Chemical reactions and equations
... Reactions start with Reactants on the left side of the equation. Reactions end with Products on the right side of the equation. An arrow in between the Reactants and Products is called the Yield sign and acts almost like an equal (=) sign in math. ...
... Reactions start with Reactants on the left side of the equation. Reactions end with Products on the right side of the equation. An arrow in between the Reactants and Products is called the Yield sign and acts almost like an equal (=) sign in math. ...
Intermolecular Forces Practice Problems
... What holds two fluorine molecules together in a sample of liquid fluorine? ...
... What holds two fluorine molecules together in a sample of liquid fluorine? ...
Ksp - ChemConnections
... Visualizing the Common Ion Effect • The solubility of a partially soluble salt is decreased when a common ion is added. • Consider the equilibrium established when acetic acid, HC2H3O2, is added to water. • At equilibrium H+ and C2H3O2- are constantly moving into and out of solution, but the co ...
... Visualizing the Common Ion Effect • The solubility of a partially soluble salt is decreased when a common ion is added. • Consider the equilibrium established when acetic acid, HC2H3O2, is added to water. • At equilibrium H+ and C2H3O2- are constantly moving into and out of solution, but the co ...
Resource for Final Exam Prep
... there should be at least one lone pair of electrons in F, O or N) Stronger the intermolecular forces high melting point, high boiling point, high viscosity, high surface tension, low vapor pressure During phase changes (such as melting, boiling, vaporization), one need to overcome these intermolec ...
... there should be at least one lone pair of electrons in F, O or N) Stronger the intermolecular forces high melting point, high boiling point, high viscosity, high surface tension, low vapor pressure During phase changes (such as melting, boiling, vaporization), one need to overcome these intermolec ...
Unit 2 (Biochemistry) Review
... This is only a brief review of the topics that we have covered within this unit. You should also use your notes, homework sheets, labs, and notebooks as a means of review. I have tried to post all of the material covered in class on the classroom webpage. *You will be allowed to construct and use on ...
... This is only a brief review of the topics that we have covered within this unit. You should also use your notes, homework sheets, labs, and notebooks as a means of review. I have tried to post all of the material covered in class on the classroom webpage. *You will be allowed to construct and use on ...
2011 Exam 2 Key
... Therefore, mass of C8H18 left un-reacted = 10.0 – 2.85 = 7.2 g (2 Sig Fig) d) (3 pts) If 6.55 g of CO2 are actually made in the laboratory under the above conditions, determine the ...
... Therefore, mass of C8H18 left un-reacted = 10.0 – 2.85 = 7.2 g (2 Sig Fig) d) (3 pts) If 6.55 g of CO2 are actually made in the laboratory under the above conditions, determine the ...
Qualitative Analysis of Anions
... Test for Chloride ion, Cl . To a 2 mL portion of the test solution (known or unknown) add a few drops of 6 M HNO3 as needed to make the solution slightly acidic (Test with litmus paper). If you sample contains sulfide, it must be removed by boiling the solution a moment. The free sulfur formed does ...
... Test for Chloride ion, Cl . To a 2 mL portion of the test solution (known or unknown) add a few drops of 6 M HNO3 as needed to make the solution slightly acidic (Test with litmus paper). If you sample contains sulfide, it must be removed by boiling the solution a moment. The free sulfur formed does ...
The Concept of Conductivity and Molar Conductivity of an Aqueous
... In fact, these two processes could be identical if the numerical values of a and b are both equal to unity. As a result, the term degree of dissociation can also be given to the strong electrolyte in such a state, in order to indicate how free the ions are. Since we still consider strong electrolyt ...
... In fact, these two processes could be identical if the numerical values of a and b are both equal to unity. As a result, the term degree of dissociation can also be given to the strong electrolyte in such a state, in order to indicate how free the ions are. Since we still consider strong electrolyt ...
EXAM REVIEW !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! The examination is scheduled
... pure substance is (G/n)p,T and for a perfect gas = o + RT ln(p/po) how does this change for a real gas. In general = o + RT ln a where a is the activity. For ideal gas a = p/po. For real gas a = f/po. What is the fugacity coefficient? What is the activity coefficient? Be able to calculate th ...
... pure substance is (G/n)p,T and for a perfect gas = o + RT ln(p/po) how does this change for a real gas. In general = o + RT ln a where a is the activity. For ideal gas a = p/po. For real gas a = f/po. What is the fugacity coefficient? What is the activity coefficient? Be able to calculate th ...
Final Exam
... name at the top of each page now. A seventh page contains a periodic chart and other information you may need. You may tear this sheet off and use it for scratch paper. Show your work on calculations, be sure to include units in the calculations, and give answers to the correct number of significant ...
... name at the top of each page now. A seventh page contains a periodic chart and other information you may need. You may tear this sheet off and use it for scratch paper. Show your work on calculations, be sure to include units in the calculations, and give answers to the correct number of significant ...
(1) Dissolves, accompanied by evolution of flammable gas (2
... For each of the following, use appropriate chemical principles to explain the observation. (a) Sodium chloride may be spread on an icy sidewalk, in order to melt the ice; equimolar amounts of calcium chloride are even more effective. (b) At room temperature, NH3 is a gas and H2O is a liquid, even th ...
... For each of the following, use appropriate chemical principles to explain the observation. (a) Sodium chloride may be spread on an icy sidewalk, in order to melt the ice; equimolar amounts of calcium chloride are even more effective. (b) At room temperature, NH3 is a gas and H2O is a liquid, even th ...
HF Manual
... notes and have agreed to abide by the recommendations, protocols and prohibitions contained herein. Your research supervisor must be aware that you are engaged in such work, and other occupants of the laboratory should also be informed. The protocols outlined in this manual constitute a COSHH assess ...
... notes and have agreed to abide by the recommendations, protocols and prohibitions contained herein. Your research supervisor must be aware that you are engaged in such work, and other occupants of the laboratory should also be informed. The protocols outlined in this manual constitute a COSHH assess ...
Preface from the Textbook - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... most of the boxed application material, thus letting instructors choose applications tailored for their course. Moreover, several topics that are important areas of research but not central to general chemistry were left out, including colloids, polymers, liquid crystals, and so forth. And mainstrea ...
... most of the boxed application material, thus letting instructors choose applications tailored for their course. Moreover, several topics that are important areas of research but not central to general chemistry were left out, including colloids, polymers, liquid crystals, and so forth. And mainstrea ...
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
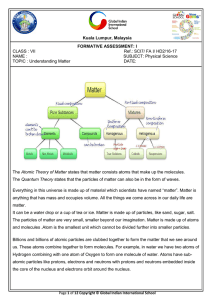
... without them - recognizing common chemical reactions in our world - understanding what happens in a chemical change - noticing and identifying common chemicals we use in our everyday lives ...
... without them - recognizing common chemical reactions in our world - understanding what happens in a chemical change - noticing and identifying common chemicals we use in our everyday lives ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... Name the first 5 PREFIXES that we use to name molecular compounds. mono à one di à two tri à three tetra à four penta à five We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their ...
... Name the first 5 PREFIXES that we use to name molecular compounds. mono à one di à two tri à three tetra à four penta à five We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their ...
QualGroupD
... Magnesium hydroxide will precipitate in aqueous ammonia, however the precipitate can be prevented from forming if the solution contains a significant concentration of NH4+. This can be understood by considering the common ion effect and the following equilibrium: NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq ...
... Magnesium hydroxide will precipitate in aqueous ammonia, however the precipitate can be prevented from forming if the solution contains a significant concentration of NH4+. This can be understood by considering the common ion effect and the following equilibrium: NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq ...
Types of Solutions
... point where you cannot dissolve any more sugar. • This is called saturated solution. • However, if you heat this solution, more sugar will dissolve • When the solution is cooled, the sugar will remain in solution • This is called a supersaturated solution. ...
... point where you cannot dissolve any more sugar. • This is called saturated solution. • However, if you heat this solution, more sugar will dissolve • When the solution is cooled, the sugar will remain in solution • This is called a supersaturated solution. ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.