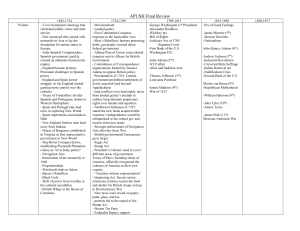
3rd Period Review Chart
... 1540s and onwards: Spain establishes missions in an attempt to convert Indian peoples from their traditional religion to Catholicism 1620: settlement of Plymouth Colony by Pilgrims seeking religious independence from England 1630s: Puritans, English Protestants that wanted to purify church. ...
... 1540s and onwards: Spain establishes missions in an attempt to convert Indian peoples from their traditional religion to Catholicism 1620: settlement of Plymouth Colony by Pilgrims seeking religious independence from England 1630s: Puritans, English Protestants that wanted to purify church. ...
Present - Images
... – He sent a fleet of four ships and 400 soldiers. – The Dutch could not resist and surrendered all of New Amsterdam and eventually all of New Netherland. – New Amsterdam was renamed New York. ...
... – He sent a fleet of four ships and 400 soldiers. – The Dutch could not resist and surrendered all of New Amsterdam and eventually all of New Netherland. – New Amsterdam was renamed New York. ...
CPUSH (Unit 1, #2)
... D. Limiting Dissent in New England 1. Puritans did not support dissent: a. Roger Williams was _____________________________ from Massachusetts when he demanded that Indians be paid for their land; He formed the _____________________________________ colony in 1636 b. Anne ___________________________ ...
... D. Limiting Dissent in New England 1. Puritans did not support dissent: a. Roger Williams was _____________________________ from Massachusetts when he demanded that Indians be paid for their land; He formed the _____________________________________ colony in 1636 b. Anne ___________________________ ...
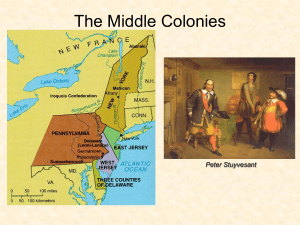
Mid-Atlantic Colonies
... colonists and Native Americans. It was named after the leader of the Native Americans. King Philip’s Native American name was Metacom. Many colonists died in the war, but it caused such a heavy loss of life among the Native American population that large areas of southern New England became English ...
... colonists and Native Americans. It was named after the leader of the Native Americans. King Philip’s Native American name was Metacom. Many colonists died in the war, but it caused such a heavy loss of life among the Native American population that large areas of southern New England became English ...
3 Colonies OH New Leaning Standards
... 4.1 The perspective of many Europeans that black Africans were inferior and uncivilized led to the forced relocation of hundreds of thousands of Africans to the American colonies. Although Africans aided ...
... 4.1 The perspective of many Europeans that black Africans were inferior and uncivilized led to the forced relocation of hundreds of thousands of Africans to the American colonies. Although Africans aided ...
Settling the Northern Colonies 1619-1700 Chapter 3
... Designed to enforce the Navigation Laws that did not allow trade between America & countries not ruled by England Andros ended town meetings, restricted the courts, press, schools, revoked land titles, & taxed w/o the consent of the governed The Glorious Revolution 1688-9 (Bloodless Revolution) ...
... Designed to enforce the Navigation Laws that did not allow trade between America & countries not ruled by England Andros ended town meetings, restricted the courts, press, schools, revoked land titles, & taxed w/o the consent of the governed The Glorious Revolution 1688-9 (Bloodless Revolution) ...
Copy of Ch. 1 Lecture Notes
... King Charles II • King Charles II granted friends and family land to rule, and they formed the Middle and Southern Colonies • In the late 1600s, a new and different phase of colonization began in the middle and southern regions. • A new king, Charles II, owed money and favors to many people. He rep ...
... King Charles II • King Charles II granted friends and family land to rule, and they formed the Middle and Southern Colonies • In the late 1600s, a new and different phase of colonization began in the middle and southern regions. • A new king, Charles II, owed money and favors to many people. He rep ...
ch. 1 us history notes
... – Began in the 1400s – They were very militaristic and used military to expand through conquering other tribes – Founded a large empire in present-day Mexico. – The Aztec capital was Tenochtitlán(today’s Mexico City). Established because gods told Aztecs to find an Eagle with a snake in its beak per ...
... – Began in the 1400s – They were very militaristic and used military to expand through conquering other tribes – Founded a large empire in present-day Mexico. – The Aztec capital was Tenochtitlán(today’s Mexico City). Established because gods told Aztecs to find an Eagle with a snake in its beak per ...
File 1.5 18th century colonies
... o Colonial Assemblies: The lower house of colonial assemblies gradually gained political influence; governors had difficulty ruling without the support of assemblies. o 1639, Fundamental Orders of Connecticut: First written constitution in America. o 1643, New England Confederation: Connecticut, New ...
... o Colonial Assemblies: The lower house of colonial assemblies gradually gained political influence; governors had difficulty ruling without the support of assemblies. o 1639, Fundamental Orders of Connecticut: First written constitution in America. o 1643, New England Confederation: Connecticut, New ...
colonial government and politics
... the popular election of a governor and judges. In 1641, Massachusetts adopted the Massachusetts Body of Liberties (1641) to limit the powers of the colonial governor and his magistrates. The document relied both on English common law and the Ten Commandments in its support for protection of individu ...
... the popular election of a governor and judges. In 1641, Massachusetts adopted the Massachusetts Body of Liberties (1641) to limit the powers of the colonial governor and his magistrates. The document relied both on English common law and the Ten Commandments in its support for protection of individu ...
Social studies review flash cards
... After suffering several defeats, Washington took his army to Valley Forge for the winter of 1777 Outbreak of small pox Martha Washington came to help care for the men The men were trained by Frederick von Steuben to become a more professional army rather than militias Thomas Paine wrote “A ...
... After suffering several defeats, Washington took his army to Valley Forge for the winter of 1777 Outbreak of small pox Martha Washington came to help care for the men The men were trained by Frederick von Steuben to become a more professional army rather than militias Thomas Paine wrote “A ...
Student Study Guide for the American Pageant
... A) France surrendered all of its territorial claims to North America. B) England turned Florida over to Spain. C) Spain ceded all of Louisiana, including New Orleans, to Britain. D) France lost all its valuable sugar islands in the West Indies. E) the British got all of Canada except Nova Scotia. As ...
... A) France surrendered all of its territorial claims to North America. B) England turned Florida over to Spain. C) Spain ceded all of Louisiana, including New Orleans, to Britain. D) France lost all its valuable sugar islands in the West Indies. E) the British got all of Canada except Nova Scotia. As ...
CHAPTER 1: BEGINNINGS TO 1763
... New England, Middle Colonies, and the South – all developed distinct economies and societies In the South, rural Plantations with a single cash crop were common Small Southern farmers (Germans, Scots-Irish) and African slaves made up the majority of people ...
... New England, Middle Colonies, and the South – all developed distinct economies and societies In the South, rural Plantations with a single cash crop were common Small Southern farmers (Germans, Scots-Irish) and African slaves made up the majority of people ...
Chapter 4 - AP US History
... plantation economies based on exporting staple crops. They depended on the labor of enslaved Africans, who often constituted the majority of the population in these areas and developed their own forms of cultural and religious autonomy. E) British conflicts with American Indians over land, resources ...
... plantation economies based on exporting staple crops. They depended on the labor of enslaved Africans, who often constituted the majority of the population in these areas and developed their own forms of cultural and religious autonomy. E) British conflicts with American Indians over land, resources ...
First Continental Congress
... – 2. Develop a plan of resistance – 3. Articulate constitutional relationship with Great Britain • 1. American rep. in Parliament • 2. Obey the King and Parliament, but not the taxes opposed ...
... – 2. Develop a plan of resistance – 3. Articulate constitutional relationship with Great Britain • 1. American rep. in Parliament • 2. Obey the King and Parliament, but not the taxes opposed ...
New York - Lee County Schools
... separation from the established church. • Separatists who left for America were known as the Pilgrims. ...
... separation from the established church. • Separatists who left for America were known as the Pilgrims. ...
AP US Ch 2 Tobin 2014
... Many newcomers to Carolina were “squatters,” people who owned no land, usually down from Virginia. North Carolinians developed a strong resistance to authority, due to geographic isolation from neighbors. Two “flavors” of Carolinians developed: (a) aristocratic and wealthier down south around ...
... Many newcomers to Carolina were “squatters,” people who owned no land, usually down from Virginia. North Carolinians developed a strong resistance to authority, due to geographic isolation from neighbors. Two “flavors” of Carolinians developed: (a) aristocratic and wealthier down south around ...
apush lecture ch 4-6
... • b. American states were bound to pay back debts to British creditors (exactly what the conflict started over) ...
... • b. American states were bound to pay back debts to British creditors (exactly what the conflict started over) ...
Final Review:
... What was a cause of the 1st Great Awakening? – It was a religious movement that contributed to the spread of democratic feeling in the colonies…helped colonist stand up for their political rights when leaders began to violate their liberties (freedoms) The French and Indian War Causes: fighting betw ...
... What was a cause of the 1st Great Awakening? – It was a religious movement that contributed to the spread of democratic feeling in the colonies…helped colonist stand up for their political rights when leaders began to violate their liberties (freedoms) The French and Indian War Causes: fighting betw ...
Key Terms and People Section Summary
... • Huguenots traveled to Americas for religious freedom in the late 1500s. • Louis Joliet and Jacques Marquette reached the Mississippi River in the late 1600s. • René-Robert de La Salle followed the Mississippi to the Gulf of Mexico and claimed the territory for France. • The Dutch claimed the land ...
... • Huguenots traveled to Americas for religious freedom in the late 1500s. • Louis Joliet and Jacques Marquette reached the Mississippi River in the late 1600s. • René-Robert de La Salle followed the Mississippi to the Gulf of Mexico and claimed the territory for France. • The Dutch claimed the land ...
Note Guide
... 1. What were the objectives of the founders of Virginia? Why did the colony survive, in spite of poor planning? 2. What were the objectives of the founders of the Puritan colonies at Plymouth and Massachusetts Bay? Compare the early years of these colonies to those of the Virginia Colony. 3. What ro ...
... 1. What were the objectives of the founders of Virginia? Why did the colony survive, in spite of poor planning? 2. What were the objectives of the founders of the Puritan colonies at Plymouth and Massachusetts Bay? Compare the early years of these colonies to those of the Virginia Colony. 3. What ro ...
Benjamin Franklin`s World 1702-1763
... Provided unusual opportunities for economic and social self-development Farming in all colonies ...
... Provided unusual opportunities for economic and social self-development Farming in all colonies ...
Middle Colonies
... Geography and History A Land of Plenty • The Middle colonies exported so much grain that they were called the Breadbasket Colonies • Farmers in the middle colonies also raised cattle and pigs. They sent tons of beef, pork, and butter to ports in New York. • In time Pennsylvania became the center of ...
... Geography and History A Land of Plenty • The Middle colonies exported so much grain that they were called the Breadbasket Colonies • Farmers in the middle colonies also raised cattle and pigs. They sent tons of beef, pork, and butter to ports in New York. • In time Pennsylvania became the center of ...
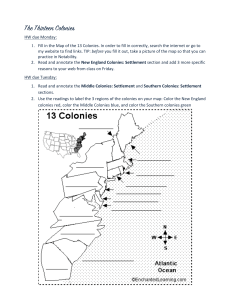
The Thirteen Colonies
... Dutch. Although the Dutch soon began trading with Native Americans for beaver and otter pelts, they did not send colonial settlers until 1624. Starting in 1625, the Dutch brought enslaved Africans to wo ...
... Dutch. Although the Dutch soon began trading with Native Americans for beaver and otter pelts, they did not send colonial settlers until 1624. Starting in 1625, the Dutch brought enslaved Africans to wo ...
Colonial Society on the Eve of Revolution
... molasses, which it’d sell to New England once it returned there. 4. Manufacturing was not as important, though many small enterprises existed. 5. Strong-backed laborers and skilled craftspeople were scarce and highly prized. 6. Perhaps the single most important manufacturing activity was lumbering. ...
... molasses, which it’d sell to New England once it returned there. 4. Manufacturing was not as important, though many small enterprises existed. 5. Strong-backed laborers and skilled craftspeople were scarce and highly prized. 6. Perhaps the single most important manufacturing activity was lumbering. ...