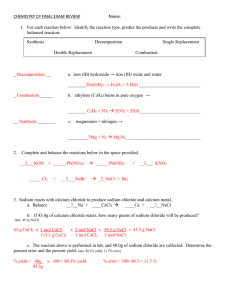
Equilibrium
... Often reactions are written with only ions that are actually involved in the reaction. This is why the nitrate and potassium ions have been left off of the equation. These ions that are left off the equation are called spectator ions. Write this equation and below each chemical list the solution col ...
... Often reactions are written with only ions that are actually involved in the reaction. This is why the nitrate and potassium ions have been left off of the equation. These ions that are left off the equation are called spectator ions. Write this equation and below each chemical list the solution col ...
Chemicals: What`s in? What`s out?
... The following chemicals can be considered for use in handson middle school science programs. However, the teacher should review the character of each chemical or compound by consulting the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet. Appropriate precautions, such as PPE and ventilation, are an absolute m ...
... The following chemicals can be considered for use in handson middle school science programs. However, the teacher should review the character of each chemical or compound by consulting the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet. Appropriate precautions, such as PPE and ventilation, are an absolute m ...
Bubbstons: stable microscopic gas bubbles in very dilute electrolytic
... @ 1992 American Institute of Physics ...
... @ 1992 American Institute of Physics ...
Single crystal structure determination using synchrotron X
... bidentate ligands (L). Typically, square planar coordinative Pd (II) ions and bidentate, organic ligands bearing two pyridyl groups as coordination sites are mixed in an organic solvent, and all the coordination bonds are formed between the Pd (II) ions and pyridyl groups to form hollow, spherical c ...
... bidentate ligands (L). Typically, square planar coordinative Pd (II) ions and bidentate, organic ligands bearing two pyridyl groups as coordination sites are mixed in an organic solvent, and all the coordination bonds are formed between the Pd (II) ions and pyridyl groups to form hollow, spherical c ...
Higher Level - State Examination Commission
... group in the periodic table. (Refer to the Mathematics Tables, p. 45.) Explain why the second ionisation energy of potassium (3070 kJ mol–1) is significantly greater than its first ionisation energy value (418 kJ mol–1). ...
... group in the periodic table. (Refer to the Mathematics Tables, p. 45.) Explain why the second ionisation energy of potassium (3070 kJ mol–1) is significantly greater than its first ionisation energy value (418 kJ mol–1). ...
lewis dot diagrams (structures) for atoms and ions predicting
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
17 - Wiley
... structures show that the phenolate anion can distribute its negative charge around the benzene ring, increasing its stability compared with that of the localized O– that results from removal of a proton from ethanol. That is why phenol is a weak acid, whereas alcohols such as ethanol are not acidic. ...
... structures show that the phenolate anion can distribute its negative charge around the benzene ring, increasing its stability compared with that of the localized O– that results from removal of a proton from ethanol. That is why phenol is a weak acid, whereas alcohols such as ethanol are not acidic. ...
Chapter 7 Review
... For the reaction CO(g) + 2 H2(g) <---> CH3OH(g) + heat; [CO(g)] = 0.025 mol/L, [H2(g) ] = 0.050 mol/L and [CH3OH(g)] = 0.0063 mol/L a) b) ...
... For the reaction CO(g) + 2 H2(g) <---> CH3OH(g) + heat; [CO(g)] = 0.025 mol/L, [H2(g) ] = 0.050 mol/L and [CH3OH(g)] = 0.0063 mol/L a) b) ...
Belarus, National Final, 2008 (PDF 405K).
... dilute sulfuric acid. The residual gas is usually released into the atmosphere. The maximum allowable concentration of SO2 in air is 0.050 mg/m3. a) Write a chemical equation representing the roasting of pyrite. b) Calculate the volume of sulfur dioxide (at 600 K and 108 kPa) generated by the oxidat ...
... dilute sulfuric acid. The residual gas is usually released into the atmosphere. The maximum allowable concentration of SO2 in air is 0.050 mg/m3. a) Write a chemical equation representing the roasting of pyrite. b) Calculate the volume of sulfur dioxide (at 600 K and 108 kPa) generated by the oxidat ...
Ksp Problem Sets 1 and 2
... Since the reactant is always a solid, there is no denominator on solubility equilibrium expressions. Assume that the denominator is always “1”. There are two basic types of Ksp problems: 1. Give the solubility (also known as the concentration of a saturated solution), find the Ksp. 2. Given the Ksp, ...
... Since the reactant is always a solid, there is no denominator on solubility equilibrium expressions. Assume that the denominator is always “1”. There are two basic types of Ksp problems: 1. Give the solubility (also known as the concentration of a saturated solution), find the Ksp. 2. Given the Ksp, ...
chemistry 2.1
... © ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd – ISBN 978-0-908340-10-1 – Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is limited to 3% under the NZ Copyright Act. ...
... © ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd – ISBN 978-0-908340-10-1 – Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is limited to 3% under the NZ Copyright Act. ...
Electric conductivity of Cu (NO ) 2∙3 Н2 О solutions in
... till 0.4 M. The further increase of copper nitrate trihydrate solution concentration in DMSO leads to gradual decrease of electric conductivity till some limiting value. At the raised concentration (above 1.4) reproducibility of measurements decreases. With increase of temperature till 318 K mobilit ...
... till 0.4 M. The further increase of copper nitrate trihydrate solution concentration in DMSO leads to gradual decrease of electric conductivity till some limiting value. At the raised concentration (above 1.4) reproducibility of measurements decreases. With increase of temperature till 318 K mobilit ...
C3 Revision Question Booklet
... Describe and give the results of an experiment which would show that citric acid is a weaker acid than hydrochloric acid of the same concentration. ...
... Describe and give the results of an experiment which would show that citric acid is a weaker acid than hydrochloric acid of the same concentration. ...
ChemFinalgeocities
... formulas for the initial and final compounds in this change. Initial: _______________; Final: _______________ The diagram, Figure 5-1, shows the way two colorless liquids with different boiling points can be separated from each other by means of distillation. Answer the following questions about thi ...
... formulas for the initial and final compounds in this change. Initial: _______________; Final: _______________ The diagram, Figure 5-1, shows the way two colorless liquids with different boiling points can be separated from each other by means of distillation. Answer the following questions about thi ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.