Here`s - Sonlight
... want to measure something short, we use the inch unit, which is equal to one-twelfth of a foot. On the other hand, if we want to measure something with small volume, we might use the quart unit, which is equal to one-fourth of a gallon. In the English system, every alternative unit has a different r ...
... want to measure something short, we use the inch unit, which is equal to one-twelfth of a foot. On the other hand, if we want to measure something with small volume, we might use the quart unit, which is equal to one-fourth of a gallon. In the English system, every alternative unit has a different r ...
Tests
... Chemistry is the study of the ________________ of matter and the __________ that matter undergoes. Matter is anything that has ___________ and takes up space. A _______________ would study the structure of the hemoglobin molecule and how it transports oxygen. An organic chemistry works mainly with _ ...
... Chemistry is the study of the ________________ of matter and the __________ that matter undergoes. Matter is anything that has ___________ and takes up space. A _______________ would study the structure of the hemoglobin molecule and how it transports oxygen. An organic chemistry works mainly with _ ...
Ammonia destruction in the reaction furnace
... SWS acid gas Amine acid gas burner at the front of the first reaction chamber. These are ...
... SWS acid gas Amine acid gas burner at the front of the first reaction chamber. These are ...
Heat Effects - Association of Chemical Engineering Students
... Heat effects discussed so far have been for physical processes. Chemical reactions also are accompanied either by the transfer of heat or by temperature changes during the course of reaction-in some cases by both. These effects are manifestations of the differences in molecular structure, and theref ...
... Heat effects discussed so far have been for physical processes. Chemical reactions also are accompanied either by the transfer of heat or by temperature changes during the course of reaction-in some cases by both. These effects are manifestations of the differences in molecular structure, and theref ...
Chemistry Standards Clarification
... expected to know and be able to do by the end of high school and outline the parameters for receiving high school credit as recently mandated by the Merit Curriculum legislation in the state of Michigan. The Science Content Expectations Documents and the Michigan Merit Curriculum Document have raise ...
... expected to know and be able to do by the end of high school and outline the parameters for receiving high school credit as recently mandated by the Merit Curriculum legislation in the state of Michigan. The Science Content Expectations Documents and the Michigan Merit Curriculum Document have raise ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
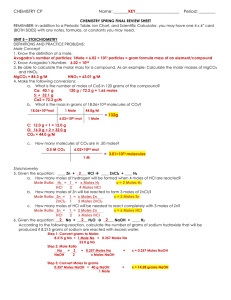
... • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
... • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
5 organic chemistry: functional groups
... Root beer hasn’t tasted the same since the use of sassafras oil as a food additive was outlawed because sassafras oil is 80% safrole, which has been shown to cause cancer in rats and mice. Identify the functional groups in the structure of safrole. OOCH2 i O Safrole ...
... Root beer hasn’t tasted the same since the use of sassafras oil as a food additive was outlawed because sassafras oil is 80% safrole, which has been shown to cause cancer in rats and mice. Identify the functional groups in the structure of safrole. OOCH2 i O Safrole ...
View/Open
... Thus if ∆V be the change in volume in case of a reaction at constant temperature and pressure, the thermal effect observed will be the sum of the change in internal energy (∆E) and the work done in expansion or contraction. That is, ∆Η = ∆E + P × ∆V Therefore, while the heat change in a process is e ...
... Thus if ∆V be the change in volume in case of a reaction at constant temperature and pressure, the thermal effect observed will be the sum of the change in internal energy (∆E) and the work done in expansion or contraction. That is, ∆Η = ∆E + P × ∆V Therefore, while the heat change in a process is e ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... compounds that dissolve in a solvent are said to be soluble, while those that do not are said to be insoluble NaCl is soluble in water, AgCl is insoluble in water the degree of solubility depends on the temperature even insoluble compounds dissolve, just not enough to be ...
... compounds that dissolve in a solvent are said to be soluble, while those that do not are said to be insoluble NaCl is soluble in water, AgCl is insoluble in water the degree of solubility depends on the temperature even insoluble compounds dissolve, just not enough to be ...
AS/A level
... Further evidence for this model comes from successive ionisation energies. Explain how these provide evidence for aspects of the model described. Sketch the expected pattern of successive ionisation energies for an atom of aluminium and use it to illustrate your answer. ...
... Further evidence for this model comes from successive ionisation energies. Explain how these provide evidence for aspects of the model described. Sketch the expected pattern of successive ionisation energies for an atom of aluminium and use it to illustrate your answer. ...
Multiple Choice
... Covalent network and molecular substances are nonconduction in all states, but C.N. has a high melting pt. Lowest melting point would be for non-polar molecule with the lowest MM (weakest dispersion forces). +H because bonds are broken; +S because liquid is more disordered; -V because water is mo ...
... Covalent network and molecular substances are nonconduction in all states, but C.N. has a high melting pt. Lowest melting point would be for non-polar molecule with the lowest MM (weakest dispersion forces). +H because bonds are broken; +S because liquid is more disordered; -V because water is mo ...
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
... 6. The equilibrium constant always has the same value at a given temperature regardless of the amounts of reactants that are mixed together initially. 7. But, the equilibrium concentrations _______________ always be the same. ...
... 6. The equilibrium constant always has the same value at a given temperature regardless of the amounts of reactants that are mixed together initially. 7. But, the equilibrium concentrations _______________ always be the same. ...
WORD - SSS Chemistry
... ___________________________ devised the Scattering Experiment, which showed that all atoms had a small dense __________________________. ...
... ___________________________ devised the Scattering Experiment, which showed that all atoms had a small dense __________________________. ...
Chemical reaction
... g. Placement of symbol for heat or catalyst over arrow Balancing the chemical reaction a. Importance of expressing all components correctly ...
... g. Placement of symbol for heat or catalyst over arrow Balancing the chemical reaction a. Importance of expressing all components correctly ...
Solutions - ChemConnections
... Ka for HF is less than one, while the other hydrogen halide acids have Ka > 1. In terms of ∆GE, HF must have a positive ∆G orxn value, while the other HX acids have ∆G°rxn < 0. The reason for the sign change in the Ka value, between HF versus HCl, HBr, and HI is entropy. ∆S for the dissociation of H ...
... Ka for HF is less than one, while the other hydrogen halide acids have Ka > 1. In terms of ∆GE, HF must have a positive ∆G orxn value, while the other HX acids have ∆G°rxn < 0. The reason for the sign change in the Ka value, between HF versus HCl, HBr, and HI is entropy. ∆S for the dissociation of H ...
Option C Energy - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... Energy is always transferred in the direction in which it goes from a more concentrated form to a less concentrated (more dispersed) form. The first law of thermodynamics simply states that energy is conserved – but if energy was transferred without any degradation we would have the basis of a perpe ...
... Energy is always transferred in the direction in which it goes from a more concentrated form to a less concentrated (more dispersed) form. The first law of thermodynamics simply states that energy is conserved – but if energy was transferred without any degradation we would have the basis of a perpe ...
5. Coenzyme HAD+ is derived
... It is necessary to equip students with knowledge that can be used when considering the physical and chemical nature and mechanisms of the processes occurring in the human body at the molecular and cellular levels and to perform when necessary calculations of these processes. An important task of opt ...
... It is necessary to equip students with knowledge that can be used when considering the physical and chemical nature and mechanisms of the processes occurring in the human body at the molecular and cellular levels and to perform when necessary calculations of these processes. An important task of opt ...
Chapter 12
... What if we had 3 moles of oxygen, how much hydrogen would we need to react and how much water would we ...
... What if we had 3 moles of oxygen, how much hydrogen would we need to react and how much water would we ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.