Carbon Compounds
... Polymers are molecules made of many monomers. (monomer + monomer = polymer) Ex. Whole necklace ...
... Polymers are molecules made of many monomers. (monomer + monomer = polymer) Ex. Whole necklace ...
AP Biology Functional Groups of Carbon
... An Example of Thiols The most important thiol in living organisms is the amino acid cysteine (cys) ...
... An Example of Thiols The most important thiol in living organisms is the amino acid cysteine (cys) ...
Organic Notes #5 - RX`ns - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... Condensation (Dehydration)-two smaller molecules are linked to create a larger molecule. This is made possible by the removal of a hydrogen form one molecule and a hydroxide from the other which creates water. Esters are made this way by reacting a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. O RCOH carboxylic ...
... Condensation (Dehydration)-two smaller molecules are linked to create a larger molecule. This is made possible by the removal of a hydrogen form one molecule and a hydroxide from the other which creates water. Esters are made this way by reacting a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. O RCOH carboxylic ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
... 2 – Enthalpy is the heat of reaction at constant pressure 3 – The solute particles can be seperated from colloides by filtration 4 – Potential energy equals m . g . h 5 – Molarity is an intensive property. 6 – There are 3 significant figures in the number 20.031. 7 – Nonmetals react with each other ...
... 2 – Enthalpy is the heat of reaction at constant pressure 3 – The solute particles can be seperated from colloides by filtration 4 – Potential energy equals m . g . h 5 – Molarity is an intensive property. 6 – There are 3 significant figures in the number 20.031. 7 – Nonmetals react with each other ...
Review Questions
... Provide the Lewis dot structures for the following compounds. (a) SCN(b) Cl2O (c) FNO (d) NO2+ (e) NO Determine the formal charge of each of the indicated atoms (not all lone pairs are shown). (a) ...
... Provide the Lewis dot structures for the following compounds. (a) SCN(b) Cl2O (c) FNO (d) NO2+ (e) NO Determine the formal charge of each of the indicated atoms (not all lone pairs are shown). (a) ...
Honors Chemistry
... 5. What is an isotope? 6. How can the number of protons be determined? Neutrons? Electrons? 7. Determine the # of p+, no and e- in the following: oxygen-14, 356210XY34- and Astatine. 8. Draw a wave. Label the wavelength and amplitude on your drawing. 9. What are the colors that make up white light? ...
... 5. What is an isotope? 6. How can the number of protons be determined? Neutrons? Electrons? 7. Determine the # of p+, no and e- in the following: oxygen-14, 356210XY34- and Astatine. 8. Draw a wave. Label the wavelength and amplitude on your drawing. 9. What are the colors that make up white light? ...
chemistry_23 - Bonar Law Memorial
... What is the general structure of an ether and how are the alkyl groups of an ether named? The general structure of an ether is R—O—R. The alkyl groups attached to the ether linkage are named in alphabetical order and are followed by the word ether. An ether is a compound in which oxygen is bonded to ...
... What is the general structure of an ether and how are the alkyl groups of an ether named? The general structure of an ether is R—O—R. The alkyl groups attached to the ether linkage are named in alphabetical order and are followed by the word ether. An ether is a compound in which oxygen is bonded to ...
South Pasadena • Chemistry Name Period Date 3 · Organic
... o State that “saturated” means “saturated with hydrogens” and describes alkanes. State that alkenes, alkynes, and cyclic hydrocarbons are all “unsaturated.” ...
... o State that “saturated” means “saturated with hydrogens” and describes alkanes. State that alkenes, alkynes, and cyclic hydrocarbons are all “unsaturated.” ...
(3) Nitrogen-containing compounds
... (A) alkaloids, a heterocyclic ring. A ring that contains both nitrogen and carbon atoms. (B) cyanogenic glycosides, (C) nonprotein amino acids ...
... (A) alkaloids, a heterocyclic ring. A ring that contains both nitrogen and carbon atoms. (B) cyanogenic glycosides, (C) nonprotein amino acids ...
Electron Arrangement
... make acid rain. Carbon dioxide is also acidic and slightly soluble in water. Nitrogen dioxide is formed by an electrical spark in a car engine or lightning storms in air. This also contributes to acid rain. Crude oil is a mixture of compounds, mainly hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a compound which c ...
... make acid rain. Carbon dioxide is also acidic and slightly soluble in water. Nitrogen dioxide is formed by an electrical spark in a car engine or lightning storms in air. This also contributes to acid rain. Crude oil is a mixture of compounds, mainly hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a compound which c ...
Organometallic Reagents: Sources of Nucleophilic Carbon for
... The alkyl group in alkylmetals is strongly basic. Carbocations are the conjugate bases of alkanes (estimated pKa’s of about 50), and as a result are extremely basic, much more so than amines or alkoxides. Because of their basicity, carbocations are extremely sensitive to moisture or other acidic fu ...
... The alkyl group in alkylmetals is strongly basic. Carbocations are the conjugate bases of alkanes (estimated pKa’s of about 50), and as a result are extremely basic, much more so than amines or alkoxides. Because of their basicity, carbocations are extremely sensitive to moisture or other acidic fu ...
Review Worksheet
... a. Copy the two bulleted items in “Elements combine to form compounds.” b. Copy the four bulleted items in “Chemical bonds hold compounds together.” c. Copy the three bulleted items in “Substances’ properties depend on their bonds.” 2. Prepare for a vocabulary test covering definitions for those ter ...
... a. Copy the two bulleted items in “Elements combine to form compounds.” b. Copy the four bulleted items in “Chemical bonds hold compounds together.” c. Copy the three bulleted items in “Substances’ properties depend on their bonds.” 2. Prepare for a vocabulary test covering definitions for those ter ...
1. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds.
... There are six functional groups that are most important to the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. All are hydrophilic and increase the solubility of organic compounds in water. In a hydroxyl group (—OH), a hydrogen atom forms a polar covalent bo ...
... There are six functional groups that are most important to the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. All are hydrophilic and increase the solubility of organic compounds in water. In a hydroxyl group (—OH), a hydrogen atom forms a polar covalent bo ...
1305- practise exam 2
... B) Ternary ionic C) Binary molecular D) Binary acid -------12. What is the term for a single atom bearing a positive or a negative charge as the result of gaining or losing valence electrons? A) Anion B) Cation C) Monoatomic ion D) Polyatomic ion -------13. The compound Na2SO4 is classified as which ...
... B) Ternary ionic C) Binary molecular D) Binary acid -------12. What is the term for a single atom bearing a positive or a negative charge as the result of gaining or losing valence electrons? A) Anion B) Cation C) Monoatomic ion D) Polyatomic ion -------13. The compound Na2SO4 is classified as which ...
cell molecules
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
Chapter 4
... 4. Functional groups contribute to the molecular diversity of life • The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in __________________ are known as _________________. • Functional groups are __________________ that replace one or more _________________ in the carbon skeleton ...
... 4. Functional groups contribute to the molecular diversity of life • The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in __________________ are known as _________________. • Functional groups are __________________ that replace one or more _________________ in the carbon skeleton ...
The Chemicals of Life Properties of Organic Compounds • Organic
... in “ene” and use a number to specify where the double bond is located, like 1-butene A carbon chain that contains one or more triple bonds is called an alkyne and the names end in “yne”, like 2-pentyne Hydroxyl Group Consists of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom It has a high electroneg ...
... in “ene” and use a number to specify where the double bond is located, like 1-butene A carbon chain that contains one or more triple bonds is called an alkyne and the names end in “yne”, like 2-pentyne Hydroxyl Group Consists of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom It has a high electroneg ...
The Chemicals of Life Properties of Organic Compounds Organic
... Are other atoms that are covalently bonded to the carbon backbone the reactive sites are unstable due to either: a) the polar character of the bond involved b) the presence of multiple bonds Hydroxyl Group Consists of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom It has a high electronegativity, so it pu ...
... Are other atoms that are covalently bonded to the carbon backbone the reactive sites are unstable due to either: a) the polar character of the bond involved b) the presence of multiple bonds Hydroxyl Group Consists of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom It has a high electronegativity, so it pu ...
Test 12
... Key Terms and Important Stuff to Know ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic molecules must contain carbon and hydrogen Covalently bonded molecules Properties of organic compounds Most non-polar Most not soluble in water (if non-polar) Low M.P./B.P. due to weak intermolecular bonds Non-electrolytes (except organ ...
... Key Terms and Important Stuff to Know ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic molecules must contain carbon and hydrogen Covalently bonded molecules Properties of organic compounds Most non-polar Most not soluble in water (if non-polar) Low M.P./B.P. due to weak intermolecular bonds Non-electrolytes (except organ ...
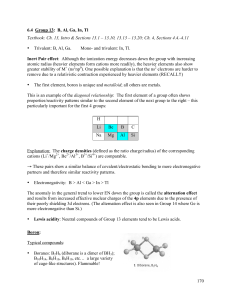
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
Carbon Compounds
... Alkynes • Hydrocarbons which have at least one triple bond between two carbons. We will always use one triple bond only. • Unsaturated • The naming prefixes are the same as for alkanes with an yne ending • The general formula is CnH2n-2 • pharmaceuticals ...
... Alkynes • Hydrocarbons which have at least one triple bond between two carbons. We will always use one triple bond only. • Unsaturated • The naming prefixes are the same as for alkanes with an yne ending • The general formula is CnH2n-2 • pharmaceuticals ...
2. Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but must be present fo ...
... catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but must be present fo ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.