System International Base Units
... o Representative particles can be atoms, ions, formula units, or molecules 1 mole = molar mass of an element or compound 1 mole of any gas = 22.4 L of gas at STP o STP for gases is 101.3 kPa and 0°C ...
... o Representative particles can be atoms, ions, formula units, or molecules 1 mole = molar mass of an element or compound 1 mole of any gas = 22.4 L of gas at STP o STP for gases is 101.3 kPa and 0°C ...
AP Chemistry Summer Packet More Chapter Two and Chapter
... e. None of the above 76. When a substance that has a positive charge is brought near a substance that has a negative charge, a force of attraction occurs between them. WHen two substances with the same sign of charge are brought near each other, a repulsive force occurs. These forces are electrostat ...
... e. None of the above 76. When a substance that has a positive charge is brought near a substance that has a negative charge, a force of attraction occurs between them. WHen two substances with the same sign of charge are brought near each other, a repulsive force occurs. These forces are electrostat ...
AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam CHAPTER 8 PRACTICE
... 15. The ionization energies for element X are listed in the table above. On the basis of the data, element X is most likely to be (A) Na (C) Al (E) P (B) Mg (D) Si ANALYSIS: Ionization energy jumps 4x from the first to the second electron removed. This tells us that there is only easily removed (val ...
... 15. The ionization energies for element X are listed in the table above. On the basis of the data, element X is most likely to be (A) Na (C) Al (E) P (B) Mg (D) Si ANALYSIS: Ionization energy jumps 4x from the first to the second electron removed. This tells us that there is only easily removed (val ...
Review for Final Exam - Short Answer and Problems
... sample of limestone which has a mass of 413 mg and treats it with oxalic acid (H2C2O4). A chemical reaction occurs between the calcium carbonate and the acid producing calcium oxalate and other products. CaCO3 (s) + H2C2O4 (aq) CaC2O4 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) The mass of CaC2O4 obtained is 472 mg. ...
... sample of limestone which has a mass of 413 mg and treats it with oxalic acid (H2C2O4). A chemical reaction occurs between the calcium carbonate and the acid producing calcium oxalate and other products. CaCO3 (s) + H2C2O4 (aq) CaC2O4 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) The mass of CaC2O4 obtained is 472 mg. ...
Bal Equations notes.cwk (WP)
... These reactions are similar to single replacement reactions. The only difference is that both the metal and nonmetal will be replaced in this reaction between two compounds. Example: Magnesium hydroxide tablets are used to neutralize stomach acid (HCl). This produces water and magnesium chloride sol ...
... These reactions are similar to single replacement reactions. The only difference is that both the metal and nonmetal will be replaced in this reaction between two compounds. Example: Magnesium hydroxide tablets are used to neutralize stomach acid (HCl). This produces water and magnesium chloride sol ...
study material class X (science)
... The first step in balancing a chemical equation is to write the number of atoms of each element present on the left hand side and right hand side. ...
... The first step in balancing a chemical equation is to write the number of atoms of each element present on the left hand side and right hand side. ...
System International Base Units
... ºC + 273 = K K - 273 = ºC °F = 9/5 (°C) + 32 °C = 5/9 (°F-32) 1 cal = 4.184 J 1000 cal = 1 Cal 6.022x1023 representative particles = 1 mole o Representative particles can be atoms, ions, formula units, or molecules 1 mole = molar mass of an element or compound 1 mole of any gas = 22.4 ...
... ºC + 273 = K K - 273 = ºC °F = 9/5 (°C) + 32 °C = 5/9 (°F-32) 1 cal = 4.184 J 1000 cal = 1 Cal 6.022x1023 representative particles = 1 mole o Representative particles can be atoms, ions, formula units, or molecules 1 mole = molar mass of an element or compound 1 mole of any gas = 22.4 ...
Chapter 14…Kinetic Theory
... 7. Indicate the relationship between the variables in each of the equations above. 8. Indicate what each variable stands for in each of the equations above. 9. Temperature is in what unit for gas laws? 10. STP stands for: 11. Standard temperature = __________ 12. Standard pressure = __________ atm, ...
... 7. Indicate the relationship between the variables in each of the equations above. 8. Indicate what each variable stands for in each of the equations above. 9. Temperature is in what unit for gas laws? 10. STP stands for: 11. Standard temperature = __________ 12. Standard pressure = __________ atm, ...
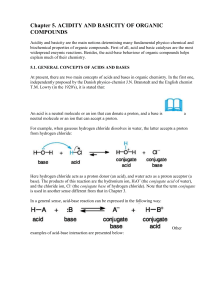
Chapter 5. ACIDITY AND BASICITY OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... Another stabilizing factor is the polarizability (opposed to polarity) of an element in the acidic site. This term means the ability of the electrons to respond to a changing electric field, as a result of its interaction with solvent or with other polar reagents. Relative polarizability increases ...
... Another stabilizing factor is the polarizability (opposed to polarity) of an element in the acidic site. This term means the ability of the electrons to respond to a changing electric field, as a result of its interaction with solvent or with other polar reagents. Relative polarizability increases ...
Question paper - Edexcel
... SECTION A Answer ALL the questions in this section. You should aim to spend no more than 20 minutes on this section. For each question, select one answer from A to D and put a cross in the box . and then mark your new answer with If you change your mind, put a line through the box a cross . 1 The r ...
... SECTION A Answer ALL the questions in this section. You should aim to spend no more than 20 minutes on this section. For each question, select one answer from A to D and put a cross in the box . and then mark your new answer with If you change your mind, put a line through the box a cross . 1 The r ...
Topic 4
... 1.) All compounds containing alkali metal cations (group I) and the ammonium ion (NH4+) are soluble. 2.) All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3.) All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag+, Pb2+, or Hg22+. 4.) All sulfates are ...
... 1.) All compounds containing alkali metal cations (group I) and the ammonium ion (NH4+) are soluble. 2.) All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3.) All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag+, Pb2+, or Hg22+. 4.) All sulfates are ...
Fundamentals Fall Final Review
... For each of the statements, identify whether it describes a solid (S), liquid (L), or gas (G). 11. Has definite volume and shape 14. When water boils it becomes this 12. Has a definite volume but no shape 15. Particles are tightly packed and neatly 13. Particles move freely is this type of matter ar ...
... For each of the statements, identify whether it describes a solid (S), liquid (L), or gas (G). 11. Has definite volume and shape 14. When water boils it becomes this 12. Has a definite volume but no shape 15. Particles are tightly packed and neatly 13. Particles move freely is this type of matter ar ...
Stoichiometry
... Incomplete – occurs when there is a limited amount of oxygen CO(g) + H2O(l) ...
... Incomplete – occurs when there is a limited amount of oxygen CO(g) + H2O(l) ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2016 revised
... 51.Write a balanced equation for the following: a.Reaction of boron trifluoride gas with water to give liquid hydrogen fluoride and solid boric ...
... 51.Write a balanced equation for the following: a.Reaction of boron trifluoride gas with water to give liquid hydrogen fluoride and solid boric ...
KEY_Reaction Types WS
... task is deciding what type of reaction is taking place. In this chapter we study three types: ...
... task is deciding what type of reaction is taking place. In this chapter we study three types: ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.






![C2_revision_slides_V3_+_questions_+_MS_-_H[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000092833_1-97fb33725e7f1ef12029ed42751d3dca-300x300.png)