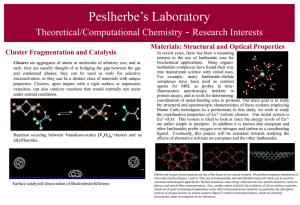
Chemistry I Final Review
... 52. How many grams of potassium bromide should be added to water to prepare 0.50 L of solution with a molarity of 0.125 M? ...
... 52. How many grams of potassium bromide should be added to water to prepare 0.50 L of solution with a molarity of 0.125 M? ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review
... 9. Will a precipitate form if sodium chloride is mixed with barium hydroxide? If so, what’s the ppt? Use the ppt chart in back of lab manual or on p. 860 fo your textbook. 10. Will a precipitate form if silver nitrate is mixed with calcium iodide? 11. Define: saturated, unsaturated, supersaturated a ...
... 9. Will a precipitate form if sodium chloride is mixed with barium hydroxide? If so, what’s the ppt? Use the ppt chart in back of lab manual or on p. 860 fo your textbook. 10. Will a precipitate form if silver nitrate is mixed with calcium iodide? 11. Define: saturated, unsaturated, supersaturated a ...
Exam practice answers
... reduced by increasing the supply of oxygen to ensure that CO2 is always produced . (There are 2 marks for the errors and 1 mark for either improvement.) Students often criticise apparatus without carefully considering the error. Given that the temperature rise was approximately 50C, if the thermome ...
... reduced by increasing the supply of oxygen to ensure that CO2 is always produced . (There are 2 marks for the errors and 1 mark for either improvement.) Students often criticise apparatus without carefully considering the error. Given that the temperature rise was approximately 50C, if the thermome ...
energy and rates practice test answers
... If for the reaction aX + bY products, the rate law is determined to be , r= [X]1[Y]0then the order of the reaction is 0 increasing the concentration of Y will have no effect on the rate increasing the concentration of X will have no effect on the rate increasing the concentration of Y will increas ...
... If for the reaction aX + bY products, the rate law is determined to be , r= [X]1[Y]0then the order of the reaction is 0 increasing the concentration of Y will have no effect on the rate increasing the concentration of X will have no effect on the rate increasing the concentration of Y will increas ...
KEY CONCEPT Enzymes are catalysts for chemical
... Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. • Enzymes are catalysts in living things. ...
... Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. • Enzymes are catalysts in living things. ...
7th Grade
... surroundings. This is an endothermic reaction. The temperature of the solution falls to about 35 F for 10 to 15 minutes. ...
... surroundings. This is an endothermic reaction. The temperature of the solution falls to about 35 F for 10 to 15 minutes. ...
snc 2do unit: chemistry unit test review questions
... G) copper (II) sulphide H) aluminum sulphate I) silicon dioxide J) phosphorus pentachloride 3. What do the elements in the same group all have in common? 4. Aluminum and oxygen react to form a compound. a) What is the name of the compound formed? b) What is the formula of the compound? c) What type ...
... G) copper (II) sulphide H) aluminum sulphate I) silicon dioxide J) phosphorus pentachloride 3. What do the elements in the same group all have in common? 4. Aluminum and oxygen react to form a compound. a) What is the name of the compound formed? b) What is the formula of the compound? c) What type ...
chemistry important question i
... Shanti, a domestic helper of Mrs. Anuradha, fainted while mopping the floor. Mrs. Anuradha immediately took her to the nearby hospital where she was diagnosed to be severely ‘anaemic’. The doctor prescribed an iron rich diet and multivitamins supplement to her. Mrs. Anuradha supported her financiall ...
... Shanti, a domestic helper of Mrs. Anuradha, fainted while mopping the floor. Mrs. Anuradha immediately took her to the nearby hospital where she was diagnosed to be severely ‘anaemic’. The doctor prescribed an iron rich diet and multivitamins supplement to her. Mrs. Anuradha supported her financiall ...
Chemistry 21 A - El Camino College
... 9. a) endothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ b) exothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ 10. The percentage yield is _____________________________________________________________________ __________ ...
... 9. a) endothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ b) exothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ 10. The percentage yield is _____________________________________________________________________ __________ ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized e ...
... represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized e ...
Chemical Reactions
... • The principle that during chemical reactions, the mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants, is known as the law of conservation of mass ...
... • The principle that during chemical reactions, the mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants, is known as the law of conservation of mass ...
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
Thermodynamics Test Study Guide—AP _____ 1. The entropy
... 80.0oC. The final temperature of the mixture is 75.3oC. Assuming that the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g-oC and that no heat is lost to or gained from the surroundings, what is the specific heat of copper, in cal/g-oC? 11. The combustion of 0.100 gram of ethane causes a temperature rise of 2.0 ...
... 80.0oC. The final temperature of the mixture is 75.3oC. Assuming that the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g-oC and that no heat is lost to or gained from the surroundings, what is the specific heat of copper, in cal/g-oC? 11. The combustion of 0.100 gram of ethane causes a temperature rise of 2.0 ...
chemistry 102 fall 2001 part 1
... Directions: (1) Put your name, S.I.D. number and signature on the free response part of the exam where indicated. (2) Each multiple choice question is actually 2 questions on your scanning sheet. If you are sure of an answer, put the same answer down for both questions for 5 pts. If you cannot decid ...
... Directions: (1) Put your name, S.I.D. number and signature on the free response part of the exam where indicated. (2) Each multiple choice question is actually 2 questions on your scanning sheet. If you are sure of an answer, put the same answer down for both questions for 5 pts. If you cannot decid ...
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes What is a chemical reaction?
... • Describe what enzymes “do” using the graph below: ...
... • Describe what enzymes “do” using the graph below: ...
Erik`s Chemistry: Thermochemistry - ECHS Chemistry
... ! In some textbooks H is written as a product or reactant ! The preceding is based upon the Law of Conservation of Energy (James Joule, 1818-1889, Joule also developed the First Law of Thermodynamics): energy is neither created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes. b. Quantitative ...
... ! In some textbooks H is written as a product or reactant ! The preceding is based upon the Law of Conservation of Energy (James Joule, 1818-1889, Joule also developed the First Law of Thermodynamics): energy is neither created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes. b. Quantitative ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.