Chapter8- Jovian Planet Systems
... • The bands of rising air are called zones. • They appear white in color because ammonia clouds form as the air rises to high, cool altitudes. • The adjacent belts of falling air are depleted in cloud forming ingredients and do not contain any white ammonia clouds. • Instead, we see the red/tan amm ...
... • The bands of rising air are called zones. • They appear white in color because ammonia clouds form as the air rises to high, cool altitudes. • The adjacent belts of falling air are depleted in cloud forming ingredients and do not contain any white ammonia clouds. • Instead, we see the red/tan amm ...
30-4 Satellites of other Planets
... • Mass = 300x Earth’s mass. • Jupiter has the most moons – 63+ • Jupiter is one of the brightest objects in the sky • Has a very stormy atmosphere. – One major storm, the Great Red Spot, is as big as the Earth. ...
... • Mass = 300x Earth’s mass. • Jupiter has the most moons – 63+ • Jupiter is one of the brightest objects in the sky • Has a very stormy atmosphere. – One major storm, the Great Red Spot, is as big as the Earth. ...
space - Kidblog
... a gas giant, rather than a terrestrial planet, and is made largely of hydrogen and helium. Jupiter was first visited by Pioneer 10 in 1973 and later by Pioneer 11, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and Ulysses. The unmanned ...
... a gas giant, rather than a terrestrial planet, and is made largely of hydrogen and helium. Jupiter was first visited by Pioneer 10 in 1973 and later by Pioneer 11, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and Ulysses. The unmanned ...
ppt
... • Bright side mainly water ice • Dark side has spectrum similar to a class of asteroid Matches mixture of organic compounds from carbonaceous meteorites, ice and hydrated silicates ...
... • Bright side mainly water ice • Dark side has spectrum similar to a class of asteroid Matches mixture of organic compounds from carbonaceous meteorites, ice and hydrated silicates ...
Jupiter - Courseweb
... (4) A system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. Students should understand a whole in terms of its components and how these components relate to each other and to the whole. All systems have basic properties that can be described in terms of space, time, energy, and ...
... (4) A system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. Students should understand a whole in terms of its components and how these components relate to each other and to the whole. All systems have basic properties that can be described in terms of space, time, energy, and ...
The Gas Giant Planets
... About 60 Earths could fit inside Neptune, the fourth largest planet in the solar system. Scientists believe it is the windiest planet. Winds blow at over 1200 miles per hour. Large storms rage above the planet. Once, Neptune had a Great Dark Spot as big as Earth. It was a storm that blew across the ...
... About 60 Earths could fit inside Neptune, the fourth largest planet in the solar system. Scientists believe it is the windiest planet. Winds blow at over 1200 miles per hour. Large storms rage above the planet. Once, Neptune had a Great Dark Spot as big as Earth. It was a storm that blew across the ...
Jupiter (Jove) was the King of the Gods
... o Jupiter has rings like Saturn's, but much fainter and smaller. o Unexpected and were only discovered when two of the Voyager 1 scientists insisted that after traveling 1 billion km it was at least worth a quick look to see if any rings might be present. o Unlike Saturn's, Jupiter's rings are dark. ...
... o Jupiter has rings like Saturn's, but much fainter and smaller. o Unexpected and were only discovered when two of the Voyager 1 scientists insisted that after traveling 1 billion km it was at least worth a quick look to see if any rings might be present. o Unlike Saturn's, Jupiter's rings are dark. ...
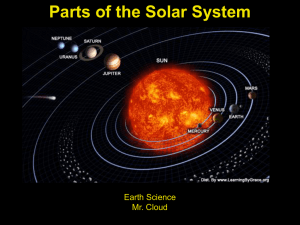
The Solar System
... the Solar System? 2. What is the Sun? 3. Which is the smallest planet in the Solar System? 4. Which is the largest planet in the Solar System? 5. Which is the hottest planet in the Solar System? 6. Why is Earth called a ...
... the Solar System? 2. What is the Sun? 3. Which is the smallest planet in the Solar System? 4. Which is the largest planet in the Solar System? 5. Which is the hottest planet in the Solar System? 6. Why is Earth called a ...
Solar System Cornell Notes - CE Williams Middle School
... (2) Titan is the largest of it's 18 moons (3) Rings made of same materials as comets (4) Voyager I ('80), Voyager 11 ('81), and Cassini (expected to arrive late 2003) main probe missions. ...
... (2) Titan is the largest of it's 18 moons (3) Rings made of same materials as comets (4) Voyager I ('80), Voyager 11 ('81), and Cassini (expected to arrive late 2003) main probe missions. ...
File
... • Remnants from the formation of the sun begin to coalesce and form planetesimals • Matter with higher density remains in close proximity to the sun forming the terrestrial planets • Low density gases move further away forming ...
... • Remnants from the formation of the sun begin to coalesce and form planetesimals • Matter with higher density remains in close proximity to the sun forming the terrestrial planets • Low density gases move further away forming ...
Pd. 4 Solar System Acts
... Why was Galileo (The scientist to discover Jupiter’s 4 largest moons) able to see only Jupiter’s 4 moons? ...
... Why was Galileo (The scientist to discover Jupiter’s 4 largest moons) able to see only Jupiter’s 4 moons? ...
The Outer Planets
... of Jupiter’s atmosphere is its Great Red Spot, a storm that is larger than Earth. Jupiter probably has a dense core of rock and iron at its center, surrounded by a thick mantle of liquid hydrogen and helium. Galileo discovered Jupiter’s four largest moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Saturn ...
... of Jupiter’s atmosphere is its Great Red Spot, a storm that is larger than Earth. Jupiter probably has a dense core of rock and iron at its center, surrounded by a thick mantle of liquid hydrogen and helium. Galileo discovered Jupiter’s four largest moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Saturn ...
a huge lake of hot liquid rock beneath the surface. This boiling hot
... the size of Earth. Jupiter spins on its axis so ...
... the size of Earth. Jupiter spins on its axis so ...
Moons of Jupiter Age of Surface
... 1. Which moon has the oldest surface? [Do not look in your book. Examine the pictures & deduce the answer.] [Hint: Compare the appearance of surfaces of earth & moon.] ...
... 1. Which moon has the oldest surface? [Do not look in your book. Examine the pictures & deduce the answer.] [Hint: Compare the appearance of surfaces of earth & moon.] ...
Make up notes
... Terrestrial Planets • Planets that have solid, rocky crusts • Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars • Earth - only one with water on the surface and can support life ...
... Terrestrial Planets • Planets that have solid, rocky crusts • Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars • Earth - only one with water on the surface and can support life ...
Jupiter-up close - NRC Publications Archive
... onto their volatiles. All those retained volatiles are what make the outer planets so large. Was our failure to detect water in Jupiter’s atmosphere a failure of our probe? Did the probe just happen to descend in a dry place, or are our ideas wrong? Is the water there as a big lump of ice deep down ...
... onto their volatiles. All those retained volatiles are what make the outer planets so large. Was our failure to detect water in Jupiter’s atmosphere a failure of our probe? Did the probe just happen to descend in a dry place, or are our ideas wrong? Is the water there as a big lump of ice deep down ...
Outer Planet review Much of what we know about the outer planets
... 2) Jupiter’s giant red spot is actually a large____. 3 times larger than the earth. 3) What minefield lies outside of the orbit of mars and presents a large obstacle for travelling to the outer solar system? 4) How does the composition of outer planets differ from that of the inner planets? 5) What ...
... 2) Jupiter’s giant red spot is actually a large____. 3 times larger than the earth. 3) What minefield lies outside of the orbit of mars and presents a large obstacle for travelling to the outer solar system? 4) How does the composition of outer planets differ from that of the inner planets? 5) What ...
Our own Earth`s interior structure, and surface features will be
... Neptune). These planets are massive, large, have many moons, ring systems, and low densities. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is an atmospheric feature. Saturn’s rings lie within the Roche Limit as do the other ring systems. Magnetic fields for jovian planets result from an interior region comprised of liq ...
... Neptune). These planets are massive, large, have many moons, ring systems, and low densities. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is an atmospheric feature. Saturn’s rings lie within the Roche Limit as do the other ring systems. Magnetic fields for jovian planets result from an interior region comprised of liq ...
Planet Jupiter
... Jupiter. We can also see Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons, which is approximately t he same size as Earth; imagine how small we are! Jupiter is a large gas planet where clouds change colours daily. Jupiter’s complex atmosphere bristles with lightening and swirls with huge storm systems. Jupiter is som ...
... Jupiter. We can also see Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons, which is approximately t he same size as Earth; imagine how small we are! Jupiter is a large gas planet where clouds change colours daily. Jupiter’s complex atmosphere bristles with lightening and swirls with huge storm systems. Jupiter is som ...
Moon and Rings - Mid
... Europa - slightly smaller than our Moon Ganymede - largest moon in Solar System, slightly larger than Mercury The closer to Jupiter, the higher the moon density (similar to behavior of terrestrial planets) => like mini “planetary” system! Intense heat of young Jupiter played role of sun. ...
... Europa - slightly smaller than our Moon Ganymede - largest moon in Solar System, slightly larger than Mercury The closer to Jupiter, the higher the moon density (similar to behavior of terrestrial planets) => like mini “planetary” system! Intense heat of young Jupiter played role of sun. ...
The Outer Planets
... Jupiter’s hydrogen-helium atmosphere also contains small amounts of methane, ammonia, water, and sulfur compounds Due to immense pressures within the atmosphere, Jupiter is thought to be a gigantic ocean of liquid hydrogen Jupiter also has a faint system of rings surrounding the planet, not discover ...
... Jupiter’s hydrogen-helium atmosphere also contains small amounts of methane, ammonia, water, and sulfur compounds Due to immense pressures within the atmosphere, Jupiter is thought to be a gigantic ocean of liquid hydrogen Jupiter also has a faint system of rings surrounding the planet, not discover ...
14-4
... Much larger than Earth and do not have solid surfaces Atmospheres are all very similar to each other Mostly hydrogen and helium gas ...
... Much larger than Earth and do not have solid surfaces Atmospheres are all very similar to each other Mostly hydrogen and helium gas ...
tire
... 8. A doughnut-shaped region outside the orbit of Pluto containing many frozen comet bodies. 9. The planet with the most prominent ring system. 10. Any of the rocky objects larger than a few hundred meters in diameter than orbit the Sun. 11. The Red Planet 12. The planet that rotates on its side. 13. ...
... 8. A doughnut-shaped region outside the orbit of Pluto containing many frozen comet bodies. 9. The planet with the most prominent ring system. 10. Any of the rocky objects larger than a few hundred meters in diameter than orbit the Sun. 11. The Red Planet 12. The planet that rotates on its side. 13. ...
Find the Planet Facts
... How long would your day and night be if you lived on the equator of Uranus? How are asteroids different from some of the planets in our solar system? Neptune: In what way is “The Great Dark Spot” on Neptune similar to the “Great Red Spot” on Jupiter? Jupiter: If you were looking for a place to visit ...
... How long would your day and night be if you lived on the equator of Uranus? How are asteroids different from some of the planets in our solar system? Neptune: In what way is “The Great Dark Spot” on Neptune similar to the “Great Red Spot” on Jupiter? Jupiter: If you were looking for a place to visit ...
Exploration of Jupiter

The exploration of Jupiter has been conducted via close observations by automated spacecraft. It began with the arrival of Pioneer 10 into the Jovian system in 1973, and, as of 2014, has continued with seven further spacecraft missions. All of these missions were undertaken by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and all but one have been flybys that take detailed observations without the probe landing or entering orbit. These probes make Jupiter the most visited of the Solar System's outer planets as all missions to the outer Solar System have used Jupiter flybys to reduce fuel requirements and travel time. Plans for more missions to the Jovian system are under development, none of which are scheduled to arrive at the planet before 2016. Sending a craft to Jupiter entails many technical difficulties, especially due to the probes' large fuel requirements and the effects of the planet's harsh radiation environment.The first spacecraft to visit Jupiter was Pioneer 10 in 1973, followed a year later by Pioneer 11. Aside from taking the first close-up pictures of the planet, the probes discovered its magnetosphere and its largely fluid interior. The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes visited the planet in 1979, and studied its moons and the ring system, discovering the volcanic activity of Io and the presence of water ice on the surface of Europa. Ulysses further studied Jupiter's magnetosphere in 1992 and then again in 2000. The Cassini probe approached the planet in 2000 and took very detailed images of its atmosphere. The New Horizons spacecraft passed by Jupiter in 2007 and made improved measurements of its and its satellites' parameters.The Galileo spacecraft is the only one to have entered orbit around Jupiter, arriving in 1995 and studying the planet until 2003. During this period Galileo gathered a large amount of information about the Jovian system, making close approaches to all of the four large Galilean moons and finding evidence for thin atmospheres on three of them, as well as the possibility of liquid water beneath their surfaces. It also discovered a magnetic field around Ganymede. As it approached Jupiter, it also witnessed the impact of Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9. In December 1995, it sent an atmospheric probe into the Jovian atmosphere, so far the only craft to do so.Future probes planned by NASA include the Juno spacecraft, launched in 2011, which will enter a polar orbit around Jupiter to determine whether it has a rocky core. The European Space Agency selected the L1-class JUICE mission in 2012 as part of its Cosmic Vision programme to explore three of Jupiter's Galilean moons, with a possible Ganymede lander provided by Roscosmos. JUICE is proposed to be launched in 2022. Some NASA administrators have even speculated as to the possibility of human exploration of Jupiter, but such missions are not considered feasible with current technology; such as radiation protection.