Chemistry exam review
... 2. A student mixes two chemicals in a test tube. The test tube turns hot and bubbles appear. What indicators of chemical reaction is the student observing? a. Change in color and formation of precipitate. b. Change in color and formation of gas. c. Change in temperature and formation of precipitate. ...
... 2. A student mixes two chemicals in a test tube. The test tube turns hot and bubbles appear. What indicators of chemical reaction is the student observing? a. Change in color and formation of precipitate. b. Change in color and formation of gas. c. Change in temperature and formation of precipitate. ...
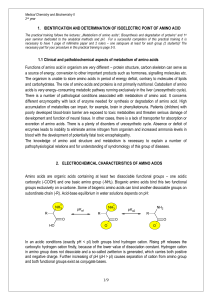
Identification and determination of pI of amino acids
... Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) is an analytical method using different distribution of substances between mobile (solvent) and stationary (sorbent on inert plate) phase. Owing to different distribution of substances between mobile and stationary phase, we obtain different migration of the substance ...
... Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) is an analytical method using different distribution of substances between mobile (solvent) and stationary (sorbent on inert plate) phase. Owing to different distribution of substances between mobile and stationary phase, we obtain different migration of the substance ...
conjugate base - DarringtonScience
... made can be used to find either [H+] or [OH-] for a dilute aqueous solution ...
... made can be used to find either [H+] or [OH-] for a dilute aqueous solution ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... When dissolved in water, very few of the covalent acid molecules dissociate (split up) into ions. With weak acids this conversion is usually less than 1% . In fact the reverse reaction dominates so an equilibrium mixture is formed that contains very few ions compared to covalent molecules. The equi ...
... When dissolved in water, very few of the covalent acid molecules dissociate (split up) into ions. With weak acids this conversion is usually less than 1% . In fact the reverse reaction dominates so an equilibrium mixture is formed that contains very few ions compared to covalent molecules. The equi ...
2 - College of Arts and Sciences
... The osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution containing 3.50 mg of a protein dissolved in sufficient water to form 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution at 25 C was found to be 1.54 torr. Treating the protein as a nonelectrolyte, calculate its molar mass. Osmotic pressure = MRT ...
... The osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution containing 3.50 mg of a protein dissolved in sufficient water to form 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution at 25 C was found to be 1.54 torr. Treating the protein as a nonelectrolyte, calculate its molar mass. Osmotic pressure = MRT ...
Final review free response ch 1-4
... 1. Write the empirical and molecular formula for the following molecule: 9 Carbons, 6 Bromines, 3 Oxygens, and 9 Hydrogens 2. Complete and balance the following reactions: a. Combination ___ H2 + ___ F2 b. Decomposition ___ B2O3 ...
... 1. Write the empirical and molecular formula for the following molecule: 9 Carbons, 6 Bromines, 3 Oxygens, and 9 Hydrogens 2. Complete and balance the following reactions: a. Combination ___ H2 + ___ F2 b. Decomposition ___ B2O3 ...
Final Exam Review
... 2.2.1 Explain the energy content of a chemical reaction 1. When a chemical cold pack is activated, it becomes cool to the touch. What is happening in terms of energy? a. An exothermic reaction is occurring, absorbing heat from its surroundings. b. An exothermic reaction is occurring, releasing heat ...
... 2.2.1 Explain the energy content of a chemical reaction 1. When a chemical cold pack is activated, it becomes cool to the touch. What is happening in terms of energy? a. An exothermic reaction is occurring, absorbing heat from its surroundings. b. An exothermic reaction is occurring, releasing heat ...
Standards Practice
... A. the balanced equation Jor a reaction B. the ionization energy of a substance C. the mass of the substance (given its chemical fOlmula) D. the number of moles present 13. What can be said for magnesium, which has an atomic number of 12 and an atomic weight of 24.3'1 A. One mole of magnesium will h ...
... A. the balanced equation Jor a reaction B. the ionization energy of a substance C. the mass of the substance (given its chemical fOlmula) D. the number of moles present 13. What can be said for magnesium, which has an atomic number of 12 and an atomic weight of 24.3'1 A. One mole of magnesium will h ...
Lab 13
... 2. Which of the following rankings correctly shows the order of increasing acidity for benzoic acid, benzensulfonic acid, ethanol and phenol? __A. phenol < ethanol < benzoic acid < benzenesulfonic acid __B. ethanol < phenol < benzenesulfonic acid < benzoic acid __C. ethanol < phenol < benzoic acid < ...
... 2. Which of the following rankings correctly shows the order of increasing acidity for benzoic acid, benzensulfonic acid, ethanol and phenol? __A. phenol < ethanol < benzoic acid < benzenesulfonic acid __B. ethanol < phenol < benzenesulfonic acid < benzoic acid __C. ethanol < phenol < benzoic acid < ...
CH30S Chemical Reactions Part 2 Unit Review
... 16. Determine the density of hydrogen gas in g/ml. Hint: use molar mass and molar volume. (9.02x10-5g/mL) 17. Calculate the mass of 8.96L of sulphur dioxide at STP.(25.64g) 18. How many molecules of methane gas (CH4) would be found in 6.4g of methane at STP? (2.4x1023molecules) 19. A student placed ...
... 16. Determine the density of hydrogen gas in g/ml. Hint: use molar mass and molar volume. (9.02x10-5g/mL) 17. Calculate the mass of 8.96L of sulphur dioxide at STP.(25.64g) 18. How many molecules of methane gas (CH4) would be found in 6.4g of methane at STP? (2.4x1023molecules) 19. A student placed ...
Acids - Beck-Shop
... will learn about the atomic masses that you see on your periodic table. You will also learn about the special code of chemistry: the formulae, and equations that allow chemists to communicate. Amount of substance and its unit the mole, provides chemists with an ability to convert between mass, conce ...
... will learn about the atomic masses that you see on your periodic table. You will also learn about the special code of chemistry: the formulae, and equations that allow chemists to communicate. Amount of substance and its unit the mole, provides chemists with an ability to convert between mass, conce ...
ION-SELECTIVE ELECTRODES - Clayton State University
... - Elements that are more powerful reducing agents than hydrogen show negative potentials - Elements that are less powerful reducing agents than hydrogen show positive potentials - Metals with more negative Eo are more active - More active metals displace less active metals from solution Fe will disp ...
... - Elements that are more powerful reducing agents than hydrogen show negative potentials - Elements that are less powerful reducing agents than hydrogen show positive potentials - Metals with more negative Eo are more active - More active metals displace less active metals from solution Fe will disp ...
Leaching of Sphalerite with Hydrogen Peroxide and Nitric Acid
... method of Levespiel [12]. From the analysis equation (10) gave straight lines, which could be concluded that the leaching process is chemical control. The rate constant, k of the reaction were determined and plotted against 1/T shown figure 6. The slope of this plot was used to determine the apparen ...
... method of Levespiel [12]. From the analysis equation (10) gave straight lines, which could be concluded that the leaching process is chemical control. The rate constant, k of the reaction were determined and plotted against 1/T shown figure 6. The slope of this plot was used to determine the apparen ...
DRAFT AP® CHEMISTRY 2005 SCORING GUIDELINES
... Should accept oxygen gas causes splint to RE_IGNITE. The popping sound presumed the accessibility of oxygen, which is not explicit in the directions. What to do if a student claims that the splint will be extinguished? I would give the credit. Also, would accept ‘re-ignite’ for oxygen. I have a prob ...
... Should accept oxygen gas causes splint to RE_IGNITE. The popping sound presumed the accessibility of oxygen, which is not explicit in the directions. What to do if a student claims that the splint will be extinguished? I would give the credit. Also, would accept ‘re-ignite’ for oxygen. I have a prob ...
MSTA WOW Chemistry
... iodide is slightly toxic by ingestion. Although the dishwashing liquid is considered non-hazardous, do not ingest the material. Do not stand over the reaction; steam and oxygen are produced quickly. Wear appropriate chemical splash goggles, chemical-resistant gloves and a chemical-resistant apron. T ...
... iodide is slightly toxic by ingestion. Although the dishwashing liquid is considered non-hazardous, do not ingest the material. Do not stand over the reaction; steam and oxygen are produced quickly. Wear appropriate chemical splash goggles, chemical-resistant gloves and a chemical-resistant apron. T ...
Example: Writing a Thermochemical Equation
... Doubling of the previous equation, you obtain 2N2(g) + 6H2(g) → 4NH3(g); ∆H = -184 kJ Suppose we reverse the first equation we wrote for the synthesis of ammonia. Then the reaction is for the dissociation of two mol of ammonia into its elements. The thermochemical equation is 2NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3H2(g ...
... Doubling of the previous equation, you obtain 2N2(g) + 6H2(g) → 4NH3(g); ∆H = -184 kJ Suppose we reverse the first equation we wrote for the synthesis of ammonia. Then the reaction is for the dissociation of two mol of ammonia into its elements. The thermochemical equation is 2NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3H2(g ...
The hydrogen bonding of cytosine with guanine
... The enthalpy of hydrogen-bond formation between guanine (G) and cytusine (C) in o-dichlorobenzene and in chloroform at 25°C has been determined by direct calorimetric measurement. We derivatized 2’-deoxyguanosine and 2‘-deoxycytidine at the 5’- and 3’-hydroxyls with triisopropylsilyl groups; these g ...
... The enthalpy of hydrogen-bond formation between guanine (G) and cytusine (C) in o-dichlorobenzene and in chloroform at 25°C has been determined by direct calorimetric measurement. We derivatized 2’-deoxyguanosine and 2‘-deoxycytidine at the 5’- and 3’-hydroxyls with triisopropylsilyl groups; these g ...
08 PowerPoint
... reaction without being used up in the reaction) S or ppt or ↓ = precipitate (solid - only found on products side) ...
... reaction without being used up in the reaction) S or ppt or ↓ = precipitate (solid - only found on products side) ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.