The Peripheral Nervous System - Advanced
... if higher level functions, such as awareness and consciousness, are lost. Such a low level of brain functioning is referred to as a vegetative state. The ANS has two subdivisions: the sympathetic division and parasympathetic division. The sympathetic division generally stimulates body systems during ...
... if higher level functions, such as awareness and consciousness, are lost. Such a low level of brain functioning is referred to as a vegetative state. The ANS has two subdivisions: the sympathetic division and parasympathetic division. The sympathetic division generally stimulates body systems during ...
Medulla oblongata
... embryonic brain stem has a central gray core with an alar plate (consisting mostly of sensory components) and a basal plate (composed primarily of motor components) ...
... embryonic brain stem has a central gray core with an alar plate (consisting mostly of sensory components) and a basal plate (composed primarily of motor components) ...
Nolte – Chapter 5 (Ventricles and Cerebrospinal
... containes higher conentrations of magnesium and chloride and less potassium and calcium can be depressed by metabolic inhibitors. formed by filtration of blood through choroidal capillaries and the active transport of substances. a route for the spread of neuroactive hormones regulation of e ...
... containes higher conentrations of magnesium and chloride and less potassium and calcium can be depressed by metabolic inhibitors. formed by filtration of blood through choroidal capillaries and the active transport of substances. a route for the spread of neuroactive hormones regulation of e ...
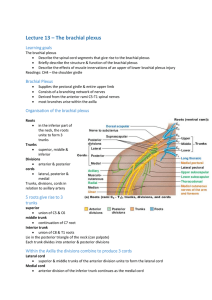
Lecture 13 – The brachial plexus
... Organisation of the brachial plexus Roots in the inferior part of the neck, the roots unite to form 3 trunks Trunks superior, middle & inferior Divisions anterior & posterior cords lateral, posterior & medial Trunks, divisions, cords in relation to axillary artery ...
... Organisation of the brachial plexus Roots in the inferior part of the neck, the roots unite to form 3 trunks Trunks superior, middle & inferior Divisions anterior & posterior cords lateral, posterior & medial Trunks, divisions, cords in relation to axillary artery ...
neuron worksheet
... 7. The space between the dendrites of one neuron and the synaptic terminal of another neuron is a 8. The spaces between the myelin sheaths are the Part B. Place the events described below in the correct sequence by writing the numbers 1 through 6 in the spaces provided. Be sure to read ALL the state ...
... 7. The space between the dendrites of one neuron and the synaptic terminal of another neuron is a 8. The spaces between the myelin sheaths are the Part B. Place the events described below in the correct sequence by writing the numbers 1 through 6 in the spaces provided. Be sure to read ALL the state ...
www.repetto5.com
... The CNS or the central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord which are located in the dorsal body cavity. The CNS is the command center of the nervous system. It interprets incoming signals based on past reflexes , experiences,and current conditions. ...
... The CNS or the central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord which are located in the dorsal body cavity. The CNS is the command center of the nervous system. It interprets incoming signals based on past reflexes , experiences,and current conditions. ...
Spinal Cord - hersheybear.org
... B. cell bodies of neurons, neuroglia, and unmyelinated axons. C. Schwann cells and satellite cells. D. myelinated axons. E. nodes of Ranvier. ...
... B. cell bodies of neurons, neuroglia, and unmyelinated axons. C. Schwann cells and satellite cells. D. myelinated axons. E. nodes of Ranvier. ...
a comparison of the intranigral distribution of nigrotectal neurons
... However, rather than being concentrated in the lateralmost zone of SNR, the labeled neurons are instead scattered throughout the mediolateral and dorsoventral expanse of SNR, with a slightly higher density ventrally near the middle of the mediolateral expanse. As in the monkey, no cell labeling occu ...
... However, rather than being concentrated in the lateralmost zone of SNR, the labeled neurons are instead scattered throughout the mediolateral and dorsoventral expanse of SNR, with a slightly higher density ventrally near the middle of the mediolateral expanse. As in the monkey, no cell labeling occu ...
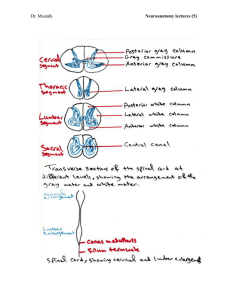
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... stimulus. Ipsilateral reflex. Several motor units at different levels of the spinal cord are recruited – intersegmental reflex arc. Reciprocal innervation occurs. ...
... stimulus. Ipsilateral reflex. Several motor units at different levels of the spinal cord are recruited – intersegmental reflex arc. Reciprocal innervation occurs. ...
Neuroanatomy/Pain Review
... and may not be stimulated for a given period of time. This limits how many action potentials may be produced Absolute refractory period: NO stimulus will create a response no matter how strong Relative refractory period: resting potential is much lower, therefore a higher stimulus is needed ...
... and may not be stimulated for a given period of time. This limits how many action potentials may be produced Absolute refractory period: NO stimulus will create a response no matter how strong Relative refractory period: resting potential is much lower, therefore a higher stimulus is needed ...
Click here for Final Jeopardy Neurons PNS
... Preparing body for “fight or flight” during threatening situations is the role of what subdivision of autonomic ...
... Preparing body for “fight or flight” during threatening situations is the role of what subdivision of autonomic ...
Begin Nervous system
... In action potential, repolarization Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com ...
... In action potential, repolarization Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com ...
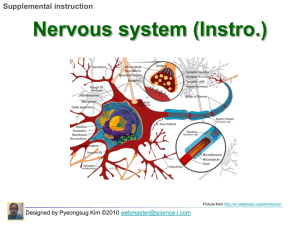
Neuron Types, structure and function_PowerPoint
... branches of dendrons are dendrites. Dendrites receive nerve impulses from other neurons. Cell body: cell body of motor neuron is irregular in shape. It contains the nucleus and controls cell activities Axon: nerve fiber that transmit nerve impulses away from cell body. Axons are usually long. Myelin ...
... branches of dendrons are dendrites. Dendrites receive nerve impulses from other neurons. Cell body: cell body of motor neuron is irregular in shape. It contains the nucleus and controls cell activities Axon: nerve fiber that transmit nerve impulses away from cell body. Axons are usually long. Myelin ...
Periph_nerves_reflex..
... Convert physical stimulus into nerve impulses Basic structure and mode of activation Classify by stimulus type that they’re most responsive to, or by location, or by structure: By stimulus type: mechano-, thermo-, photo-, chemo-, nociBy location: extero-, intero-, proprioBy structure: Simple (unenca ...
... Convert physical stimulus into nerve impulses Basic structure and mode of activation Classify by stimulus type that they’re most responsive to, or by location, or by structure: By stimulus type: mechano-, thermo-, photo-, chemo-, nociBy location: extero-, intero-, proprioBy structure: Simple (unenca ...
anterior spinothalamic tract.
... from the motor area of the cerebral cortex and then down till the medulla oblongata. The majority of these fibers cross to other side in the medulla oblongata in the decussation region that called the pyramid. These crossed fibers are called the lateral corticospinal tract. The rest of the fibers ar ...
... from the motor area of the cerebral cortex and then down till the medulla oblongata. The majority of these fibers cross to other side in the medulla oblongata in the decussation region that called the pyramid. These crossed fibers are called the lateral corticospinal tract. The rest of the fibers ar ...
Chapter 7 Notes Part 2
... roll–like fashion Nodes of Ranvier—gaps in myelin sheath along the axon Multiple Sclerosis (MS) – myelin sheaths ...
... roll–like fashion Nodes of Ranvier—gaps in myelin sheath along the axon Multiple Sclerosis (MS) – myelin sheaths ...
Ross Chezem
... lead in to the brainstem. From the brainstem he would reach the cerebellum and from the cerebellum he would reach the occipital lobe. After crossing the occipital lobe he would reach the parietal lobe. From the parietal lobe he would enter the frontal lobe and move down to the bottom of the frontal ...
... lead in to the brainstem. From the brainstem he would reach the cerebellum and from the cerebellum he would reach the occipital lobe. After crossing the occipital lobe he would reach the parietal lobe. From the parietal lobe he would enter the frontal lobe and move down to the bottom of the frontal ...
PNS - General
... sensory neurons of each spinal nerve innervate the skin and skeletal muscles in the roughly same order in which they emerge from the spinal cord detailed mapping of the skin surface reveals a close relationship between the source of nerve fibers and the location (superior to inferior) of the skin se ...
... sensory neurons of each spinal nerve innervate the skin and skeletal muscles in the roughly same order in which they emerge from the spinal cord detailed mapping of the skin surface reveals a close relationship between the source of nerve fibers and the location (superior to inferior) of the skin se ...
Schwann cells
... • Transmits them along axolemma (neuron cell membrane) to axon terminal – Secretory region – Neurotransmitters released into extracellular space • Either excite or inhibit neurons with which axons in close contact ...
... • Transmits them along axolemma (neuron cell membrane) to axon terminal – Secretory region – Neurotransmitters released into extracellular space • Either excite or inhibit neurons with which axons in close contact ...
Astrocyte

For the cell in the gastrointestinal tract, see Interstitial cell of Cajal.Astrocytes (Astro from Greek astron = star and cyte from Greek ""kyttaron"" = cell), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined. Depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. They perform many functions, including biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries.Research since the mid-1990s has shown that astrocytes propagate intercellular Ca2+ waves over long distances in response to stimulation, and, similar to neurons, release transmitters (called gliotransmitters) in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Data suggest that astrocytes also signal to neurons through Ca2+-dependent release of glutamate. Such discoveries have made astrocytes an important area of research within the field of neuroscience.