Nervous System
... Your tongue is filled with sensory structures known as taste buds. They are also found in the throat and roof of your mouth. ...
... Your tongue is filled with sensory structures known as taste buds. They are also found in the throat and roof of your mouth. ...
PDF version
... Circadian Rhythms, Effect of the Biological Clock on Metabolism, Effect of Redox on Circadian Rhythms, Projection from the SCN to Regions in Hypothalamus, Effect of SCN on Energy Balance, Body Temperature and Wakefulness ...
... Circadian Rhythms, Effect of the Biological Clock on Metabolism, Effect of Redox on Circadian Rhythms, Projection from the SCN to Regions in Hypothalamus, Effect of SCN on Energy Balance, Body Temperature and Wakefulness ...
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve
... Passes nerve impulse into the spinal cord through the dorsal root to the posterior horn of the gray matter. 3. Center - region of the spinal cord where the incoming sensory information generates an outgoing motor impulse - usually contains internuncial neurons 4. Motor Neuron - transmits impulses to ...
... Passes nerve impulse into the spinal cord through the dorsal root to the posterior horn of the gray matter. 3. Center - region of the spinal cord where the incoming sensory information generates an outgoing motor impulse - usually contains internuncial neurons 4. Motor Neuron - transmits impulses to ...
L2-Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
... • Transverse bridge of grey matter connecting the anterior and posterior gray horns on each side • Is pierced by the central canal that divides it into anterior and posterior parts ...
... • Transverse bridge of grey matter connecting the anterior and posterior gray horns on each side • Is pierced by the central canal that divides it into anterior and posterior parts ...
Cerebrospinal Fluid
... Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear bodily fluid that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. The CSF occupies the space between the Arachnoid and the Pia . It constitutes the content of all intra-cerebral, cisterns, and Sulci as well ...
... Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear bodily fluid that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. The CSF occupies the space between the Arachnoid and the Pia . It constitutes the content of all intra-cerebral, cisterns, and Sulci as well ...
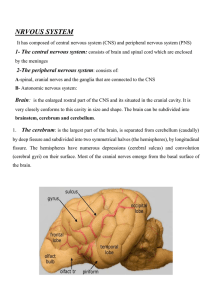
1- The central nervous system
... by the other two parts. Its consists of the continuations of the spinal cord (medulla oblongata) following Rostral by the transversely oriented pons, Mesencephalon and diencephalon . Dorsally one recognizes the rhomboid fossa at the level of the pons and medulla oblongata. This fossa represents the ...
... by the other two parts. Its consists of the continuations of the spinal cord (medulla oblongata) following Rostral by the transversely oriented pons, Mesencephalon and diencephalon . Dorsally one recognizes the rhomboid fossa at the level of the pons and medulla oblongata. This fossa represents the ...
Neurons Notes
... - axon - the extension of a neuron that carries information (electrical impulses called action potentials) away from the cell body - can be very long, projecting several feet through the body - myelin sheath - a layer of white, fatty tissue segmentally encasing the axons of neurons; enables vastly g ...
... - axon - the extension of a neuron that carries information (electrical impulses called action potentials) away from the cell body - can be very long, projecting several feet through the body - myelin sheath - a layer of white, fatty tissue segmentally encasing the axons of neurons; enables vastly g ...
File
... - axon - the extension of a neuron that carries information (electrical impulses called action potentials) away from the cell body - can be very long, projecting several feet through the body - myelin sheath - a layer of white, fatty tissue segmentally encasing the axons of neurons; enables vastly g ...
... - axon - the extension of a neuron that carries information (electrical impulses called action potentials) away from the cell body - can be very long, projecting several feet through the body - myelin sheath - a layer of white, fatty tissue segmentally encasing the axons of neurons; enables vastly g ...
MSI - NERVOUS SYSTEM
... impulse travels into the neuron on the dendrite(s) and out on the axon. At the end of the axon, a NEUROTRANSMITTER is released that carries the impulse across the SYNAPSE, to the next dendrite. ...
... impulse travels into the neuron on the dendrite(s) and out on the axon. At the end of the axon, a NEUROTRANSMITTER is released that carries the impulse across the SYNAPSE, to the next dendrite. ...
Nervous System Review PPt
... – Composed of myelinated nerve cell processes, or axons, which connect various gray matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other and carry nerve impulses between neurons – Forms the bulk of the deep parts of the brain and the superficial parts of the spinal cord • Gen ...
... – Composed of myelinated nerve cell processes, or axons, which connect various gray matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other and carry nerve impulses between neurons – Forms the bulk of the deep parts of the brain and the superficial parts of the spinal cord • Gen ...
The Sympathetic Nervous System
... A nerve impulse starts when a stimulus causes a reversal in the electrical charge (action potential), which travels down the membrane like an electric current. When the reversal of electric charges occurs, the membrane is depolarized. When the membrane returns back to its resting state, it is repola ...
... A nerve impulse starts when a stimulus causes a reversal in the electrical charge (action potential), which travels down the membrane like an electric current. When the reversal of electric charges occurs, the membrane is depolarized. When the membrane returns back to its resting state, it is repola ...
Nervous System
... Above: Spinal Chord ( Silver Stain & H + E stain) Dotted Lines = (Cell bodies); Outer Surrounding Area= White Matter(Myelinated Axons) ...
... Above: Spinal Chord ( Silver Stain & H + E stain) Dotted Lines = (Cell bodies); Outer Surrounding Area= White Matter(Myelinated Axons) ...
Nervous system notes
... Action potential=rapid depolarization of plasma membrane followed by repolarization as moving ions restore resting potential==nerve impulse p.247 c. Conduction of impulse=wave of ionic reversals as impulse travels down neuron (1). Myelin sheath==a.p. Jumps from node to node, saltatory conduction, fa ...
... Action potential=rapid depolarization of plasma membrane followed by repolarization as moving ions restore resting potential==nerve impulse p.247 c. Conduction of impulse=wave of ionic reversals as impulse travels down neuron (1). Myelin sheath==a.p. Jumps from node to node, saltatory conduction, fa ...
Hannah
... Interaction of Two Neurons The synapse is the site where chemical signals pass between neurons. Neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron terminals into the extracellular space, the synaptic cleft or synaptic space. The released neurotransmitter molecules can then bind to specific ...
... Interaction of Two Neurons The synapse is the site where chemical signals pass between neurons. Neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron terminals into the extracellular space, the synaptic cleft or synaptic space. The released neurotransmitter molecules can then bind to specific ...
Nervous Tissue: Neurons
... • The entry of calcium into the axon terminal causes ______openings to form, releasing the transmitter ...
... • The entry of calcium into the axon terminal causes ______openings to form, releasing the transmitter ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Lecture Outline Adapted from Martini
... Sequence of events: An action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane This triggers the release of a neurotransmitter from the axon vesicles The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse The neurotransmitter binds to the postsynaptic membrane This binding action causes a change in the perme ...
... Sequence of events: An action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane This triggers the release of a neurotransmitter from the axon vesicles The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse The neurotransmitter binds to the postsynaptic membrane This binding action causes a change in the perme ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 13 Martini Lecture Outline
... Sequence of events: An action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane This triggers the release of a neurotransmitter from the axon vesicles The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse The neurotransmitter binds to the postsynaptic membrane This binding action causes a change in the perme ...
... Sequence of events: An action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane This triggers the release of a neurotransmitter from the axon vesicles The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse The neurotransmitter binds to the postsynaptic membrane This binding action causes a change in the perme ...
Nervous System Study Guide
... d) axon—carry a nerve impulse away from the cell body e) axon tips—release the nerve impulse 5. Describe how two neurons are always joined. (_______ end to ________ end). Neurons are always joined axon end to dendrite end. 6. Identify what a synapse is and how two joined neurons overcome a synapse. ...
... d) axon—carry a nerve impulse away from the cell body e) axon tips—release the nerve impulse 5. Describe how two neurons are always joined. (_______ end to ________ end). Neurons are always joined axon end to dendrite end. 6. Identify what a synapse is and how two joined neurons overcome a synapse. ...
Notes: Divisions of the Nervous System
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • Somatic Division of the Nervous System – motor neurons that you have control over. • Voluntary movement – skeletal muscle control • Autonomic Division of the Nervous System – motor neurons that you do NOT have control over. (heart rate, breath rate, etc.) • This co ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • Somatic Division of the Nervous System – motor neurons that you have control over. • Voluntary movement – skeletal muscle control • Autonomic Division of the Nervous System – motor neurons that you do NOT have control over. (heart rate, breath rate, etc.) • This co ...
Control and Coordination
... Control and Coordination I. The Nervous System A. Your nervous system helps your body make adjustments to changes in your environment. 1. Stimulus—any change inside or outside your body that brings about a(n) response 2. Homeostasis—the regulation of steady conditions inside an organism B. Neurons a ...
... Control and Coordination I. The Nervous System A. Your nervous system helps your body make adjustments to changes in your environment. 1. Stimulus—any change inside or outside your body that brings about a(n) response 2. Homeostasis—the regulation of steady conditions inside an organism B. Neurons a ...
The Nervous System
... A. Your nervous system helps your body make adjustments to changes in your environment. 1. Stimulus—any change inside or outside your body that brings about a(n) response 2. Homeostasis—the regulation of steady conditions inside an organism B. Neurons are made up of a cell body and branches called d ...
... A. Your nervous system helps your body make adjustments to changes in your environment. 1. Stimulus—any change inside or outside your body that brings about a(n) response 2. Homeostasis—the regulation of steady conditions inside an organism B. Neurons are made up of a cell body and branches called d ...
File
... use body parts below the injury. • Little or no sensation occurs in effected body parts. ...
... use body parts below the injury. • Little or no sensation occurs in effected body parts. ...
Astrocyte

For the cell in the gastrointestinal tract, see Interstitial cell of Cajal.Astrocytes (Astro from Greek astron = star and cyte from Greek ""kyttaron"" = cell), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined. Depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. They perform many functions, including biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries.Research since the mid-1990s has shown that astrocytes propagate intercellular Ca2+ waves over long distances in response to stimulation, and, similar to neurons, release transmitters (called gliotransmitters) in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Data suggest that astrocytes also signal to neurons through Ca2+-dependent release of glutamate. Such discoveries have made astrocytes an important area of research within the field of neuroscience.