* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Outer Planets
Eight Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
Juno (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Jumping-Jupiter scenario wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
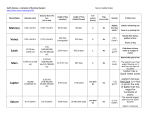
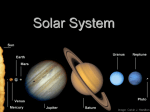
The Outer Planets Chapter 23, Section 3 Jupiter: Giant Among Planets Jupiter has a mass that is 2 ½ times greater than the mass of all other planets and moons combined If Jupiter had been about 10 times larger, it would have become a star One rotation around its axis take 10 Earth hours The most striking feature of Jupiter is its Great Red Spot, it is a cyclonic storm in the upper atmosphere Jupiter’s hydrogen-helium atmosphere also contains small amounts of methane, ammonia, water, and sulfur compounds Due to immense pressures within the atmosphere, Jupiter is thought to be a gigantic ocean of liquid hydrogen Jupiter also has a faint system of rings surrounding the planet, not discovered until Voyager 1 flew past in 1979 Jupiter’s Atmosphere Jupiter’s Moons Jupiter’s satellite system, consisting of 28 moons discovered so far, looks like a mini solar system The four largest moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto) were discovered by Galileo Io is one of three known volcanically active bodies in our solar system (Neptune’s moon Triton is another) The largest of the moons is Ganymede Europa is covered with ice and shows many linear features Callisto is heavily cratered and greatly Jupiter and its Moons Saturn: The Elegant Planet The most prominent feature of Saturn is its system of rings Saturn’s atmosphere is very active, with wind speeds up to 1500 kilometers per hour Large “cyclonic” storms occur in the atmosphere The main rings of Saturn (A and B) are very dense and contain many “moonlets” that often collide with each other Saturn’s faintest ring (E) is composed of very fine particles that are spread apart Saturn’s satellite system consists of 31 moons (Titan is the largest and has an atmosphere that obscures its surface from view) Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, was found to emit liquid geysers Saturn and its Moons Saturn’s Rings Uranus: The Sideways Planet Instead of being generally perpendicular to the plane of its orbit, Uranus’s axis of rotation lies nearly parallel with the plane of its orbit Uranus has a set of at least nine distinct rings Uranus has five large moons, and many smaller ones, that are very varied in their geology: deep canyons, linear scars, large-smooth areas on otherwise cratered surfaces Uranus Neptune: The Windy Planet Winds exceeding 1000 kilometers per hour encircle Neptune, making it one of the windiest places in the solar system It has an Earth-size storm called the Great Dark Spot There are white, cirrus-like clouds that occupy a layer about 50 kilometers above the main cloud deck, thought to be frozen methane Triton, Neptune’s largest moon, exhibits retrograde motion, indicating that it formed separately from Neptune and was gravitationally captured Neptune Pluto: Planet X Pluto lies on the fringe of the solar system, almost 40 times farther from the sun than Earth Because of its great distance, and slow orbital period, it takes Pluto 248 Earth-years to orbit the sun Pluto’s orbit is highly eccentric, causing it to occasionally travel inside the orbit of Neptune, where it resided from 1979 through February 1999 In 1978, the moon Charon was found to be orbiting Pluto The average temperature on Pluto is estimated at 210ºC In 2006, Pluto’s status as a planet was revoked, it is now considered a dwarf planet along with many other Kuiper belt objects Assignment Read Chapter 23, Section 3 (pg. 654-659) Do Section 23.3 Assessment #1-7 (pg. 659)