* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pre-Lecture Questions - Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
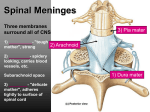
Biology 2121 – Pre-Lecture Questions – Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves – Chapters 12-13 I. Spinal Cord – General 1. The spinal cord is __________long and ____________ thick. 2. The dura mater of the spinal cord is ________layer thick and the ___________ space is between the dura mater and the bone of the vertebrae. 3. The epidural space is filled with ________________. 4. Between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater is the __________ space. 5. Between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater is the ____________________. 6. Where would a doctor perform a lumbar puncture or tap? ______________________________________ 7. The spinal cord terminates at the ________________. 8. The fibrous extensions from the conus are called _____________________ they extend to the _________ of the pelvis. 9. The spinal cord is secured to the dura mater via the _____________ ligaments. 10. Humans have _________ pairs of spinal nerves. 11. Where do enlargements occur in the spinal cord? __________________ What causes these enlargements? 12. The _______________ are nerve roots at the inferior end of the vertebral canal. 13. The outer part of the spinal cord is composed of _________ matter and the inner horns are composed of __________ matter. 14. A cross section of a spinal cord shows a tiny opening called the _______________. It allows for __________________ to flow through the spinal cord. II. Gray Matter – Spinal Cord 1. The gray ____________ attaches the left and right horns of gray. 2. The dorsal horns are also called the ___________ horns of gray and the ventral horns are also called the __________________ horns of gray. 3. The _____________ horns are found in the middle of the horns of gray. 4. All neurons in the spinal cord gray matter are composed of ________________ (type of neuron). 5. The dorsal horns are composed of only _______________ and the ventral horns contain some of these neurons but contain cell bodies of _____________- neurons. 6. The sensory neurons enter the ________________ horns of gray and the motor neurons exit the _____________ horns of gray. 7. Both the ____________ and ______________ sensory neurons enter the dorsal horns. 8. Both the _____________ and _____________ motor neurons exit the ventral horns. 9. The ______________ ganglion is associated with the dorsal horn. What is contained within the ganglion? 10. The __________ ventral root and the dorsal or sensory root combine to produce a short ___________ nerve. II. White Matter of the Spinal Cord. 1. The three types of fibers that compose the white matter in the spinal cord are the ____________, _____________ and ______________ fibers. 2. White matter on each side of the column is divided into three white columns or ______________. 3. All of these spinal tracts are part of a ________________ pathway that connect the brain to the body periphery. 4. The ascending pathways are related to _____________ neurons that run from the spinal cord to the cerebral cortex. 5. The ___________________ ascending pathway is the oldest. 6. The lateral, and anterior _____________ pathways are examples of the nonspecific pathways. 7. What are the function(s) of the spinothalamic nonspecific ascending pathways? 8. The specific sensory pathways are referred to as the _______________ and _______________tracts. Summarize the functions of these pathways. 9. The spinocerebellar tracts transmit information concerning muscle or tendon stretch to the ____________. 10. The specific and nonspecific ascending tracts all _________ - over to the other side of the body. 11. The ____________________ tracts do not cross over. 12. The descending tracts consist of _______________ neurons. (motor or sensory) 13. The Direct or Pyramidal descending tracts are composed of __________________ neurons. 14. The corticospinal tracts contain ______________ neurons. These large corticospinal tracts crossover where? 15. Why are they called the ‘direct pathway’? 16. Why are some of the descending pathways called indirect pathways? 17. What is the difference between flaccid and spastic paralysis? III. Spinal Nerves and Plexuses 1. All spinal nerves are ___________ nerves. Do they contain only sensory, motor or mixed? 2. There are ______ pairs of cervical spinal nerves, ________ pairs of thoracic nerves, _______ pairs of lumbar nerves and _________ pairs of sacral nerves and ________ pair of coccygeal nerves. 3. Ventral horn motor neurons innervate ____________ muscles. 4. Dorsal horn __________ neurons bring in information from the sensory receptors throughout the body. 5. A spinal nerve is only __________ cm in length. 6. The spinal nerves branch into a small ________ ramus, larger __________ and a tiny ____________ branch. 7. Which area of the spinal cord do not have nerve plexuses? ___________________________________ 8. Only _______________ rami form nerve plexuses. 9. The ventral rami of T1-T12 become the _______________ nerve. 10. Cutaneous branches serve the _____________. 11. What is a plexus? 12. Answer the following questions concerning nerves of various plexuses. (a). The __________ nerve serves the diaphragm. It is a part of the ______________ plexus. (b). The nerves that make up the cervical plexus are C1 - __________. (c). The median nerve is a part of the ____________ plexus, and its functions are ________________________ (d). The ulnar and radial nerves are part of the _____________ plexus. (e). The axillary nerve is a part of the ____________ plexus and serves the following muscles: ____________ (f). The musculotaneous, thoracic, scapular and subscapular nerves are the part of the ________ plexus. (g). The femoral and obturator nerves are part of the ___________ plexus. (h). The lumbar plexus contains nerves ___________ to _________. (i). The femoral nerve serves the ________________________________ and the obturator nerve serves the _____________________________________. (j). The sacral plexus contains nerves __________ to __________. (k). The largest nerve in the body is the _________________ nerve. It is composed of two smaller nerves, the __________________ and the __________________. 13. What are dermatomes? 14. Dermatomes are found in all spinal nerves except ________.