. An atom is the smallest particle or "building block" of a substance. An element is a substance made up of all the same ...
Canyon High School Chemistry
... 37. Define Transmutation; by what two ways can nuclear transmutation occur? 38. Write the balanced nuclear equation for the union of an alpha particle with a nitrogen-14 atom to produce a proton and one other atom. 39. Compare and contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. 40. What is the most com ...
... 37. Define Transmutation; by what two ways can nuclear transmutation occur? 38. Write the balanced nuclear equation for the union of an alpha particle with a nitrogen-14 atom to produce a proton and one other atom. 39. Compare and contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. 40. What is the most com ...
CH4
... PERIODIC TABLE: Is an arrangement of elements organized in groups or rows with respect to similar traits shared by different elements. Groups – Or families, are vertical columns of elements that have similar chemical and physical properties Periods – There are 7 horizontal rows known as periods in ...
... PERIODIC TABLE: Is an arrangement of elements organized in groups or rows with respect to similar traits shared by different elements. Groups – Or families, are vertical columns of elements that have similar chemical and physical properties Periods – There are 7 horizontal rows known as periods in ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
... Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
... Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
The Atom
... Conclusions from Experiment: 1. Rays cast shadow on other end of tube- light 2. Rays push paddle along- some form of matter 3. Rays deflected by magnet- not light 4. Rays deflected by negative charge- therefore cathode rays are made up of negatively charged particles called electrons. ...
... Conclusions from Experiment: 1. Rays cast shadow on other end of tube- light 2. Rays push paddle along- some form of matter 3. Rays deflected by magnet- not light 4. Rays deflected by negative charge- therefore cathode rays are made up of negatively charged particles called electrons. ...
The ingredients of life. - Waterford Public Schools
... Organic compounds all contain… carbon! Carbon is special. It’s atomic properties cause it to easily bond with lots of other atoms and molecules. Carbon atoms love to form strong bonds to other carbon atoms, creating chains and rings. ...
... Organic compounds all contain… carbon! Carbon is special. It’s atomic properties cause it to easily bond with lots of other atoms and molecules. Carbon atoms love to form strong bonds to other carbon atoms, creating chains and rings. ...
All you need to know about Additional Science
... relative atomic mass is therefore calculated using the equation: • (% of isotope 1 × mass of isotope 1) + (% of isotope 2 × mass of isotope 2) ÷ 100 So in the case of chlorine: ...
... relative atomic mass is therefore calculated using the equation: • (% of isotope 1 × mass of isotope 1) + (% of isotope 2 × mass of isotope 2) ÷ 100 So in the case of chlorine: ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.