UNIT 1—Water AB
... This review is simply a guide. Anything we’ve covered is considered “fair game” on the final. However, we did try to give example problems from all the topics we’ve studied. So if you run across something during your studying that is not found on this sheet, please bring it to our attention. The mat ...
... This review is simply a guide. Anything we’ve covered is considered “fair game” on the final. However, we did try to give example problems from all the topics we’ve studied. So if you run across something during your studying that is not found on this sheet, please bring it to our attention. The mat ...
Unit 4 - cloudfront.net
... 1. Individual half-cell potentials cannot be determined, because there must be a potential difference (waterfall analogy). Therefore in order to determine the cell potentials of half reactions, there must be a standard reaction that all others are compared to. 2. Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE): T ...
... 1. Individual half-cell potentials cannot be determined, because there must be a potential difference (waterfall analogy). Therefore in order to determine the cell potentials of half reactions, there must be a standard reaction that all others are compared to. 2. Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE): T ...
CBSE-12th/2011/CHEMISTRY
... larger in size. so lp repulsion is less significant. Also, S-S bond is stronger than O-O bond & S=S is less strong(less than 2 S-S bonds). This is also affected by the fact that O forms strong bonds with mostly other elements than itself. Ans.13 (i)In aqueous solution, Cu+ ion undergoes oxidation to ...
... larger in size. so lp repulsion is less significant. Also, S-S bond is stronger than O-O bond & S=S is less strong(less than 2 S-S bonds). This is also affected by the fact that O forms strong bonds with mostly other elements than itself. Ans.13 (i)In aqueous solution, Cu+ ion undergoes oxidation to ...
Kompleksni soedinenija
... In this experiment, the flux at the electrode (i.e., the rate of the electrode reaction, thus the current), depends on the diffusion rate only (i.e., depends on the mass transfer only). According to the First Fick law, the rate of diffusion depends on the diffusion coefficient (D) and the concentrat ...
... In this experiment, the flux at the electrode (i.e., the rate of the electrode reaction, thus the current), depends on the diffusion rate only (i.e., depends on the mass transfer only). According to the First Fick law, the rate of diffusion depends on the diffusion coefficient (D) and the concentrat ...
Midterm Review Answers
... sodium fluoride, and sodium hydroxide you need to separate the barium, mercury(II), and magnesium ions. How would you go about separating these ions? Discuss your experimental procedure and defend your answer. Using the solubility rules, chloride compounds are generally soluble, but mercury is an ex ...
... sodium fluoride, and sodium hydroxide you need to separate the barium, mercury(II), and magnesium ions. How would you go about separating these ions? Discuss your experimental procedure and defend your answer. Using the solubility rules, chloride compounds are generally soluble, but mercury is an ex ...
Science 10 Chem - Holy Trinity Academy
... Molecular elements: elements that naturally occur in combinations of 2-3 atoms. Ex: H2, O2, N2, F2, Cl2, P4, S8 Compound: when two or more elements are chemically combined together. o They can’t be separated by ordinary physical means o Fixed ratio of elements/never change o e.g., water (H2O) an ...
... Molecular elements: elements that naturally occur in combinations of 2-3 atoms. Ex: H2, O2, N2, F2, Cl2, P4, S8 Compound: when two or more elements are chemically combined together. o They can’t be separated by ordinary physical means o Fixed ratio of elements/never change o e.g., water (H2O) an ...
Chemical Reactions and Equations
... I. Direct Combination Reactions (also called synthesis reactions). General form: A + B → AB (two reactants make a single product) A, B = elements or compounds AB = compound consisting of A and B ...
... I. Direct Combination Reactions (also called synthesis reactions). General form: A + B → AB (two reactants make a single product) A, B = elements or compounds AB = compound consisting of A and B ...
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
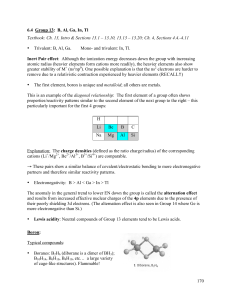
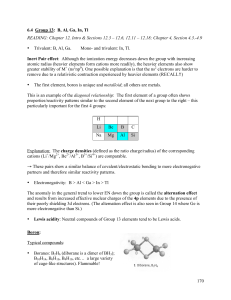
... Amphoterism and Isopolyoxo Ions Amphoterism: Being able to do two opposite things at the same time. In chemistry: Acid/Base amphoterism, Redox amphoterism ...
... Amphoterism and Isopolyoxo Ions Amphoterism: Being able to do two opposite things at the same time. In chemistry: Acid/Base amphoterism, Redox amphoterism ...
Document
... A cheese maker added 4.00 L of milk to a small sample of bacterial culture. He knew that once the concentration of lactic acid reached 1.25 x 10-2 mol L-1 the cheese would be ready. He took a 10.00 mL sample of the whey, added several drops of phenolphthalein, and titrated the sample against a 0.111 ...
... A cheese maker added 4.00 L of milk to a small sample of bacterial culture. He knew that once the concentration of lactic acid reached 1.25 x 10-2 mol L-1 the cheese would be ready. He took a 10.00 mL sample of the whey, added several drops of phenolphthalein, and titrated the sample against a 0.111 ...
AP Chemistry
... Part 2: Measure the change in mass of the zinc electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas produced during electrolysis, calculate the molar mass of zinc and compare the value to the periodic table. Fill a 150 mL beaker ¾ full with conducting solution. Fill the 50 mL volumetric flask with the conductin ...
... Part 2: Measure the change in mass of the zinc electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas produced during electrolysis, calculate the molar mass of zinc and compare the value to the periodic table. Fill a 150 mL beaker ¾ full with conducting solution. Fill the 50 mL volumetric flask with the conductin ...
AP Chemistry Review Assignment Brown and LeMay: Chemistry the
... The last part of this section, including how to determine the formula of a hydrate, and how to use combustion analyses to determine empirical formulas will be addressed early in the semester, probably Thurs., Aug. 20. 43. Give the empirical formula of each of the following compounds if a sample cont ...
... The last part of this section, including how to determine the formula of a hydrate, and how to use combustion analyses to determine empirical formulas will be addressed early in the semester, probably Thurs., Aug. 20. 43. Give the empirical formula of each of the following compounds if a sample cont ...
Solution
... We would also expect further reactions to occur in the aqueous solution, e.g., hydrolysis, and polymerization. As more and more solid dissolves, these aqueous phase interactions also increase in extent until finally, the reverse process, i.e., precipitation, starts. Thus, in effect, the dissolution ...
... We would also expect further reactions to occur in the aqueous solution, e.g., hydrolysis, and polymerization. As more and more solid dissolves, these aqueous phase interactions also increase in extent until finally, the reverse process, i.e., precipitation, starts. Thus, in effect, the dissolution ...
Notes 2 Balancing
... • The products including this gas, if captured, is the same mass per mole as the reactants consumed. ...
... • The products including this gas, if captured, is the same mass per mole as the reactants consumed. ...
Ch13ov1
... Pg = partial pressure of the gas over the solution K = a constant for the particular gas in the particular solvent at a given temperature χg = mole fraction of the gas in the solution. L At the low concentrations typical of dissolved non-reactive gases, mole fraction is proportional to concentration ...
... Pg = partial pressure of the gas over the solution K = a constant for the particular gas in the particular solvent at a given temperature χg = mole fraction of the gas in the solution. L At the low concentrations typical of dissolved non-reactive gases, mole fraction is proportional to concentration ...
Chem Unit 3 Vocabulary
... 5 the volume of a fixed mass of gas varies inversely with the pressure at constant temperature 6 the volume of a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure varies directly with Kelvin temperature 7 an expression of the relationship between pressure, volume, & temperature of a fixed amount of gas 8 the ...
... 5 the volume of a fixed mass of gas varies inversely with the pressure at constant temperature 6 the volume of a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure varies directly with Kelvin temperature 7 an expression of the relationship between pressure, volume, & temperature of a fixed amount of gas 8 the ...
The Chemistry of Solutions Page | 1 Unit 7: The Chemistry of
... At what temperature do saturated solutions of sodium chloride and potassium chloride contain the same mass of solute per 100 mL of water? _____________ ...
... At what temperature do saturated solutions of sodium chloride and potassium chloride contain the same mass of solute per 100 mL of water? _____________ ...
Chemistry I Exams and Keys 2014 Season
... During the late 18th century, French chemist Antoine Lavoisier, with the help of his wife Marie-Anne, conducted several experiments involving heating substances in sealed containers with air inside them. Chemical changes were observed within the containers during the heating process, and the records ...
... During the late 18th century, French chemist Antoine Lavoisier, with the help of his wife Marie-Anne, conducted several experiments involving heating substances in sealed containers with air inside them. Chemical changes were observed within the containers during the heating process, and the records ...
6.5 Main Group
... Amphoterism and Isopolyoxo Ions Amphoterism: Being able to do two opposite things at the same time. In chemistry: Acid/Base amphoterism, Redox amphoterism ...
... Amphoterism and Isopolyoxo Ions Amphoterism: Being able to do two opposite things at the same time. In chemistry: Acid/Base amphoterism, Redox amphoterism ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.