Carbon and Organic Compounds
... • When the carbon in organic compounds forms only single bonds we say that the compound is saturated (can’t add anything more). • If there are double or triple bonds, these can be broken to add more atoms. In this case we say that the compound is unsaturated. ...
... • When the carbon in organic compounds forms only single bonds we say that the compound is saturated (can’t add anything more). • If there are double or triple bonds, these can be broken to add more atoms. In this case we say that the compound is unsaturated. ...
Chemistry-Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Page
... CHEMICAL BONDS continued HYDROGEN BONDS - Form weak attraction within or between polar molecules - Involves association between slightly positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
... CHEMICAL BONDS continued HYDROGEN BONDS - Form weak attraction within or between polar molecules - Involves association between slightly positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
Functional Groups - SISIBChemistry2012
... - The condensed way of writing an aldehyde is RCHO, with the O written last, not to be confused with the alcohols RCOH. - To name this functional group, count the carbons in the longest chain and replace the ‘e’ ending with ‘al’. No number is necessary, as the aldehyde will always occur on the end o ...
... - The condensed way of writing an aldehyde is RCHO, with the O written last, not to be confused with the alcohols RCOH. - To name this functional group, count the carbons in the longest chain and replace the ‘e’ ending with ‘al’. No number is necessary, as the aldehyde will always occur on the end o ...
Assignment 4 Task 1a
... have been assigned to a new case and are working as part of a team to solve the case. Working in the laboratory you will need to have a good understanding of the conventions adopted to ensure that all chemical compounds have unambiguous names. You also need to understand how a combination of element ...
... have been assigned to a new case and are working as part of a team to solve the case. Working in the laboratory you will need to have a good understanding of the conventions adopted to ensure that all chemical compounds have unambiguous names. You also need to understand how a combination of element ...
Chapter 4
... component of DNA that has been modified by addition of the methyl group. Addition of a methyl group to DNA, or to molecules bound to DNA, affects expression of genes. Arrangement of methyl groups in male and female ...
... component of DNA that has been modified by addition of the methyl group. Addition of a methyl group to DNA, or to molecules bound to DNA, affects expression of genes. Arrangement of methyl groups in male and female ...
Organic Compounds
... • Identify substances which contain organic compounds • Sketch and describe isomer structures ...
... • Identify substances which contain organic compounds • Sketch and describe isomer structures ...
Lecture #5 - Suraj @ LUMS
... Macromolecule: Large organic polymer. Most macromolecules are constructed from about 70 simple monomers. Only about 70 monomers are used by all living things on earth to construct a huge variety of molecules Structural variation of macromolecules is the basis for the enormous diversity of life on ea ...
... Macromolecule: Large organic polymer. Most macromolecules are constructed from about 70 simple monomers. Only about 70 monomers are used by all living things on earth to construct a huge variety of molecules Structural variation of macromolecules is the basis for the enormous diversity of life on ea ...
Organic
... Single bond Double bond C-C, C-N, C-S, C-O….? S-S Because S is the closest in chemical structure to C its possible their would be unique compounds with sulfur and in areas with lots of sulfur (ocean vents) their would be S-S life forms (instead of C based life forms…… Hydrogen bonding and sulfur bon ...
... Single bond Double bond C-C, C-N, C-S, C-O….? S-S Because S is the closest in chemical structure to C its possible their would be unique compounds with sulfur and in areas with lots of sulfur (ocean vents) their would be S-S life forms (instead of C based life forms…… Hydrogen bonding and sulfur bon ...
Formal Charge
... the formal charge, if any, borne by the atom. Bonds to atoms with equal electronegativity (i.e., bonds to another atom of the same element) need not be considered. Only F is more electronegative than O so NO is always –2 unless an F-O bond is present. In commonly encountered organic compounds, only ...
... the formal charge, if any, borne by the atom. Bonds to atoms with equal electronegativity (i.e., bonds to another atom of the same element) need not be considered. Only F is more electronegative than O so NO is always –2 unless an F-O bond is present. In commonly encountered organic compounds, only ...
reactions of the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones
... A curly arrow is a symbol used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of an electron pair in the braking or forming of a covalent bond ...
... A curly arrow is a symbol used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of an electron pair in the braking or forming of a covalent bond ...
Sample Exam 1 Key
... Average atomic mass is 63.5 (from periodic table). x = fraction of Cu-63; y = fraction of Cu-65. x + y = 1.0, so x = 1.0 - y x (63) + y (65) = 63.5 or 63 (1.0 – y) + 65 y = 63.5 63 – 63 y + 65 y = 63.5 or 2 y = 0.5 so y = 0.25; x = 0.75 25% Cu-65 and 75% Cu-63 2. Aluminum metal is produced from the ...
... Average atomic mass is 63.5 (from periodic table). x = fraction of Cu-63; y = fraction of Cu-65. x + y = 1.0, so x = 1.0 - y x (63) + y (65) = 63.5 or 63 (1.0 – y) + 65 y = 63.5 63 – 63 y + 65 y = 63.5 or 2 y = 0.5 so y = 0.25; x = 0.75 25% Cu-65 and 75% Cu-63 2. Aluminum metal is produced from the ...
Organic Functional Groups: Aldehydes, Ketones, Acids, Esters
... • Carbon’s ability to share more than one electron with an atom is often exploited by greedy oxygen atoms. • Oxygen will form double bonds with carbon nearly as easily as carbon does with itself. • These carbon-oxygen double bonds are called carbonyl groups. There are two types of carbonyl groups. ...
... • Carbon’s ability to share more than one electron with an atom is often exploited by greedy oxygen atoms. • Oxygen will form double bonds with carbon nearly as easily as carbon does with itself. • These carbon-oxygen double bonds are called carbonyl groups. There are two types of carbonyl groups. ...
Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]
... 1. Write the condensed structural formula of each of the following alcohols a. 1-propanol ...
... 1. Write the condensed structural formula of each of the following alcohols a. 1-propanol ...
Build a Monomer Project
... Almost all molecules made by cells are composed of carbon atoms bonded to one another and to atoms of other elements (especially H, O, N). Compounds made by cells and containing carbon are known as organic compounds. Carbon can form four covalent bonds with other carbons or other types of atoms. Cel ...
... Almost all molecules made by cells are composed of carbon atoms bonded to one another and to atoms of other elements (especially H, O, N). Compounds made by cells and containing carbon are known as organic compounds. Carbon can form four covalent bonds with other carbons or other types of atoms. Cel ...
Oxidation Number Rules
... c. Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1 except in metallic hydrides where it then has an oxidation number of -1 Examples: HCl, hydrogen is +1; NaH, hydrogen is -1. d. The halogens, unless bonded to an element with a higher electronegativity, have an oxidation number of -1. Examples: NaCl, ...
... c. Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1 except in metallic hydrides where it then has an oxidation number of -1 Examples: HCl, hydrogen is +1; NaH, hydrogen is -1. d. The halogens, unless bonded to an element with a higher electronegativity, have an oxidation number of -1. Examples: NaCl, ...
Number of carbons
... • Poly means “many” • So it’s a large molecule made up of a series of “ethenes” (C2H4) • Plastic in soda bottles, etc. made of long noodle-like chains of these units. ...
... • Poly means “many” • So it’s a large molecule made up of a series of “ethenes” (C2H4) • Plastic in soda bottles, etc. made of long noodle-like chains of these units. ...
Biochemistry: Part 2
... 90 naturally occurring elements on Earth’s crust 11 are common to living organisms 20 found in trace amounts 4 elements make up approximately 96.3% of the total weight of the human body: nitrogen carbon oxygen hydrogen In varying combinations and amounts, these four elements make up mostly a ...
... 90 naturally occurring elements on Earth’s crust 11 are common to living organisms 20 found in trace amounts 4 elements make up approximately 96.3% of the total weight of the human body: nitrogen carbon oxygen hydrogen In varying combinations and amounts, these four elements make up mostly a ...
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section
... Directed Reading B Section: Ionic and Covalent Compounds _____ 1. What is a chemical bond? a. the outermost energy level of an atom b. the interaction that holds atoms and ions together c. a repeating three-dimensional pattern d. a positively charged ion _____ 2. What are the electrons found in the ...
... Directed Reading B Section: Ionic and Covalent Compounds _____ 1. What is a chemical bond? a. the outermost energy level of an atom b. the interaction that holds atoms and ions together c. a repeating three-dimensional pattern d. a positively charged ion _____ 2. What are the electrons found in the ...
Powerpoint File - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... on its carbon skeleton, but also on certain groups of atoms that are covalently linked to the skeleton. These groups of atoms are called functional groups, the name reflecting the fact that these parts of the organic molecules usually are involved in chemical reactions. See Table 4.1 in Campbell and ...
... on its carbon skeleton, but also on certain groups of atoms that are covalently linked to the skeleton. These groups of atoms are called functional groups, the name reflecting the fact that these parts of the organic molecules usually are involved in chemical reactions. See Table 4.1 in Campbell and ...
CHM121 Exam I Review
... factors, periodic table (periods/groups), chemical formula, balancing equations, nomenclature, molecular/formula weight, percent composition (mass percent), stoichiometry. Be able to define the following terms: states of matter, element, compound, ionic vs. molecular compounds, atom, atomic symbol, ...
... factors, periodic table (periods/groups), chemical formula, balancing equations, nomenclature, molecular/formula weight, percent composition (mass percent), stoichiometry. Be able to define the following terms: states of matter, element, compound, ionic vs. molecular compounds, atom, atomic symbol, ...
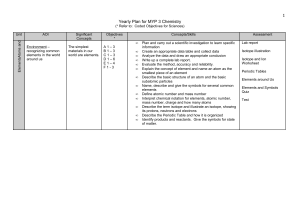
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... Describe ions and what subatomic particles they have Name and give the formulas for some common compound ions Write the formula for simple compounds that include compound ions from their names Name simple compounds that include compound ions from their formulas Define and describe ionic and covalent ...
... Describe ions and what subatomic particles they have Name and give the formulas for some common compound ions Write the formula for simple compounds that include compound ions from their names Name simple compounds that include compound ions from their formulas Define and describe ionic and covalent ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.














![Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010780770_1-3445600a9b56e890a0f283c789afe8fb-300x300.png)