How many grams of oxygen are made if 3.75 moles of KClO 3
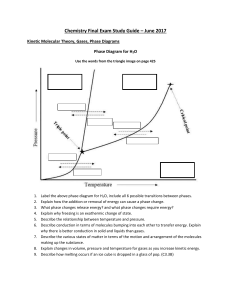
... Label the above phase diagram for H2O, include all 6 possible transitions between phases. Explain how the addition or removal of energy can cause a phase change. What phase changes release energy? and what phase changes require energy? Explain why freezing is an exothermic change of state. Describe ...
... Label the above phase diagram for H2O, include all 6 possible transitions between phases. Explain how the addition or removal of energy can cause a phase change. What phase changes release energy? and what phase changes require energy? Explain why freezing is an exothermic change of state. Describe ...
Slide 1 of 24
... Propane gas reacts with oxygen to produce water vapor and carbon dioxide. Choose the correct word equation for this reaction. A. propane + carbon dioxide → water + oxygen B. propane + oxygen + water → carbon dioxide C. propane + oxygen + water + carbon dioxide D. propane + oxygen → water + carbon ...
... Propane gas reacts with oxygen to produce water vapor and carbon dioxide. Choose the correct word equation for this reaction. A. propane + carbon dioxide → water + oxygen B. propane + oxygen + water → carbon dioxide C. propane + oxygen + water + carbon dioxide D. propane + oxygen → water + carbon ...
materials: metals and non—metals
... hydrogen. The reaction is slow at room temperature, but its rate can be increased by the addition of a little copper (II) sulphate. Zinc displaces copper metal, which acts as a catalyst. In general, ...
... hydrogen. The reaction is slow at room temperature, but its rate can be increased by the addition of a little copper (II) sulphate. Zinc displaces copper metal, which acts as a catalyst. In general, ...
Loeblein chemistry clicker questions2013
... •Describe a molecular model of gas pressure •Describe what happens to the measurable quantities if changes to the gas system are made. •Make sense of the measurable quantities of gases by analyzing examples of macroscopic things that are similar •Explain using physics what is happening on a molecula ...
... •Describe a molecular model of gas pressure •Describe what happens to the measurable quantities if changes to the gas system are made. •Make sense of the measurable quantities of gases by analyzing examples of macroscopic things that are similar •Explain using physics what is happening on a molecula ...
Chemical Equations and Reaction Types Lab
... number of atoms of that element on both sides of the equation. This is done by placing the appropriate coefficient in front of the formula of the element or compound on the other side of the arrow that contains that same element. The coefficient is chosen so that when the coefficient is multiplied b ...
... number of atoms of that element on both sides of the equation. This is done by placing the appropriate coefficient in front of the formula of the element or compound on the other side of the arrow that contains that same element. The coefficient is chosen so that when the coefficient is multiplied b ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... -ide becomes hydro _____ic Acid Example: Cl- is the Chloride ion so HCl = hydrochloric acid When the anion name ends in –ite, the acid name is the stem of the anion with the suffix –ous, followed by the word acid. -ite becomes ______ous Acid Example: ClO2- is the Chlorite ion so HClO2 = Chlorous aci ...
... -ide becomes hydro _____ic Acid Example: Cl- is the Chloride ion so HCl = hydrochloric acid When the anion name ends in –ite, the acid name is the stem of the anion with the suffix –ous, followed by the word acid. -ite becomes ______ous Acid Example: ClO2- is the Chlorite ion so HClO2 = Chlorous aci ...
Full answers
... MgCl2·6H2O dissolves to give Mg2+ + 2Cl-: three particles per mole. Hence, the number of moles of MgCl2·6H2O required to give this concentration of particles in 1.0 L is: number of moles = 0.236 / 3 mol = 0.0786 mol Hence, the mass of MgCl2·6H2O required is: mass = number of moles × molar mass = 0.0 ...
... MgCl2·6H2O dissolves to give Mg2+ + 2Cl-: three particles per mole. Hence, the number of moles of MgCl2·6H2O required to give this concentration of particles in 1.0 L is: number of moles = 0.236 / 3 mol = 0.0786 mol Hence, the mass of MgCl2·6H2O required is: mass = number of moles × molar mass = 0.0 ...
Structures and Bonding
... Possible problems with making chemicals: 1) Reactions often produce chemicals that aren’t commercially useful or that can’t be sold 2) Reactions also need to be fast to be economical but not so fast that they’re dangerous! ...
... Possible problems with making chemicals: 1) Reactions often produce chemicals that aren’t commercially useful or that can’t be sold 2) Reactions also need to be fast to be economical but not so fast that they’re dangerous! ...
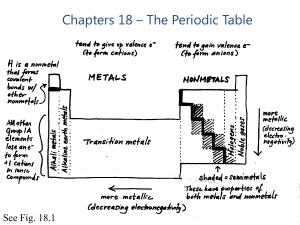
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... H2 (g); H2 molecules dissociate at the metal surface and H atoms occupy holes in the crystal structure (potential use as a portable fuel) ...
... H2 (g); H2 molecules dissociate at the metal surface and H atoms occupy holes in the crystal structure (potential use as a portable fuel) ...
Unit 11 acids and bases part 1
... Arrhenius’s acid-base theory to include this behavior. They defined acids and bases as follows: ...
... Arrhenius’s acid-base theory to include this behavior. They defined acids and bases as follows: ...
Unit 2 Notes Name - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... named by describing the molecular formula, using prefixes for the numbers. o You will need to memorize the number prefixes for the numbers 1–10. o E.g., P2O5 is diphosphorus pentoxide. **Note that the prefix “mono—“ is never used with the first element. SO3 is simply sulfur trioxide. However, “mono— ...
... named by describing the molecular formula, using prefixes for the numbers. o You will need to memorize the number prefixes for the numbers 1–10. o E.g., P2O5 is diphosphorus pentoxide. **Note that the prefix “mono—“ is never used with the first element. SO3 is simply sulfur trioxide. However, “mono— ...
Six-Way Galvanic Cell
... 7. Place the prepared filter paper in a Petri dish or on a sheet of acetate transparency or plastic wrap. 8. Using a clean, Beral-type pipet, add 4–5 drops of potassium nitrate solution in the center of the filter paper. This will serve as the salt bridge. 9. Using a separate Beral-type pip ...
... 7. Place the prepared filter paper in a Petri dish or on a sheet of acetate transparency or plastic wrap. 8. Using a clean, Beral-type pipet, add 4–5 drops of potassium nitrate solution in the center of the filter paper. This will serve as the salt bridge. 9. Using a separate Beral-type pip ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.