Nervous System Nerve Transmission Saltatory Conduction
... During an action potential, depolarization can change the membrane potential from –70 mV to about +30 mV. During repolarization the membrane potential returns to –70 mV. The nerve fiber cannot be stimulated again until repolarization is complete. This period is called the refractory period. If the s ...
... During an action potential, depolarization can change the membrane potential from –70 mV to about +30 mV. During repolarization the membrane potential returns to –70 mV. The nerve fiber cannot be stimulated again until repolarization is complete. This period is called the refractory period. If the s ...
Excitatory pathways
... excitatory: mediates excitatory Na+ influx into postsynaptic neuron. excitatory: mediates nociception (pain) within the spinal cord. ` mediates analgesia as well as other central nervous system effects. ...
... excitatory: mediates excitatory Na+ influx into postsynaptic neuron. excitatory: mediates nociception (pain) within the spinal cord. ` mediates analgesia as well as other central nervous system effects. ...
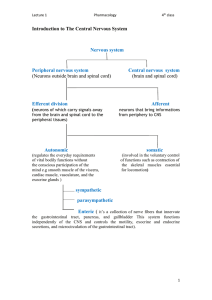
Divisions of the Nervous System
... hearing, motor control – Pons – breathing, sleep – Medulla oblongata involuntary activities (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure) ...
... hearing, motor control – Pons – breathing, sleep – Medulla oblongata involuntary activities (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure) ...
Nervous System Part Three Name: Sec 1: Peripheral NS Sec 2
... o Epineurium- tough fibrous sheath around a nerve o Ganglia Contain neuron cell bodies associated with nerves Dorsal root ganglia (sensory, somatic) Autonomic ganglia (motor, visceral) o Regeneration of nerve fibers Mature neurons are ______________ If the soma of a damaged nerve is intact ...
... o Epineurium- tough fibrous sheath around a nerve o Ganglia Contain neuron cell bodies associated with nerves Dorsal root ganglia (sensory, somatic) Autonomic ganglia (motor, visceral) o Regeneration of nerve fibers Mature neurons are ______________ If the soma of a damaged nerve is intact ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... hearing, motor control – Pons – breathing, sleep – Medulla oblongata involuntary activities (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure) ...
... hearing, motor control – Pons – breathing, sleep – Medulla oblongata involuntary activities (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure) ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-02-11
... Spinal cord lies in dural sac (within CSF fluid) Spinal segments do not coincide with vertebral level Spinal cord ends at L1 vertebra as the conus medullaris The spinal nerves below this level form the cauda equine “horse’s tail” The conus medullaris is anchored to Dura via the filum terminale ...
... Spinal cord lies in dural sac (within CSF fluid) Spinal segments do not coincide with vertebral level Spinal cord ends at L1 vertebra as the conus medullaris The spinal nerves below this level form the cauda equine “horse’s tail” The conus medullaris is anchored to Dura via the filum terminale ...
Ch 14: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... Gray commissures contain axons that cross from one side to the other ...
... Gray commissures contain axons that cross from one side to the other ...
Pre-Lecture Questions - Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... 1. The spinal cord is __________long and ____________ thick. 2. The dura mater of the spinal cord is ________layer thick and the ___________ space is between the dura mater and the bone of the vertebrae. 3. The epidural space is filled with ________________. 4. Between the dura mater and the arachno ...
... 1. The spinal cord is __________long and ____________ thick. 2. The dura mater of the spinal cord is ________layer thick and the ___________ space is between the dura mater and the bone of the vertebrae. 3. The epidural space is filled with ________________. 4. Between the dura mater and the arachno ...
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior
... `carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
... `carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... – partially cut axon while in rabbits it is about 3 – neurolemma is intact mm. per day. • regeneration starts in the nerve cell by resuming its normal shape and contents. ...
... – partially cut axon while in rabbits it is about 3 – neurolemma is intact mm. per day. • regeneration starts in the nerve cell by resuming its normal shape and contents. ...
Spinal Cord
... and bs, where the info is 1st processed (through dorsal column). *synapse at relay nucleus in medulla: dorsal column nucleus. ii. Axons of these neurons from the dorsal column nucleus cross over (decussate) here at the medulla and continue as the medial lemniscus thalamus. iii. These next thalamic ...
... and bs, where the info is 1st processed (through dorsal column). *synapse at relay nucleus in medulla: dorsal column nucleus. ii. Axons of these neurons from the dorsal column nucleus cross over (decussate) here at the medulla and continue as the medial lemniscus thalamus. iii. These next thalamic ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Links peripheral nervous system & brain Located in & protected by vertebral column Continuous tube from occipital bone to ...
... Links peripheral nervous system & brain Located in & protected by vertebral column Continuous tube from occipital bone to ...
Axon Terminal / Synapse / Dendrite Mitochondria ______ Node of R
... OCCIPITAL LOBE: CEREBELLUM: BRAINSTEM: TEMPORAL LOBE: LIMBIC SYSTEM (Thalamus, Amygdala, Hippocampus, Frontal Cortex, others): ...
... OCCIPITAL LOBE: CEREBELLUM: BRAINSTEM: TEMPORAL LOBE: LIMBIC SYSTEM (Thalamus, Amygdala, Hippocampus, Frontal Cortex, others): ...
Anatomy of spinal cord
... The arrangement of grey matter in the spinal cord resembles the shape of the letter H, having two posterior, two anterior and two lateral horns/columns. ...
... The arrangement of grey matter in the spinal cord resembles the shape of the letter H, having two posterior, two anterior and two lateral horns/columns. ...
Chapter 9.13 Spinal Cord powerpoint
... Descending tracts conducts motor impulses that originates in the cerebrum to muscles and glands It descends through tracts in the spinal cord in the lateral and ventral horns of gray matter This type of tract delivers information to the periphery Corticospinal tracts also called pyramidal tracts, pa ...
... Descending tracts conducts motor impulses that originates in the cerebrum to muscles and glands It descends through tracts in the spinal cord in the lateral and ventral horns of gray matter This type of tract delivers information to the periphery Corticospinal tracts also called pyramidal tracts, pa ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... hearing, motor control – Pons – breathing, sleep – Medulla oblongata involuntary activities (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure) ...
... hearing, motor control – Pons – breathing, sleep – Medulla oblongata involuntary activities (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure) ...
TSM7 - Somatosensory Pathways
... Nociceptor afferents synapse in the substantia gelatinosa in the dorsal-most area of the horn (Rexed’s laminae I to III) o Other associated afferents synapse in Rexed’s lamina V with so-called lamina V cells Second order neurones arising from the dorsal horn decussate and pass over to the contralate ...
... Nociceptor afferents synapse in the substantia gelatinosa in the dorsal-most area of the horn (Rexed’s laminae I to III) o Other associated afferents synapse in Rexed’s lamina V with so-called lamina V cells Second order neurones arising from the dorsal horn decussate and pass over to the contralate ...
PPT
... •Axons are often very long. The cytons for the nerves of the legs are located in the spinal cord and the axons travel the entire length of the legs. ...
... •Axons are often very long. The cytons for the nerves of the legs are located in the spinal cord and the axons travel the entire length of the legs. ...
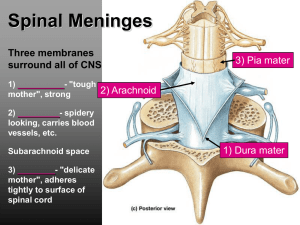
pia mater
... • The coverings of the brain and spinal cord are the meninges (singular meninx). • They include, from deep to superficial – the pia mater – the arachnoid – the dura mater. ...
... • The coverings of the brain and spinal cord are the meninges (singular meninx). • They include, from deep to superficial – the pia mater – the arachnoid – the dura mater. ...
Nervous System
... • Nerves (neurons) are the basic units of structure and function for the nervous system. • Nerves are capable of sending electrical messages called impulses. • There are two main types of nerves: – Sensory nerves – Motor nerves ...
... • Nerves (neurons) are the basic units of structure and function for the nervous system. • Nerves are capable of sending electrical messages called impulses. • There are two main types of nerves: – Sensory nerves – Motor nerves ...
Spinal Cord Anatomy - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... • Divided into three funiculi (columns) – posterior, lateral, and anterior – Columns contain 3 different types of fibers (Ascend., Descend., ...
... • Divided into three funiculi (columns) – posterior, lateral, and anterior – Columns contain 3 different types of fibers (Ascend., Descend., ...
Astrocyte

For the cell in the gastrointestinal tract, see Interstitial cell of Cajal.Astrocytes (Astro from Greek astron = star and cyte from Greek ""kyttaron"" = cell), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined. Depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. They perform many functions, including biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries.Research since the mid-1990s has shown that astrocytes propagate intercellular Ca2+ waves over long distances in response to stimulation, and, similar to neurons, release transmitters (called gliotransmitters) in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Data suggest that astrocytes also signal to neurons through Ca2+-dependent release of glutamate. Such discoveries have made astrocytes an important area of research within the field of neuroscience.