Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
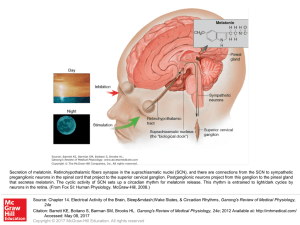
... Secretion of melatonin. Retinohypothalamic fibers synapse in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), and there are connections from the SCN to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord that project to the superior cervical ganglion. Postganglionic neurons project from this ganglion to the pinea ...
... Secretion of melatonin. Retinohypothalamic fibers synapse in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), and there are connections from the SCN to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord that project to the superior cervical ganglion. Postganglionic neurons project from this ganglion to the pinea ...
•The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... (3) Center – region of the spinal cord where the incoming sensory information generates an outgoing motor impulse, usually contains internuncial neurons (4) Motor Neuron transmit nerve impulses to muscle or gland through the ventral root to the spinal nerve (5) Effector the organ (gland or muscle) t ...
... (3) Center – region of the spinal cord where the incoming sensory information generates an outgoing motor impulse, usually contains internuncial neurons (4) Motor Neuron transmit nerve impulses to muscle or gland through the ventral root to the spinal nerve (5) Effector the organ (gland or muscle) t ...
Brain motor control
... • Other trinucleotide repeat diseases: fragile X syndrome, • myotonic dystrophy, • and others • sometimes they get worse from generation to generation (anticipation) ...
... • Other trinucleotide repeat diseases: fragile X syndrome, • myotonic dystrophy, • and others • sometimes they get worse from generation to generation (anticipation) ...
Amber Benton Anatomical Organization of Nervous System Central
... B. Peripheral Nervous system – everything outside of CNS -Cranial nerves (attached to brain) – 12 pairs -Spinal nerves (attached to spinal cord) – 31 pairs (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal) Ganglion and Nerve are components of the PNS: -ganglion is a collection of neuronal c ...
... B. Peripheral Nervous system – everything outside of CNS -Cranial nerves (attached to brain) – 12 pairs -Spinal nerves (attached to spinal cord) – 31 pairs (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal) Ganglion and Nerve are components of the PNS: -ganglion is a collection of neuronal c ...
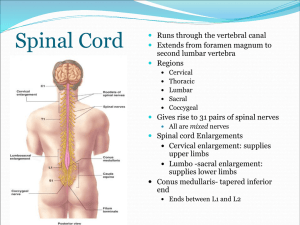
Spinal Cord
... Clinical Case Of Spinal Cord cont.. MRI of a patient indicated to have an extramedullary ...
... Clinical Case Of Spinal Cord cont.. MRI of a patient indicated to have an extramedullary ...
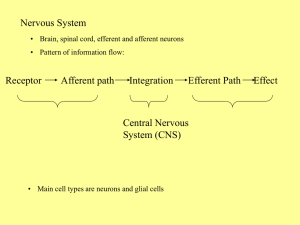
The Central Nervous System
... – Dorsal carries sensory information – Ventral carries motor information out ...
... – Dorsal carries sensory information – Ventral carries motor information out ...
Nerve and Muscle
... - Transmits impulses away from soma toward target cell. - Axon hillock or initial segment (= beginning of axon + part of soma where axon joins it) is the trigger zone where electric signals are generated in most neurons. Signals are then propagated along axon. - Axon may have branches = collaterals. ...
... - Transmits impulses away from soma toward target cell. - Axon hillock or initial segment (= beginning of axon + part of soma where axon joins it) is the trigger zone where electric signals are generated in most neurons. Signals are then propagated along axon. - Axon may have branches = collaterals. ...
What happens to the resting membrane potential of the membrane
... What will determine whether this postsynaptic neuron will ...
... What will determine whether this postsynaptic neuron will ...
3-As.Tracts 2016-17
... • Some of this information eventually reaches a conscious level (the cerebral cortex), • while some is destined for subconscious centers (e.g. the cerebellum). ...
... • Some of this information eventually reaches a conscious level (the cerebral cortex), • while some is destined for subconscious centers (e.g. the cerebellum). ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
... precentral sulcus area of the cerebrum. In case of spinal cord, they form lateral corticospinal tracts of white matter LOWER MOTOR NEURON: Has its cell body in the anterior horn of grey matter in the spinal cord. Lower motor neuron described as the final common pathway for the transmission of nerve ...
... precentral sulcus area of the cerebrum. In case of spinal cord, they form lateral corticospinal tracts of white matter LOWER MOTOR NEURON: Has its cell body in the anterior horn of grey matter in the spinal cord. Lower motor neuron described as the final common pathway for the transmission of nerve ...
Sensory neurons (감각 신경)
... 2. Motor neurons (운동 뉴런) • Motor neuron (efferent or effector neurons) transmit impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles or ...
... 2. Motor neurons (운동 뉴런) • Motor neuron (efferent or effector neurons) transmit impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles or ...
PNS Teacher
... • A reflex is involuntary- it occurs without any conscious through • A reflex response is rapid- only a small number of neurons are involved • A reflex response is stereotyped- it occurs in the same way each time ...
... • A reflex is involuntary- it occurs without any conscious through • A reflex response is rapid- only a small number of neurons are involved • A reflex response is stereotyped- it occurs in the same way each time ...
Questions on the Nervous system
... - neuron processes running in CNS are called--------------while that outside it called-- the CNS is composed of-------------and-------------- white matter consists of --------------------while grey matter of-----------------and------- cell bodies of afferent and association neurons are always found ...
... - neuron processes running in CNS are called--------------while that outside it called-- the CNS is composed of-------------and-------------- white matter consists of --------------------while grey matter of-----------------and------- cell bodies of afferent and association neurons are always found ...
Neural Grafting: Repairing the Brain and Spinal Cord (Part 5 of 18)
... produced. Most glial cells, on the other hand, maintain the capacity to replicate. The mechanisms by which neurons migrate to the proper location and axons find their way to the proper target site and form synapses are not fully understood. The process of axonal growth is thought to include an initi ...
... produced. Most glial cells, on the other hand, maintain the capacity to replicate. The mechanisms by which neurons migrate to the proper location and axons find their way to the proper target site and form synapses are not fully understood. The process of axonal growth is thought to include an initi ...
3-As.Tracts 2015 (final).
... • Some of this information eventually reaches a conscious level (the cerebral cortex), • while some is destined for subconscious centers (e.g. the cerebellum). ...
... • Some of this information eventually reaches a conscious level (the cerebral cortex), • while some is destined for subconscious centers (e.g. the cerebellum). ...
Chapter 6 Notes - Biological Psych
... • The surface of the cerebrum appears wrinkled and is made up of deep grooves and bumps or folds. The outer part of the cerebrum is called gray matter and contains nerve cells. The inner part is called white matter and contains connections of nerves. • The brainstem is located in front of the cereb ...
... • The surface of the cerebrum appears wrinkled and is made up of deep grooves and bumps or folds. The outer part of the cerebrum is called gray matter and contains nerve cells. The inner part is called white matter and contains connections of nerves. • The brainstem is located in front of the cereb ...
Slide ()
... Development of the cranial nuclei. A–D. Schematic section through the hind brain at three developmental time points (A–C) and maturity (D). The space within the sections is the fourth ventricle. During development the fourth ventricle, initially flattened dorsoventrally just like the spinal cord, ex ...
... Development of the cranial nuclei. A–D. Schematic section through the hind brain at three developmental time points (A–C) and maturity (D). The space within the sections is the fourth ventricle. During development the fourth ventricle, initially flattened dorsoventrally just like the spinal cord, ex ...
What will happen at this area of membrane?
... What will determine whether this postsynaptic neuron will ...
... What will determine whether this postsynaptic neuron will ...
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue and Brain
... brains of monkeys by researchers at MIT, these timekeeping neurons fire consistently at certain rhythms . ...
... brains of monkeys by researchers at MIT, these timekeeping neurons fire consistently at certain rhythms . ...
Chapter 6: Body and Behavior
... • Axon terminals: release ____________________ to stimulate _______________ of other neurons ...
... • Axon terminals: release ____________________ to stimulate _______________ of other neurons ...
6c Important Tissue Concepts
... • Contractile tissue made of bundles muscle fibers (cells); ATP drive proteins actin and mysosin to cause shortening of cell -Striated (skeletal) muscle: voluntary, striated, multinucleate, cylindrical; muscles that connect bones together -Smooth muscle: involuntary, not striated, single nuclei, spi ...
... • Contractile tissue made of bundles muscle fibers (cells); ATP drive proteins actin and mysosin to cause shortening of cell -Striated (skeletal) muscle: voluntary, striated, multinucleate, cylindrical; muscles that connect bones together -Smooth muscle: involuntary, not striated, single nuclei, spi ...
Astrocyte

For the cell in the gastrointestinal tract, see Interstitial cell of Cajal.Astrocytes (Astro from Greek astron = star and cyte from Greek ""kyttaron"" = cell), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined. Depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. They perform many functions, including biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries.Research since the mid-1990s has shown that astrocytes propagate intercellular Ca2+ waves over long distances in response to stimulation, and, similar to neurons, release transmitters (called gliotransmitters) in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Data suggest that astrocytes also signal to neurons through Ca2+-dependent release of glutamate. Such discoveries have made astrocytes an important area of research within the field of neuroscience.