Solubility Rules The following rules are used in several chemistry
... The strong bases are: NaOH, LiOH, KOH, Li2 O. When you look at the solubility chart, you will notice that other bases, such as Ca(OH) 2 and Ba(OH)2, are said to be soluble as well. However, except for the strong bases listed, all other bases are only SLIGHTLY soluble. Slightly soluble compounds mean ...
... The strong bases are: NaOH, LiOH, KOH, Li2 O. When you look at the solubility chart, you will notice that other bases, such as Ca(OH) 2 and Ba(OH)2, are said to be soluble as well. However, except for the strong bases listed, all other bases are only SLIGHTLY soluble. Slightly soluble compounds mean ...
Exam Review_Key_All Topics.082
... 8. Describe the concept of the mole and its importance to measurement in chemistry. Without the mole, amounts of reactants and products in chemical equations could not be predicted—unless all chemicals are gases at STP—since different compounds have different masses. Furthermore, since Avogadro’s n ...
... 8. Describe the concept of the mole and its importance to measurement in chemistry. Without the mole, amounts of reactants and products in chemical equations could not be predicted—unless all chemicals are gases at STP—since different compounds have different masses. Furthermore, since Avogadro’s n ...
CP - Fundamentals
... came along in the early 1800s and proposed that these elemental materials were made up of very small, indivisible particles he called atoms. Dalton was to provide the framework for a theory, which although not perfect, launched the modern age of chemistry and physics. Here are some ideas of Dalton’s ...
... came along in the early 1800s and proposed that these elemental materials were made up of very small, indivisible particles he called atoms. Dalton was to provide the framework for a theory, which although not perfect, launched the modern age of chemistry and physics. Here are some ideas of Dalton’s ...
«Классы и номенклатура неорганических соединений»
... particles, which 1 mole of substance consist B. 6,02 ∙ 1022 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 g of substance consist C. 6,02 ∙ 1020 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 g of substance consist D. 6,02 ∙ 1019 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 kg of substanc ...
... particles, which 1 mole of substance consist B. 6,02 ∙ 1022 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 g of substance consist C. 6,02 ∙ 1020 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 g of substance consist D. 6,02 ∙ 1019 mole-1 the number of structure particles, which 1 kg of substanc ...
Topic 4 - Lloyd Crosby
... 2. Strong/weak distinctions in acid/base reactions a. Arrhenius acids will react with Arrhenius bases – whether they are strong or weak. b. The distinctions between strong and weak arise when writing the net ionic equation. c. Examples of acid base with strong/weak (1) A sulfuric acid solution is mi ...
... 2. Strong/weak distinctions in acid/base reactions a. Arrhenius acids will react with Arrhenius bases – whether they are strong or weak. b. The distinctions between strong and weak arise when writing the net ionic equation. c. Examples of acid base with strong/weak (1) A sulfuric acid solution is mi ...
OCR Gateway Science
... (a) What volume of 2 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid is required to neutralise 0.03 moles of sodium hydroxide? (b) 160 cm3 of hydrochloric acid neutralises exactly 20 cm3 of 0.4 mol/dm3 sodium hydroxide. Calculate the concentration of the hydrochloric acid. (c) How many grams of sodium hydroxide are there ...
... (a) What volume of 2 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid is required to neutralise 0.03 moles of sodium hydroxide? (b) 160 cm3 of hydrochloric acid neutralises exactly 20 cm3 of 0.4 mol/dm3 sodium hydroxide. Calculate the concentration of the hydrochloric acid. (c) How many grams of sodium hydroxide are there ...
Chapter 13: Water and the Lithosphere Preview
... material at the plate boundaries, which are found at continental margins. Volatile compounds, such as H2O, HCl, CO2, SO2 and N2 were expelled from the interior in volcanic eruptions, forming the oceans and the atmosphere. This natural separation of volatile and non-volatile compounds was also a sepa ...
... material at the plate boundaries, which are found at continental margins. Volatile compounds, such as H2O, HCl, CO2, SO2 and N2 were expelled from the interior in volcanic eruptions, forming the oceans and the atmosphere. This natural separation of volatile and non-volatile compounds was also a sepa ...
Section 11.1 Assessment How many mole ratios can be written for
... the start of a chemical reaction determines how much product can form. ...
... the start of a chemical reaction determines how much product can form. ...
chemistry 110 final exam
... N2(g) + 3H2(g) ! 2NH3(g) At some time during the reaction, the [N2]=0.036 M, [H2]=4.6"10#3 M, and [NH3]=9.1"10#4 M. Which of the following is true? A. Q = K so the reaction is at equilibrium; the concentrations will not change B. Q > K so the reaction will produce more product. C. Q > K so the react ...
... N2(g) + 3H2(g) ! 2NH3(g) At some time during the reaction, the [N2]=0.036 M, [H2]=4.6"10#3 M, and [NH3]=9.1"10#4 M. Which of the following is true? A. Q = K so the reaction is at equilibrium; the concentrations will not change B. Q > K so the reaction will produce more product. C. Q > K so the react ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER 2016
... 60. A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. ...
... 60. A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. ...
TANNIC ACID
... sources; the substance is not an acid in the chemical sense. The common name "Tannic acid" has been adopted to distinguish the commercial substance from other tannins, such as condensed tannins. These specifications relate only to hydrolysable gallotannins, i.e., those which yield gallic acid on hyd ...
... sources; the substance is not an acid in the chemical sense. The common name "Tannic acid" has been adopted to distinguish the commercial substance from other tannins, such as condensed tannins. These specifications relate only to hydrolysable gallotannins, i.e., those which yield gallic acid on hyd ...
Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... Unlike these three ionic compounds, AgCl does not dissolve in water to a signi cant extent, as signi ed by its physical state notation, s. Explicitly representing all dissolved ions results in a complete ionic equation. In this particular case, the formulas for the dissolved ionic compounds are repl ...
... Unlike these three ionic compounds, AgCl does not dissolve in water to a signi cant extent, as signi ed by its physical state notation, s. Explicitly representing all dissolved ions results in a complete ionic equation. In this particular case, the formulas for the dissolved ionic compounds are repl ...
pdfCfE Higher - Unit 3 - Pupil Booklet 2 MB
... zero but the aim is to learn from mistakes and reduce the rate to a minimum. It is essential at this stage to revise all of your National 5 calculations that were based on moles and equations. ...
... zero but the aim is to learn from mistakes and reduce the rate to a minimum. It is essential at this stage to revise all of your National 5 calculations that were based on moles and equations. ...
Unit 6 Review Answers
... considered a modernized Arrhenius acid, however.) Ammonia can’t be an Arrhenius base, because it does not contain hydroxide ions. (Ammonia could be considered a modernized Arrhenius base, however.) Students should disagree. A solution with a pH of 4 has [H3O+] = 0.0001 mol/L, whereas a solution with ...
... considered a modernized Arrhenius acid, however.) Ammonia can’t be an Arrhenius base, because it does not contain hydroxide ions. (Ammonia could be considered a modernized Arrhenius base, however.) Students should disagree. A solution with a pH of 4 has [H3O+] = 0.0001 mol/L, whereas a solution with ...
AP 2005 chemistry form b free
... (b) Calculate the minimum volume of 5.0 M H2SO4 that the student must use to react completely with 2.7 g of aluminum metal. (c) As the reaction solution cools, alum crystals precipitate. The student filters the mixture and dries the crystals, then measures their mass. (i) If the student weighs the c ...
... (b) Calculate the minimum volume of 5.0 M H2SO4 that the student must use to react completely with 2.7 g of aluminum metal. (c) As the reaction solution cools, alum crystals precipitate. The student filters the mixture and dries the crystals, then measures their mass. (i) If the student weighs the c ...
ksp - lozon.ca
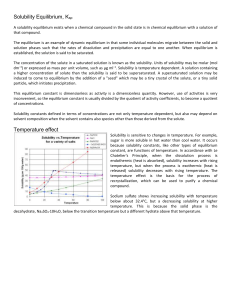
... The solubility of a sparingly soluble salt is reduced in a solution that contains an ion in common with that salt. For instance, the solubility of silver chloride in water is reduced if a solution of sodium chloride is added to a suspension of silver chloride in water. A practical example used very ...
... The solubility of a sparingly soluble salt is reduced in a solution that contains an ion in common with that salt. For instance, the solubility of silver chloride in water is reduced if a solution of sodium chloride is added to a suspension of silver chloride in water. A practical example used very ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.