Molecules and Ions
... Discussion: Are acids and bases typically ionic or molecular compounds (trick question!)? What is ‘special’ about them and their formulas? ...
... Discussion: Are acids and bases typically ionic or molecular compounds (trick question!)? What is ‘special’ about them and their formulas? ...
Molecules and Ions
... Discussion: Are acids and bases typically ionic or molecular compounds (trick question!)? What is ‘special’ about them and their formulas? ...
... Discussion: Are acids and bases typically ionic or molecular compounds (trick question!)? What is ‘special’ about them and their formulas? ...
CHEM 113 GENERAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
... A physical property is one that a sample of matter displays without changing its composition. Melting point, boiling point, density, solubility, physical state, colour, and crystal structure can be given as an example of physical properties. In physical changes, appearance of the substance changes, ...
... A physical property is one that a sample of matter displays without changing its composition. Melting point, boiling point, density, solubility, physical state, colour, and crystal structure can be given as an example of physical properties. In physical changes, appearance of the substance changes, ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... • ACCURACY refers to how closely a measured value agrees with the correct value • PRECISION refers to how closely individual measurements agree with one another. ...
... • ACCURACY refers to how closely a measured value agrees with the correct value • PRECISION refers to how closely individual measurements agree with one another. ...
File
... completely with 49.0 grams of H2O. 47. The last step in the production of nitric acid is the reaction of nitrogen dioxide with water. 3NO2 (g) + H2O (l) 2HNO3 (aq) + NO (g) How many grams of nitrogen dioxide must react with water to produce 5.00 x 1022 molecules of nitrogen monoxide? 48. How are m ...
... completely with 49.0 grams of H2O. 47. The last step in the production of nitric acid is the reaction of nitrogen dioxide with water. 3NO2 (g) + H2O (l) 2HNO3 (aq) + NO (g) How many grams of nitrogen dioxide must react with water to produce 5.00 x 1022 molecules of nitrogen monoxide? 48. How are m ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... • ACCURACY refers to how closely a measured value agrees with the correct value • PRECISION refers to how closely individual measurements agree with one another. ...
... • ACCURACY refers to how closely a measured value agrees with the correct value • PRECISION refers to how closely individual measurements agree with one another. ...
The CPA EoS, proposed by Kontogeorgis et
... association term Association equations of state like CPA and SAFT usually model alcohols using the twosite association scheme i.e. the alcohol molecules are assumed to form linear oligomers. More specifically, these theories employ the so-called “2B” scheme (notation following Huang and Radosz10), w ...
... association term Association equations of state like CPA and SAFT usually model alcohols using the twosite association scheme i.e. the alcohol molecules are assumed to form linear oligomers. More specifically, these theories employ the so-called “2B” scheme (notation following Huang and Radosz10), w ...
electrochemical processing of regeneration solutions from ion
... Figure 1. Dependence of pH in the cathodic area (1, 2), in the work area (3, 4) and alkalinity in the anodic area (5, 6) on the acidic electrolysis (C (H2SO4) = 625 mgeq/dm3, C(Na2SO4) = 324 mg -eq/dm3) (1, 3, 5) and alkalic electrolysis (C (NaOH) = 53 mg-eq/dm3, C (Na2SO4) = 423 mg-eq/dm3) (2, 4, ...
... Figure 1. Dependence of pH in the cathodic area (1, 2), in the work area (3, 4) and alkalinity in the anodic area (5, 6) on the acidic electrolysis (C (H2SO4) = 625 mgeq/dm3, C(Na2SO4) = 324 mg -eq/dm3) (1, 3, 5) and alkalic electrolysis (C (NaOH) = 53 mg-eq/dm3, C (Na2SO4) = 423 mg-eq/dm3) (2, 4, ...
2011 Chem Facts Key
... 53. Acids and bases are both good electrolytes. Their solutions conduct electricity well. Which of the following is a nonelectrolyte? LiOH, HBr, CH3COOH, C2H5OH 54. Weak acids taste sour and react with metals to produce H2. 55. Weak bases taste bitter and feel slippery. 56. Acids and bases turn indi ...
... 53. Acids and bases are both good electrolytes. Their solutions conduct electricity well. Which of the following is a nonelectrolyte? LiOH, HBr, CH3COOH, C2H5OH 54. Weak acids taste sour and react with metals to produce H2. 55. Weak bases taste bitter and feel slippery. 56. Acids and bases turn indi ...
Chemistry Section 2
... pH Scale: The pH scale is a mathematical ranking system for the acidity or basicity of aqueous solutions. The solution being ranked could be water only, water + acid, water + base, or water + base + acid. Notice, however, that water is always there. In fact, as you’ll see in the next section, the pH ...
... pH Scale: The pH scale is a mathematical ranking system for the acidity or basicity of aqueous solutions. The solution being ranked could be water only, water + acid, water + base, or water + base + acid. Notice, however, that water is always there. In fact, as you’ll see in the next section, the pH ...
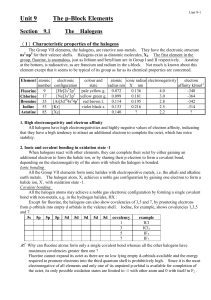
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
Chapter 8 Brønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and Bases
... Remember, liquids are not included in equilibrium expressions ...
... Remember, liquids are not included in equilibrium expressions ...
Document
... NaCl possesses the following intermolecular forces: ionic bonding and dispersion forces. Benzene possesses the following intermolecular forces: dispersion forces. Therefore, NaCl is polar and benzene is non-polar (non polar compounds are those that possess exclusively dispersion forces), and that is ...
... NaCl possesses the following intermolecular forces: ionic bonding and dispersion forces. Benzene possesses the following intermolecular forces: dispersion forces. Therefore, NaCl is polar and benzene is non-polar (non polar compounds are those that possess exclusively dispersion forces), and that is ...
Final Exam Review- no solutions
... 16. A 1.000 g sample of octane (C8H18) is burned in a bomb calorimeter containing 1200 grams of water at an initial temperature of 25.00ºC. After the reaction, the final temperature of the water is 33.20ºC. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 837 J/ºC. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g ºC. ...
... 16. A 1.000 g sample of octane (C8H18) is burned in a bomb calorimeter containing 1200 grams of water at an initial temperature of 25.00ºC. After the reaction, the final temperature of the water is 33.20ºC. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 837 J/ºC. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g ºC. ...
chem 100 class notes - Louisiana Tech University
... Faster chemical reactions occur in gas phase compared to reactions of solids and liquids. Some solids when mixed do not show a reaction. However, when they are dissolved in a solvent, an immediate reaction is usually observed. The molecules or the ions of solids are broken down to individual particl ...
... Faster chemical reactions occur in gas phase compared to reactions of solids and liquids. Some solids when mixed do not show a reaction. However, when they are dissolved in a solvent, an immediate reaction is usually observed. The molecules or the ions of solids are broken down to individual particl ...
PEA: Chemistry: Mole City Worksheet
... More Mole City 4. How many grams of the aqueous product would be formed in double replacement reaction when 10.0 grams of aqueous barium chloride is reacted with an excess amount of aqueous silver nitrate. ...
... More Mole City 4. How many grams of the aqueous product would be formed in double replacement reaction when 10.0 grams of aqueous barium chloride is reacted with an excess amount of aqueous silver nitrate. ...
groups (families) vs rows
... Quantitative analysis shows that a compound contains 32.38% sodium, 22.65% sulfur and 44.99% oxygen. Find the empirical formula of this compound. ...
... Quantitative analysis shows that a compound contains 32.38% sodium, 22.65% sulfur and 44.99% oxygen. Find the empirical formula of this compound. ...
2nd Semester final review
... 87. Know what numbers are acidic, basic, and neutral on the pH and pOH scales. pH: acid <7 neutral = 7 base > 7 pOH: base <7 neutral = 7 acid >7 88. If a solution is a pH of 2 and another is a pH of 8, which is more acidic and by how many times? pH 2 is 1,000,000 times more acidic 89. Why is the pH ...
... 87. Know what numbers are acidic, basic, and neutral on the pH and pOH scales. pH: acid <7 neutral = 7 base > 7 pOH: base <7 neutral = 7 acid >7 88. If a solution is a pH of 2 and another is a pH of 8, which is more acidic and by how many times? pH 2 is 1,000,000 times more acidic 89. Why is the pH ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.