Topic #4 Notes
... When diluting a concentrated acid it is often found that combining water and the acid is a very exothermic process, i.e. one that releases energy. In some cases this energy can be very significant and may even cause the water present to turn into the gaseous state (steam). As the steam leaves the sy ...
... When diluting a concentrated acid it is often found that combining water and the acid is a very exothermic process, i.e. one that releases energy. In some cases this energy can be very significant and may even cause the water present to turn into the gaseous state (steam). As the steam leaves the sy ...
HCC9 Chapter 9 Objectives and Notes
... 9.4. Naming and Writing Formulas for Acids and Bases 1. acid: A compound whose formula begins with hydrogen. This is really a terribly incomplete definition, but it will suffice for now. a. Examples: HCl, H2SO4. b. Note: There are some exceptions to this rule; H2O and H2O2 both begin with an "H", y ...
... 9.4. Naming and Writing Formulas for Acids and Bases 1. acid: A compound whose formula begins with hydrogen. This is really a terribly incomplete definition, but it will suffice for now. a. Examples: HCl, H2SO4. b. Note: There are some exceptions to this rule; H2O and H2O2 both begin with an "H", y ...
Northgate High School Chemistry Department
... explain that the shape of a simple molecule is determined by repulsion between electron pairs surrounding a central atom; state that lone pairs of electrons repel more than bonded pairs; explain the shapes of, and bond angles in, molecules and ions with up to six electron pairs (including lone pairs ...
... explain that the shape of a simple molecule is determined by repulsion between electron pairs surrounding a central atom; state that lone pairs of electrons repel more than bonded pairs; explain the shapes of, and bond angles in, molecules and ions with up to six electron pairs (including lone pairs ...
Chemistry Lesson Plans #07 - Chemical Reactions
... o If we consider all the different possible chemical reactions, we would quickly conclude that there are millions of them possible, with millions of possible compounds o Just as we learned how to identify compounds (molecular and ionic) there are several ways to categorize chemical reactions Combina ...
... o If we consider all the different possible chemical reactions, we would quickly conclude that there are millions of them possible, with millions of possible compounds o Just as we learned how to identify compounds (molecular and ionic) there are several ways to categorize chemical reactions Combina ...
Solubility and Solubility Equilibrium
... (break apart) in solution and (2) which ions combine to form precipitates when you mix solutions. The other part of this is that if you are given the name of a compound, you have to know the associated chemical formula. This means that it is assumed that you've memorized most of the standard polyato ...
... (break apart) in solution and (2) which ions combine to form precipitates when you mix solutions. The other part of this is that if you are given the name of a compound, you have to know the associated chemical formula. This means that it is assumed that you've memorized most of the standard polyato ...
b - PianetaChimica
... Mass spectrometry is an important tool in the determination of the structures of organic compounds. The process begins with the ionisation of the sample to form a positively charged ion, the molecular ion. At this stage, the molecular ion commonly fragments to form additional cations. These cations ...
... Mass spectrometry is an important tool in the determination of the structures of organic compounds. The process begins with the ionisation of the sample to form a positively charged ion, the molecular ion. At this stage, the molecular ion commonly fragments to form additional cations. These cations ...
chem A exercise package C
... Many formulas for substances cannot be explained in terms of ionic bonding. Consider the substance Cl2O. Both the chlorine and the oxygen atom need more electrons for a stable electron population. A model proposed that would allow both atoms to gain electrons is shown in the diagram on this page. Th ...
... Many formulas for substances cannot be explained in terms of ionic bonding. Consider the substance Cl2O. Both the chlorine and the oxygen atom need more electrons for a stable electron population. A model proposed that would allow both atoms to gain electrons is shown in the diagram on this page. Th ...
NOMENCLATURE OF IONIC COMPOUNDS CHEMISTRY 1411
... (II) and this is incorrect. Oxidation number is expressed in parenthesis only for transistion metal ions or metal ions which show variable oxidation numbers. Barium belongs to group 2 and all elements in group 2 have a fixed oxidation number of +2. ...
... (II) and this is incorrect. Oxidation number is expressed in parenthesis only for transistion metal ions or metal ions which show variable oxidation numbers. Barium belongs to group 2 and all elements in group 2 have a fixed oxidation number of +2. ...
Electrochemistry 2
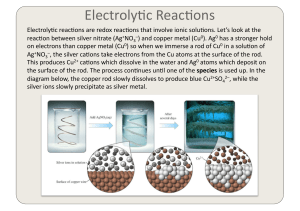
... Note the func)on of the salt bridge. If we have no salt bridge, the Cu half cell anode will start to lose electrons and generate Cu2+ ca)ons but it will not have enough nega)ve counter ions. ...
... Note the func)on of the salt bridge. If we have no salt bridge, the Cu half cell anode will start to lose electrons and generate Cu2+ ca)ons but it will not have enough nega)ve counter ions. ...
HONG KONG DIPLOMA OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
... If there are 20 litres of gaseous mixture from Mars, calculate the volume, in litres, of carbon dioxide gas and nitrogen gas in the mixture. ...
... If there are 20 litres of gaseous mixture from Mars, calculate the volume, in litres, of carbon dioxide gas and nitrogen gas in the mixture. ...
Extra Unit 3 Problems for the Web Site (Honors
... How many grams of ammonia will be required to react with 80. g of O2? 4. In the commercial preparation of hydrogen chloride gas, what mass of HCl in grams may be obtained by heating 234 g of NaCl with excess H2SO4? The balanced equation for the reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + 2HCl 5. A chemi ...
... How many grams of ammonia will be required to react with 80. g of O2? 4. In the commercial preparation of hydrogen chloride gas, what mass of HCl in grams may be obtained by heating 234 g of NaCl with excess H2SO4? The balanced equation for the reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + 2HCl 5. A chemi ...
3.10 Neutralization
... • Transfer of electrons from one species to another 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) NaCl(s) consists of ions: 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2Na+(s) + 2Cl-(s) Na(s) → Na+(s) ⇒ loss of 1e- by Na Cl2(g) → 2Cl-(s) ⇒ gain of 2e- by Cl2 Result: transfer of electrons from Na to Cl2 ...
... • Transfer of electrons from one species to another 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) NaCl(s) consists of ions: 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2Na+(s) + 2Cl-(s) Na(s) → Na+(s) ⇒ loss of 1e- by Na Cl2(g) → 2Cl-(s) ⇒ gain of 2e- by Cl2 Result: transfer of electrons from Na to Cl2 ...
Chemistry
... unit is a factor of 10 in hydrogen ion concentration. Acids and bases are important classes of chemicals that are recognized by easily observed properties in the laboratory. Acids and bases will neutralize each other. Acid formulas usually begin with hydrogen, and base formulas are a metal with a hy ...
... unit is a factor of 10 in hydrogen ion concentration. Acids and bases are important classes of chemicals that are recognized by easily observed properties in the laboratory. Acids and bases will neutralize each other. Acid formulas usually begin with hydrogen, and base formulas are a metal with a hy ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood
... A. Pure Substances and Mixtures 1. _______ matter is composed of particles called ___________ 2. Atoms form ______________ and come together in different ways to form _________________ and __________________ 3. ______ _____________ unit of an ___________ and maintain the ______________ of that ele ...
... A. Pure Substances and Mixtures 1. _______ matter is composed of particles called ___________ 2. Atoms form ______________ and come together in different ways to form _________________ and __________________ 3. ______ _____________ unit of an ___________ and maintain the ______________ of that ele ...
Chemical equations must be balanced.
... This equation is not balanced. There is one C on each side of the equation, so C is balanced. However, on the left side, H has a subscript of 4, which means there are four hydrogen atoms. On the right side, H has a subscript of 2, which means there are two hydrogen atoms. Also, there are two oxygen ...
... This equation is not balanced. There is one C on each side of the equation, so C is balanced. However, on the left side, H has a subscript of 4, which means there are four hydrogen atoms. On the right side, H has a subscript of 2, which means there are two hydrogen atoms. Also, there are two oxygen ...
dutch national chemistry olympiad
... 6p 3 Calculate on average how many H+ ions a citric acid molecule has parted with when the gas production, occurring after the Aspro-Clear tablet is put into water, has finished. Assume for the calculation that all of the acetylsalicylic acid and all of the hydrogen carbonate have reacted. Often t ...
... 6p 3 Calculate on average how many H+ ions a citric acid molecule has parted with when the gas production, occurring after the Aspro-Clear tablet is put into water, has finished. Assume for the calculation that all of the acetylsalicylic acid and all of the hydrogen carbonate have reacted. Often t ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... *5. Solder is a SOLUTION of metal tin [Sn] and metal lead [Pb]; LOW MELTING point and is used to join METALS together *6. Wood’s metal is a SOLUTION of metal bismuth [Bi], metal lead [Pb], metal tin [Sn], and metal cadmium [Cd]; used in sprinkler systems in buildings *c. Concentration is a wa ...
... *5. Solder is a SOLUTION of metal tin [Sn] and metal lead [Pb]; LOW MELTING point and is used to join METALS together *6. Wood’s metal is a SOLUTION of metal bismuth [Bi], metal lead [Pb], metal tin [Sn], and metal cadmium [Cd]; used in sprinkler systems in buildings *c. Concentration is a wa ...
Chapter 14, Section 1, pages 494-501
... To describe chemical equilibrium To give examples of chemical equilibrium Demo Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? Completion Reactions are reactions that use up all or almost all of the reactant ...
... To describe chemical equilibrium To give examples of chemical equilibrium Demo Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? Completion Reactions are reactions that use up all or almost all of the reactant ...
odd - WWW2
... Reasons for its exothermicity: (a) the formation of dinitrogen, with its strong triple bond; (b) the formation of water with strong (O H) bonds; (c) the formation of aluminum oxide with the very high lattice energy It would be a good propellant because of the large volume of gas produced per ...
... Reasons for its exothermicity: (a) the formation of dinitrogen, with its strong triple bond; (b) the formation of water with strong (O H) bonds; (c) the formation of aluminum oxide with the very high lattice energy It would be a good propellant because of the large volume of gas produced per ...
practice final examination
... 10. Answer true or false for each of the following questions below (circle your choice): a) ...
... 10. Answer true or false for each of the following questions below (circle your choice): a) ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.