Prep UK-intro.p65
... The aim of the scientific committee has been that as many as possible of the preparatory problems should take their starting point in issues of general chemical, public or environmental interest. Therefore some of the problems cover several topics from the International Chemistry Olympiad. We have a ...
... The aim of the scientific committee has been that as many as possible of the preparatory problems should take their starting point in issues of general chemical, public or environmental interest. Therefore some of the problems cover several topics from the International Chemistry Olympiad. We have a ...
Summer Resources - mvhs
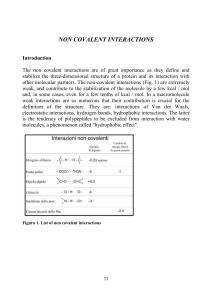
... Bonds form because the energy of the system is lowered, making the molecule more stable. Bond Energy is the energy required to break a bond. Types of chemical bond: There are two types of chemical bonds: 1) Intramolecular Bonds: holds atoms WITHIN a molecule, much stronger than intermolecular bo ...
... Bonds form because the energy of the system is lowered, making the molecule more stable. Bond Energy is the energy required to break a bond. Types of chemical bond: There are two types of chemical bonds: 1) Intramolecular Bonds: holds atoms WITHIN a molecule, much stronger than intermolecular bo ...
Nanostructured Li Ion Insertion Electrodes. 1
... impedance on frequency and/or position is determined by the transport properties in each phase, whereas ζ is an impedance length describing faradaic currents and polarization at the distributed interface. The model of eq 1 represented in the scheme of Figure 2a is formulated in terms of differential ...
... impedance on frequency and/or position is determined by the transport properties in each phase, whereas ζ is an impedance length describing faradaic currents and polarization at the distributed interface. The model of eq 1 represented in the scheme of Figure 2a is formulated in terms of differential ...
File
... Iodine is a black, shiny, non-metallic solid and a member of Group VII. It sublimes easily on heating to give a purple vapour. A sample of iodine vapour of mass 6.35 g has a volume of 1.247 dm3 when maintained at constant temperature and a pressure of 1.00 × 105 Pa. If iodine vapour acts as an ideal ...
... Iodine is a black, shiny, non-metallic solid and a member of Group VII. It sublimes easily on heating to give a purple vapour. A sample of iodine vapour of mass 6.35 g has a volume of 1.247 dm3 when maintained at constant temperature and a pressure of 1.00 × 105 Pa. If iodine vapour acts as an ideal ...
E:\My Documents\sch4u\SCH4U review McKay answers.wpd
... c) Determine the solubility in mol/L and in g/L for the least soluble silver salt in pure water. (Ans: 9.2X10-9 mol/L and 2.2X10-6 g/L) molar mass of AgI is mN = 107.87 g/mol + 126.90 g/mol = 234.77 g/mol molar solubility = 9.2x10 -9 mol/L mass solubility = CN x mN = 9.2x10 -9 mol/L x 234.77 g/mol = ...
... c) Determine the solubility in mol/L and in g/L for the least soluble silver salt in pure water. (Ans: 9.2X10-9 mol/L and 2.2X10-6 g/L) molar mass of AgI is mN = 107.87 g/mol + 126.90 g/mol = 234.77 g/mol molar solubility = 9.2x10 -9 mol/L mass solubility = CN x mN = 9.2x10 -9 mol/L x 234.77 g/mol = ...
13. transition metal chemistry
... NOTE IUPAC gives the definition of a transition element as ‘An element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell.’ Elemental zinc does not contain an incomplete d sub-shell either ([Ar] 4s2 3d10) so can also be ruled out on the basis o ...
... NOTE IUPAC gives the definition of a transition element as ‘An element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell.’ Elemental zinc does not contain an incomplete d sub-shell either ([Ar] 4s2 3d10) so can also be ruled out on the basis o ...
chapter 7 - chemical formulas and chemical compounds
... of the name of the second element, and (c) the ending –ide (if only contains two elements) 3) the “o” or “a” at the end of a prefix is usually dropped when the word following the prefix begins with another vowel ______________________________ and _____________________________are usually names second ...
... of the name of the second element, and (c) the ending –ide (if only contains two elements) 3) the “o” or “a” at the end of a prefix is usually dropped when the word following the prefix begins with another vowel ______________________________ and _____________________________are usually names second ...
Slides
... has killed four workers and injured at least 10 others, several critically, Japanese media and officials have reported. Kyodo News Service and public broadcaster NHK reported that four workers had died after suffering severe burns, and that at least one other worker was in critical condition. Those ...
... has killed four workers and injured at least 10 others, several critically, Japanese media and officials have reported. Kyodo News Service and public broadcaster NHK reported that four workers had died after suffering severe burns, and that at least one other worker was in critical condition. Those ...
Chem 1B Fa2015 FinalExam Review
... (a) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of all species if a mixture containing 1.00 mole of CO and 1.00 mole of H2O(g) are placed in 1.00-L reaction vessel and is allowed to come to equilibrium at 700 K. (b) A 1.00-L sample of an equilibrium mixture containing CO, H2O(g), CO2, and H2 is compress ...
... (a) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of all species if a mixture containing 1.00 mole of CO and 1.00 mole of H2O(g) are placed in 1.00-L reaction vessel and is allowed to come to equilibrium at 700 K. (b) A 1.00-L sample of an equilibrium mixture containing CO, H2O(g), CO2, and H2 is compress ...
Chapter 8
... 1. Some oxy-acids, when heated, decompose to form water and the nonmetal oxide. Example: Sulfuric acid is heated Example: Nitric acid is heated 2. Some metallic hydroxides (bases), when heated, decompose to form the metal oxide and water. Example: Sodium hydroxide is heated Example: Calcium hydroxid ...
... 1. Some oxy-acids, when heated, decompose to form water and the nonmetal oxide. Example: Sulfuric acid is heated Example: Nitric acid is heated 2. Some metallic hydroxides (bases), when heated, decompose to form the metal oxide and water. Example: Sodium hydroxide is heated Example: Calcium hydroxid ...
SUPPORTING INFORMATION: Solvent
... To parameterize the anion-cation interactions for MgSO4 and CsCl we perform several production runs for each 2.5 m solution. All simulation details are given in the main text. Each run differs only in the value of the parameter to be optimized: tMg,Osul f or εCsCl . We test the values tMg,Osul f = 1 ...
... To parameterize the anion-cation interactions for MgSO4 and CsCl we perform several production runs for each 2.5 m solution. All simulation details are given in the main text. Each run differs only in the value of the parameter to be optimized: tMg,Osul f or εCsCl . We test the values tMg,Osul f = 1 ...
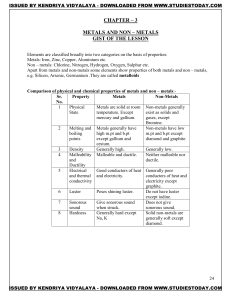
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... 3. Solubility: soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene and pertrol. 4. Conduction of electricity:ionic compounds in solid state-----does not conduct electricity. Reason—Ions can not move due to rigid solid structure. Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state. Reason-- Ions can move free ...
... 3. Solubility: soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene and pertrol. 4. Conduction of electricity:ionic compounds in solid state-----does not conduct electricity. Reason—Ions can not move due to rigid solid structure. Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state. Reason-- Ions can move free ...
2003
... Silver salts (AgNO3, AgCl, AgBr, AgI) can be decomposed using light energy. e.g. AgNO3 forms a black colour as a result of the Ag+ forming Ag (s) and thus decomposing the AgNO3. ...
... Silver salts (AgNO3, AgCl, AgBr, AgI) can be decomposed using light energy. e.g. AgNO3 forms a black colour as a result of the Ag+ forming Ag (s) and thus decomposing the AgNO3. ...
AP_chemical reaction and quantities
... • A balanced chemical equation is one in which the number of atoms of each element in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms of that same element in the products. • A reaction can be balanced by applying the law of conservation of matter. • Coefficients (in red below) are written to the le ...
... • A balanced chemical equation is one in which the number of atoms of each element in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms of that same element in the products. • A reaction can be balanced by applying the law of conservation of matter. • Coefficients (in red below) are written to the le ...
June 2010 Regents Exam Part C Questions
... (1) grams of NaCl per liter of water (2) grams of NaCl per liter of solution (3) moles of NaCl per liter of water (4) moles of NaCl per liter of solution Q 15 A real gas behaves least like an ideal gas under the conditions of (1) low temperature and low pressure (2) low temperature and high pressu ...
... (1) grams of NaCl per liter of water (2) grams of NaCl per liter of solution (3) moles of NaCl per liter of water (4) moles of NaCl per liter of solution Q 15 A real gas behaves least like an ideal gas under the conditions of (1) low temperature and low pressure (2) low temperature and high pressu ...
model paper-1 - WordPress.com
... Sodium and potassium both are electropositive elements. The ionization enthalpy of potassium is lesser than that of sodium. That is why potassium is more reactive than sodium. So, sodium is less reactive than potassium. 1+2=3M 19. a) When Borax is heated strongly, it loses water of crystallization a ...
... Sodium and potassium both are electropositive elements. The ionization enthalpy of potassium is lesser than that of sodium. That is why potassium is more reactive than sodium. So, sodium is less reactive than potassium. 1+2=3M 19. a) When Borax is heated strongly, it loses water of crystallization a ...
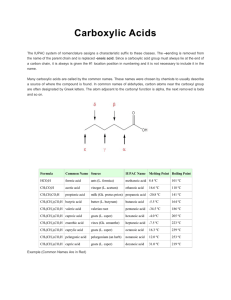
Carboxylic Acids
... The IUPAC system of nomenclature assigns a characteristic suffix to these classes. The –eending is removed from the name of the parent chain and is replaced -anoic acid. Since a carboxylic acid group must always lie at the end of a carbon chain, it is always is given the #1 location position in numb ...
... The IUPAC system of nomenclature assigns a characteristic suffix to these classes. The –eending is removed from the name of the parent chain and is replaced -anoic acid. Since a carboxylic acid group must always lie at the end of a carbon chain, it is always is given the #1 location position in numb ...
PART 2 – CHEMISTRY
... where the atom has more than one shell, then the atom is said to be stable. This means that the atom does not react with any other kind of atom and thus remains isolated and inert. For example, this is so in the case of the rare gases, argon, neon, helium etc. meaning that they cannot form compounds ...
... where the atom has more than one shell, then the atom is said to be stable. This means that the atom does not react with any other kind of atom and thus remains isolated and inert. For example, this is so in the case of the rare gases, argon, neon, helium etc. meaning that they cannot form compounds ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.