Conserved and Convergent Organization in the Optic Lobes of
... or homoplasic? The argument for a common origin of a lobula plate would be strengthened if isopods and insects share additional characters in the optic lobes, such as similar layer relationships and arrangements amongst comparable assemblies of neurons. The argument for a basal origin of the malacos ...
... or homoplasic? The argument for a common origin of a lobula plate would be strengthened if isopods and insects share additional characters in the optic lobes, such as similar layer relationships and arrangements amongst comparable assemblies of neurons. The argument for a basal origin of the malacos ...
Nervous System Review
... Drug blocks the receptor site so that neurotransmitters cannot fuse with the receptor site stopping action potential. Drug blocks the reuptake of the neurotransmitter so that it stays in the synapse longer and fuses with the receptor sites more often causing more action potential. ...
... Drug blocks the receptor site so that neurotransmitters cannot fuse with the receptor site stopping action potential. Drug blocks the reuptake of the neurotransmitter so that it stays in the synapse longer and fuses with the receptor sites more often causing more action potential. ...
Slide 1
... • Places upper limit on number of action potentials that can pass through neuron in unit of time. • Action potentials carried in one direction, from cell body to end of axon. QuickTi me™ and a decompressor are needed to see thi s pi ctur e. ...
... • Places upper limit on number of action potentials that can pass through neuron in unit of time. • Action potentials carried in one direction, from cell body to end of axon. QuickTi me™ and a decompressor are needed to see thi s pi ctur e. ...
CNS Blood Supply
... arteries and anastomose with their branches. From these varied sources of blood supply, a series of circumferential anastomotic channels are formed around the spinal cord, called the arterial vasocorona, from which short branches penetrate and supply the lateral parts of the cord ...
... arteries and anastomose with their branches. From these varied sources of blood supply, a series of circumferential anastomotic channels are formed around the spinal cord, called the arterial vasocorona, from which short branches penetrate and supply the lateral parts of the cord ...
Thoracic Viscera -> by following Cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerve
... □ CN 10 to intrinsic ganglia of organs => Parasympathetic control of Thorax (lungs/heart) and upper 2/3 of abdominal organs CRANIAL NERVES HAVE NO SYMPATHETIC FUNCTION ONLY PARASYMPATHETIC ○ Lateral horn of Sacral Spinal cord (S2-4) Axons of PrG leave via pelvic splanchnic nerve Exert Parasymp ...
... □ CN 10 to intrinsic ganglia of organs => Parasympathetic control of Thorax (lungs/heart) and upper 2/3 of abdominal organs CRANIAL NERVES HAVE NO SYMPATHETIC FUNCTION ONLY PARASYMPATHETIC ○ Lateral horn of Sacral Spinal cord (S2-4) Axons of PrG leave via pelvic splanchnic nerve Exert Parasymp ...
Respiratory Rhythm: Control of Breathing - Dr. Costanzo
... response of central chemoreceptors to changes in PCO2. The effects of increased PCO2 and decreased PO2 are additive in peripheral chemoreceptors. 3. Peripheral chemoreceptors also detect decreases in arterial pH, independent of changes in PCO2, and direct an increase in breathing rate. The effect of ...
... response of central chemoreceptors to changes in PCO2. The effects of increased PCO2 and decreased PO2 are additive in peripheral chemoreceptors. 3. Peripheral chemoreceptors also detect decreases in arterial pH, independent of changes in PCO2, and direct an increase in breathing rate. The effect of ...
7.1 Functions of the Nervous System
... Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve ...
... Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... under your control, such as waving your hand or kicking a ball. The girl pictured below ( Figure 1.4) is using her somatic nervous system to control the muscles needed to play the violin. Her brain sends messages to motor neurons that move her hands so she can play. Without the messages from her bra ...
... under your control, such as waving your hand or kicking a ball. The girl pictured below ( Figure 1.4) is using her somatic nervous system to control the muscles needed to play the violin. Her brain sends messages to motor neurons that move her hands so she can play. Without the messages from her bra ...
Learning Modules - Medical Gross Anatomy Nervous System
... nervous system is the neuron. In addition to neurons, there are also numerous support cells that will be covered in detail in other courses. Here, we will focus on neurons. A neuron's job is basically to pass messages from one part of the body to another. There are several types of neurons based on ...
... nervous system is the neuron. In addition to neurons, there are also numerous support cells that will be covered in detail in other courses. Here, we will focus on neurons. A neuron's job is basically to pass messages from one part of the body to another. There are several types of neurons based on ...
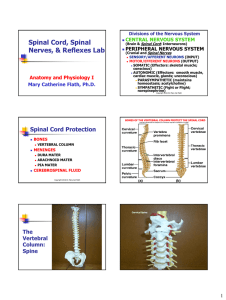
Spinal Cord PPT
... The dura mater of the spinal cord is not directly attached to the bone of the vertebrae ...
... The dura mater of the spinal cord is not directly attached to the bone of the vertebrae ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry, Matter, and Life
... • Support nervous tissue • Aid in cell repair • Remove pathogens and impurities • Regulation composition of fluids around and between cells • Schwann cells (type of neuroglia) Copyright © 2013 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... • Support nervous tissue • Aid in cell repair • Remove pathogens and impurities • Regulation composition of fluids around and between cells • Schwann cells (type of neuroglia) Copyright © 2013 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
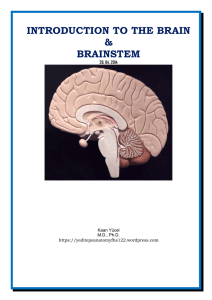
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs122.wordpress.com Introduction
... The brainstem (a collective term for the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain) is that part of the brain that remains after the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum are removed. The brainstem is the oldest part of the CNS. The brainstem is made up of the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain ...
... The brainstem (a collective term for the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain) is that part of the brain that remains after the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum are removed. The brainstem is the oldest part of the CNS. The brainstem is made up of the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain ...
Neurons in the dorsal column nuclei of the rat emit a moderate
... ventrobasal thalamus. Since in the calculation the midline nucleus of Bischoff was not involved, the portion of ipsilaterally projecting cells from the total thalamopetal population appears to be very slightly smaller as the number of the labelled Bischoff’s cells did not exceed 70 in neither cases. I ...
... ventrobasal thalamus. Since in the calculation the midline nucleus of Bischoff was not involved, the portion of ipsilaterally projecting cells from the total thalamopetal population appears to be very slightly smaller as the number of the labelled Bischoff’s cells did not exceed 70 in neither cases. I ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... Stretch receptor signals are also carried rostrally in the anterolateral system (ALS) and the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (Fig. 8, green arrows) to visceral sensory cortex and eventually reach the medial prefrontal cortex. From there, they are sent caudally to the periaqueductal gray matt ...
... Stretch receptor signals are also carried rostrally in the anterolateral system (ALS) and the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (Fig. 8, green arrows) to visceral sensory cortex and eventually reach the medial prefrontal cortex. From there, they are sent caudally to the periaqueductal gray matt ...
9. Motor
... nucleus of oculomotor n., nucleus trochlear n., motor nucleus of trigeminal n., nucleus of abducent n., ambiguus nucleus, nucleus of accessory n., superior part of facial nucleus. facial nucleus ...
... nucleus of oculomotor n., nucleus trochlear n., motor nucleus of trigeminal n., nucleus of abducent n., ambiguus nucleus, nucleus of accessory n., superior part of facial nucleus. facial nucleus ...
nervous system
... (A)The end-bulb of the presynaptic (transmitting) axon has vesicles containing neurotransmitter, which is released into the synaptic cleft to the membrane of the postsynaptic (receiving) cell. (B) Close-up of a synapse showing receptors for neurotransmitter in the postsynaptic cell membrane. Copyrig ...
... (A)The end-bulb of the presynaptic (transmitting) axon has vesicles containing neurotransmitter, which is released into the synaptic cleft to the membrane of the postsynaptic (receiving) cell. (B) Close-up of a synapse showing receptors for neurotransmitter in the postsynaptic cell membrane. Copyrig ...
Neuroanatomy I
... Vagus, the tenth cranial nerve, arises from the medulla and carries both afferent and efferent fibers. The afferent vagal fibers connect to the nucleus of the solitary tract which in turn projects connections to other locations in the central nervous system. Little is understood about exactly how va ...
... Vagus, the tenth cranial nerve, arises from the medulla and carries both afferent and efferent fibers. The afferent vagal fibers connect to the nucleus of the solitary tract which in turn projects connections to other locations in the central nervous system. Little is understood about exactly how va ...
Slide 1
... Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System • There are two divisions of the peripheral nervous system: – the somatic, or voluntary portion – the autonomic, or involuntary portion Somatic Nervous System: The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles ...
... Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System • There are two divisions of the peripheral nervous system: – the somatic, or voluntary portion – the autonomic, or involuntary portion Somatic Nervous System: The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles ...
Протокол
... projects directly into the brain stem, and ascends as far as the cerebral cortex in the parietal lobe. Gustatory receptors transduce soluble chemical stimuli into electrical signals that are perceived by the brain as basic taste categories. In conjunction with the olfactory and somatic sensory syste ...
... projects directly into the brain stem, and ascends as far as the cerebral cortex in the parietal lobe. Gustatory receptors transduce soluble chemical stimuli into electrical signals that are perceived by the brain as basic taste categories. In conjunction with the olfactory and somatic sensory syste ...
Adenosine triphosphate as a neurotransmitter and
... their proportions in NANC inhibitory nerves vary considerably in different regions of the gut and between species. P2X and P2Y receptor subtypes are present on neurons in both myenteric and submucosal nerve plexuses and in intestinal blood vessels as well as mucosal epithelial cells (Burnstock, 2001 ...
... their proportions in NANC inhibitory nerves vary considerably in different regions of the gut and between species. P2X and P2Y receptor subtypes are present on neurons in both myenteric and submucosal nerve plexuses and in intestinal blood vessels as well as mucosal epithelial cells (Burnstock, 2001 ...
Lecture 2
... maintained, repetitive stimulus Cause / 1-different conduction velocities of afferents 2-different number of interneurons with short & long pathways to the motor neurons (AHCs ) (impulses do not reach AHCs at same time but reach them gradually, so maintained stimulation allow more neurons to be stim ...
... maintained, repetitive stimulus Cause / 1-different conduction velocities of afferents 2-different number of interneurons with short & long pathways to the motor neurons (AHCs ) (impulses do not reach AHCs at same time but reach them gradually, so maintained stimulation allow more neurons to be stim ...
Laboratory 08 Peripheral Nervous System
... As you can see from this image above, the spinal cord is bisected into “mirror-‐image” left and right halves (in a similar fashion to the brain) by the anterior median fissure in front and the ...
... As you can see from this image above, the spinal cord is bisected into “mirror-‐image” left and right halves (in a similar fashion to the brain) by the anterior median fissure in front and the ...
vestibular system - (canvas.brown.edu).
... semicircular canal. T F 2. Nystagmus resulting from vestibular stimulation normally affects both eyes. T F 3. The adequate stimulus for excitation of utricular hair cells is bending of their cilia. T F 4. Cell bodies of neurons innervating a semicircular canal are found in Scarpa's ...
... semicircular canal. T F 2. Nystagmus resulting from vestibular stimulation normally affects both eyes. T F 3. The adequate stimulus for excitation of utricular hair cells is bending of their cilia. T F 4. Cell bodies of neurons innervating a semicircular canal are found in Scarpa's ...
Astrocyte

For the cell in the gastrointestinal tract, see Interstitial cell of Cajal.Astrocytes (Astro from Greek astron = star and cyte from Greek ""kyttaron"" = cell), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined. Depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. They perform many functions, including biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries.Research since the mid-1990s has shown that astrocytes propagate intercellular Ca2+ waves over long distances in response to stimulation, and, similar to neurons, release transmitters (called gliotransmitters) in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Data suggest that astrocytes also signal to neurons through Ca2+-dependent release of glutamate. Such discoveries have made astrocytes an important area of research within the field of neuroscience.