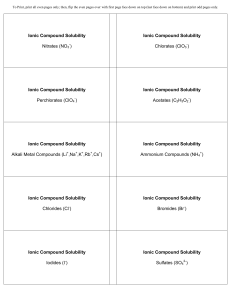
Ionic Compound Solubility Nitrates (NO3 ) Ionic Compound
... Definition A substance that is able to donate a H+ ion (a proton) and, hence, increases the concentration of H+(aq) when it dissolves in water. ...
... Definition A substance that is able to donate a H+ ion (a proton) and, hence, increases the concentration of H+(aq) when it dissolves in water. ...
ADSORPTION OF MOLECULES OF BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE AT
... bands in the SNIFTIRS s p e c t m indicates that the DMPC bilayer displays a tail-to-tail configuration with the polar heads t m e d towards the electrode surface. The peak positions of h t h CH2 stretching and C=O stretching bands show Little variation with the electrode potentials although their i ...
... bands in the SNIFTIRS s p e c t m indicates that the DMPC bilayer displays a tail-to-tail configuration with the polar heads t m e d towards the electrode surface. The peak positions of h t h CH2 stretching and C=O stretching bands show Little variation with the electrode potentials although their i ...
(K c ) [A] - Knockhardy
... CALCULATIONS INVOLVING Kc • construct the balanced equation, including state symbols (aq), (g) etc. • determine the number of moles of each species at equilibrium • divide moles by volume (in dm3) to get the equilibrium concentrations in mol dm-3 (If no volume is quoted, use a V; it will probably c ...
... CALCULATIONS INVOLVING Kc • construct the balanced equation, including state symbols (aq), (g) etc. • determine the number of moles of each species at equilibrium • divide moles by volume (in dm3) to get the equilibrium concentrations in mol dm-3 (If no volume is quoted, use a V; it will probably c ...
CHAPTER 12 Study Guide
... your students can go online to access an interactive version of the Student Edition and a self-test. with ChemASAP ...
... your students can go online to access an interactive version of the Student Edition and a self-test. with ChemASAP ...
Type - Enrico Fermi High
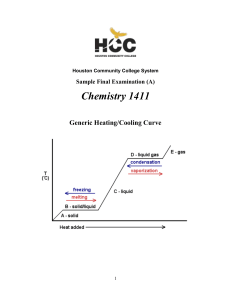
... Describe the behavior of the molecules in a liquid. Explain this behavior in terms of intermolecular forces. In a liquid, the molecules can move relatively freely, the intermolecular forces keep them close, but not locked in place. As the intermolecular forces get stronger the molecules are less fre ...
... Describe the behavior of the molecules in a liquid. Explain this behavior in terms of intermolecular forces. In a liquid, the molecules can move relatively freely, the intermolecular forces keep them close, but not locked in place. As the intermolecular forces get stronger the molecules are less fre ...
Scientific Jury of the 30th International
... electron density diagrams coordination number unit cell structures of: - NaCl - CsCl - close-packed (2 types) determining of the Avogadro constant from X-ray data ...
... electron density diagrams coordination number unit cell structures of: - NaCl - CsCl - close-packed (2 types) determining of the Avogadro constant from X-ray data ...
High temperature semiconductor sensor for the detection of fluorine
... molecules before the concentration step (state I), [F2]II is the fluorine concentration after the concentration step (state II). Substituting Eq. (6) into Eq. (7) we get: D[F2]ads/Dt = k2([F2]II −[F2]I) ...
... molecules before the concentration step (state I), [F2]II is the fluorine concentration after the concentration step (state II). Substituting Eq. (6) into Eq. (7) we get: D[F2]ads/Dt = k2([F2]II −[F2]I) ...
formula writing and nomenclature of inorganic - Parkway C-2
... 3. Determine the oxidation number of Cu in CuSO4. Cu is an element that can have more than one oxidation state (see Tables 10.1 and 10.2). To determine the oxidation number of Cu in this compound, it is easier to use the oxidation number of the sulfate polyatomic ion instead of determining the oxida ...
... 3. Determine the oxidation number of Cu in CuSO4. Cu is an element that can have more than one oxidation state (see Tables 10.1 and 10.2). To determine the oxidation number of Cu in this compound, it is easier to use the oxidation number of the sulfate polyatomic ion instead of determining the oxida ...
LABORATORY MANUAL FOR GENERAL CHEMISTRY I
... Chemistry is an experimental science. The knowledge that has been accumulated through previous experiments provides the basis for today’s chemistry courses. The information now being gathered will form the basis of future courses. There are basically two types of experiments that chemists conduct: 1 ...
... Chemistry is an experimental science. The knowledge that has been accumulated through previous experiments provides the basis for today’s chemistry courses. The information now being gathered will form the basis of future courses. There are basically two types of experiments that chemists conduct: 1 ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.


![(K c ) [A] - Knockhardy](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011755527_1-914ea907d1ff7656ef398ad87316c94c-300x300.png)